8 Squared + 15 Squared
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 5 min read
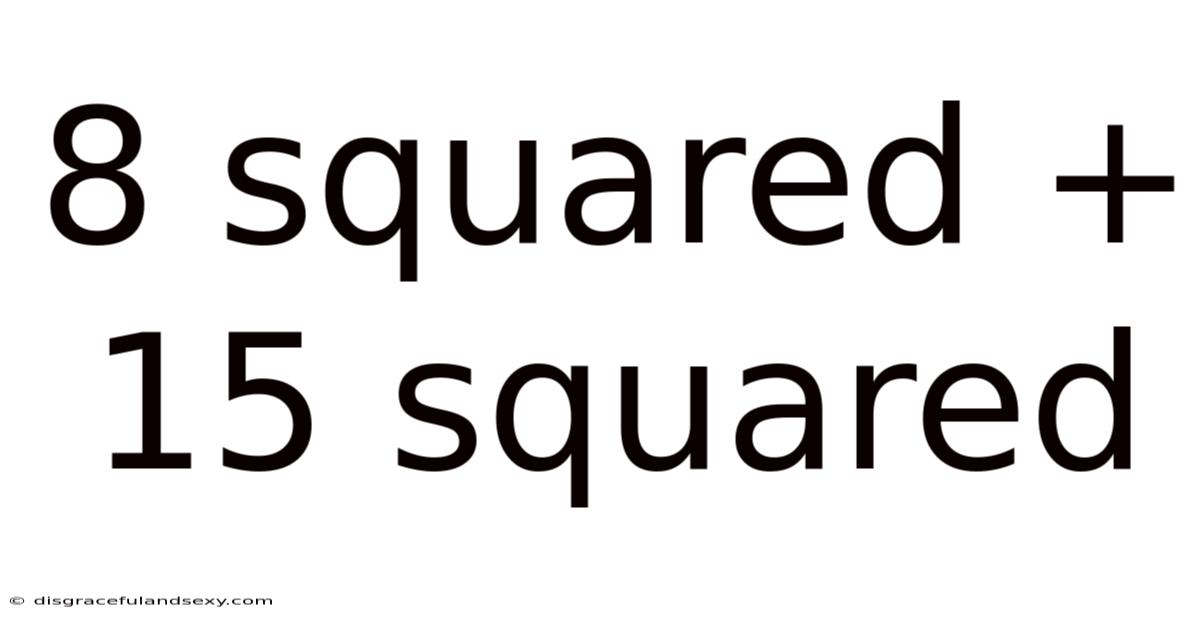
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: 8 Squared + 15 Squared and its Implications
This article delves into the seemingly simple mathematical expression "8 squared + 15 squared," exploring its calculation, underlying principles, its connection to the Pythagorean theorem, applications in various fields, and its broader significance in mathematics and beyond. We'll unpack the problem step-by-step, making it accessible to everyone, regardless of their mathematical background. Understanding this seemingly simple equation unlocks a deeper appreciation for fundamental mathematical concepts and their real-world applications.
Understanding Squares and the Calculation
The expression "8 squared + 15 squared" involves the concept of squaring a number. Squaring a number means multiplying the number by itself. Therefore:
- 8 squared (8²) = 8 x 8 = 64
- 15 squared (15²) = 15 x 15 = 225
Adding these results together, we get:
- 64 + 225 = 289
Therefore, 8 squared + 15 squared equals 289. This seemingly simple calculation forms the basis for understanding much more complex mathematical concepts.
The Pythagorean Theorem: A Cornerstone of Geometry
The result of 8² + 15² = 289 is deeply connected to the Pythagorean theorem, a fundamental concept in geometry. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (called legs or cathetus). The theorem is expressed as:
a² + b² = c²
where 'a' and 'b' are the lengths of the two shorter sides, and 'c' is the length of the hypotenuse.
In our case, 8 and 15 can be considered as the lengths of the two shorter sides of a right-angled triangle. The result, 289, represents the square of the hypotenuse. To find the length of the hypotenuse, we calculate the square root of 289:
- √289 = 17
This means that a right-angled triangle with sides of length 8 and 15 has a hypotenuse of length 17. This specific 8-15-17 triangle is a Pythagorean triple – a set of three positive integers that satisfy the Pythagorean theorem.
Exploring Pythagorean Triples and their Significance
Pythagorean triples are sets of three integers (a, b, c) that satisfy the equation a² + b² = c². The 8-15-17 triple is just one example; others include the well-known 3-4-5 triple (3² + 4² = 5²), and many others exist. These triples are not just mathematical curiosities; they have practical applications in various fields.
-
Construction and Engineering: Understanding Pythagorean triples is crucial in construction and engineering for accurate measurements and calculations involving right angles. For example, ensuring the corners of a building are perfectly square relies on the principles of the Pythagorean theorem.
-
Navigation and Surveying: Surveyors and navigators use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate distances and positions. This is particularly important in situations where direct measurement is difficult or impossible.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: The Pythagorean theorem is fundamental to computer graphics and game development, used extensively in calculating distances between points and objects in two and three-dimensional space.
-
Physics and Astronomy: The Pythagorean theorem has applications in physics, particularly in calculating vectors and distances in various physical systems. In astronomy, it's used in calculations related to celestial distances and orbits.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Other Mathematical Connections
The equation 8² + 15² = 289 also has connections to other mathematical concepts:
-
Number Theory: The study of numbers and their properties, including prime numbers, factors, and divisibility, reveals further insights into the significance of this equation. The numbers 8, 15, and 17 have unique properties within the number system.
-
Algebra: The equation can be expressed algebraically, opening doors to more advanced mathematical manipulations and problem-solving techniques. It can be part of larger algebraic expressions and equations.
-
Trigonometry: The relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle, as defined by the Pythagorean theorem, forms the foundation of trigonometry, a branch of mathematics dealing with angles and triangles.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The applications of the Pythagorean theorem, and consequently the calculation 8² + 15² = 289, are numerous and span across diverse disciplines:
-
Building a Rectangular Frame: Imagine you're building a rectangular frame. To ensure the frame is perfectly rectangular (has four right angles), you can measure the sides (8 units and 15 units) and then measure the diagonal (hypotenuse). If the diagonal measures 17 units, you know that the frame is perfectly rectangular.
-
Calculating Distance: Suppose you walk 8 blocks east and then 15 blocks north. To find the shortest distance back to your starting point (the straight-line distance), you would use the Pythagorean theorem: √(8² + 15²) = 17 blocks.
-
Determining Screen Size: The diagonal measurement of a rectangular screen (e.g., a television or computer monitor) is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. Knowing the width and height of the screen allows you to determine the diagonal size.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Are there other Pythagorean triples besides 8-15-17?
A: Yes, there are infinitely many Pythagorean triples. Some examples include 3-4-5, 5-12-13, 7-24-25, and many more. There are formulas and algorithms to generate Pythagorean triples.
Q: Why is the Pythagorean theorem so important?
A: The Pythagorean theorem is a cornerstone of geometry and has profound implications across mathematics and numerous scientific disciplines. It's used in countless calculations involving distances, angles, and shapes.
Q: Is there a simple way to remember Pythagorean triples?
A: While there isn't a single method to remember all triples, memorizing a few common ones (like 3-4-5 and 5-12-13) can be helpful. Understanding the underlying concept and its application is more important than rote memorization.
Q: Can the Pythagorean theorem be applied to triangles that are not right-angled?
A: No, the Pythagorean theorem only applies to right-angled triangles. For other types of triangles, different trigonometric laws are used.
Conclusion: A Simple Equation with Profound Implications
The seemingly simple calculation of 8 squared + 15 squared might seem trivial at first glance. However, a deeper exploration reveals its profound connections to the Pythagorean theorem, geometry, number theory, and various real-world applications. Understanding this equation unlocks a gateway to appreciating the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their importance in various fields. From construction and engineering to computer graphics and astronomy, the principles embedded within this simple equation underpin many aspects of our world. By mastering this fundamental concept, we build a stronger foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and broaden our understanding of the world around us. The seemingly simple 289 is much more than just a number; it's a gateway to a universe of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8 Squared + 15 Squared . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.