8/6 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
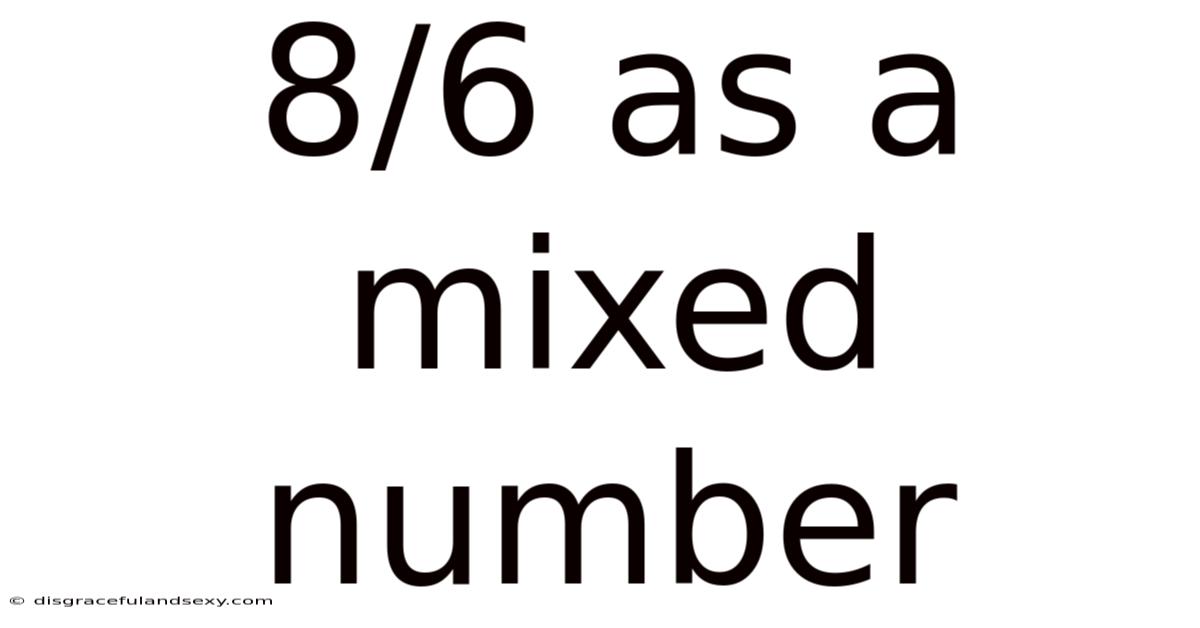
Table of Contents
Understanding 8/6 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 8/6, also known as eight-sixths, represents a quantity greater than one whole. Understanding how to express this as a mixed number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from baking to engineering. This article provides a detailed explanation of converting improper fractions like 8/6 into mixed numbers, exploring the underlying principles and offering practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll cover the process step-by-step, delve into the mathematical reasoning behind it, and address frequently asked questions.
Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before we dive into converting 8/6, let's establish a firm grasp of the basics. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). The denominator indicates the number of equal parts the whole is divided into, while the numerator shows how many of those parts are being considered.
For instance, in the fraction 1/4 (one-quarter), the denominator 4 tells us the whole is divided into four equal parts, and the numerator 1 indicates we are considering only one of those parts.
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. This signifies a quantity equal to or greater than one whole. Examples include 8/6, 5/4, and 7/7.
A mixed number, on the other hand, combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator smaller than its denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/8, 5/6). Mixed numbers are a convenient way to represent quantities larger than one whole in a more easily understandable format. For example, 1 1/2 (one and a half) is a mixed number representation of the improper fraction 3/2.
Converting 8/6 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting an improper fraction like 8/6 to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. Here's the breakdown:
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
Divide the numerator (8) by the denominator (6):
8 ÷ 6 = 1 with a remainder of 2
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number and the Remainder
The result of the division gives us two crucial pieces of information:
- The quotient (1) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number.
- The remainder (2) becomes the numerator of the fractional part of the mixed number.
Step 3: Construct the Mixed Number
The denominator of the fractional part remains the same as the original fraction's denominator (6). Therefore, combining the whole number and the fractional part, we get the mixed number:
1 2/6
Therefore, 8/6 as a mixed number is 1 2/6.
Simplifying the Mixed Number: Reducing the Fraction
While 1 2/6 is a correct mixed number representation of 8/6, it can be simplified. Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to its lowest terms by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator and dividing both by it.
In this case, the GCD of 2 and 6 is 2. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 2, we get:
2 ÷ 2 = 1 6 ÷ 2 = 3
Thus, the simplified fraction is 1/3. Substituting this into our mixed number, we obtain the simplified form:
1 1/3
Therefore, the simplest form of 8/6 as a mixed number is 1 1/3. This means that 8/6 represents one whole and one-third.
The Mathematical Reasoning Behind the Conversion
The conversion process is based on the fundamental principle of dividing a quantity into equal parts. When we divide 8 by 6, we are essentially determining how many times 6 goes into 8. It goes in once (the whole number), with a remainder of 2 (the remaining portion). This remainder, still expressed in sixths (the original denominator), represents the fractional part of the whole.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 8 equal-sized slices of pizza. Each slice represents 1/6 of a whole pizza. To understand 8/6, picture having 8 of these slices. You can group these slices into sets of 6. You'll have one complete pizza (6 slices) and 2 slices remaining. These 2 slices represent 2/6 of a pizza, which simplifies to 1/3. Therefore, you have one whole pizza and one-third of another. This visual representation solidifies the concept of 1 1/3.
Practical Applications of Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is crucial in various real-world situations:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often require measurements in fractions. Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers makes it easier to understand quantities. For instance, a recipe might call for 11/4 cups of flour, which is easier to measure as 2 3/4 cups.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are vital in these fields. Representing quantities as mixed numbers offers clarity and precision, especially when dealing with dimensions and materials.
-
Time Management: Dividing time into fractions and expressing them as mixed numbers aids in task scheduling and project planning.
-
Data Analysis: In statistics and data analysis, representing numerical data as mixed numbers can provide a clearer and more understandable interpretation of results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can all improper fractions be converted into mixed numbers?
A1: Yes, all improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers. The process remains the same regardless of the numerator and denominator values.
Q2: What if the remainder is 0 after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A2: If the remainder is 0, it means the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, 6/3 = 2. There is no fractional part in this case.
Q3: Is simplifying the fraction in the mixed number essential?
A3: While not strictly necessary, simplifying the fraction is good mathematical practice. It presents the answer in its most concise and easily understandable form.
Q4: Can I convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction?
A4: Absolutely! To do this, multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place the result over the original denominator. For example, to convert 1 1/3 back to an improper fraction: (1 x 3) + 1 = 4, so the improper fraction is 4/3.
Conclusion
Converting the improper fraction 8/6 to the mixed number 1 1/3 is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding this process not only helps in solving mathematical problems but also offers a practical application in numerous real-world scenarios. By grasping the underlying principles and following the step-by-step guide, you can confidently convert any improper fraction into a mixed number and simplify it to its lowest terms, enhancing your mathematical proficiency and problem-solving abilities. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and build confidence in your mathematical skills. The more you practice, the easier and more intuitive this process will become.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8/6 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.