8 X 16 X 2
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
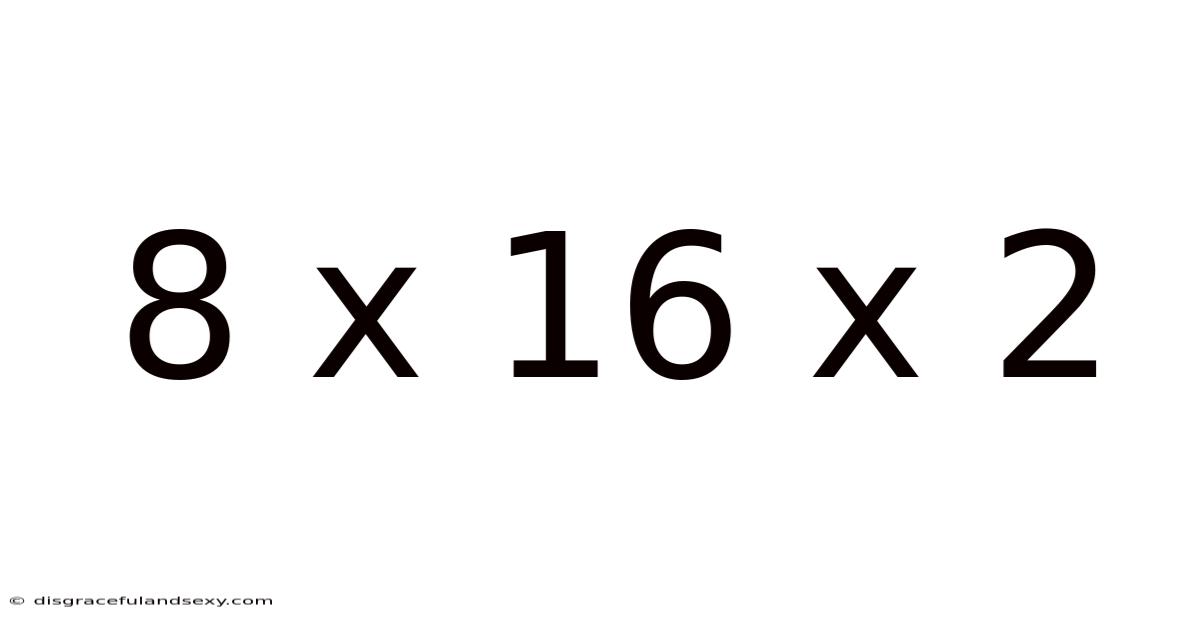
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into 8 x 16 x 2
This article explores the multifaceted meaning and applications of the numerical sequence "8 x 16 x 2," examining its significance across various fields like mathematics, computer science, engineering, and even everyday life. We will uncover its underlying mathematical properties, explore its practical implications in different contexts, and delve into potential interpretations beyond the purely numerical. Understanding this seemingly simple sequence reveals a surprisingly rich tapestry of concepts and applications.
Introduction: Beyond the Obvious Multiplication
At first glance, 8 x 16 x 2 appears to be a straightforward multiplication problem, resulting in 256. However, the context in which this sequence appears significantly alters its interpretation. This exploration goes beyond basic arithmetic, investigating how this specific combination of numbers plays a role in various systems and disciplines. We'll dissect its properties, explore its applications, and consider the broader implications of its structure.
Mathematical Properties and Interpretations
The numbers 8, 16, and 2 themselves hold mathematical significance. Eight is a power of two (2³), sixteen is also a power of two (2⁴), and two is the base of the binary system, fundamental to computer science. The product of these numbers, 256, is also a power of two (2⁸). This reveals a significant underlying structure based on powers of two, a crucial element in many computational and data representation systems.
-
Powers of Two: The consistent use of powers of two indicates a likely connection to binary systems and data structures. The number 256, the result of the multiplication, is particularly significant because it represents 2 to the power of 8 (2⁸), a common unit in computing (e.g., 256 bytes = 1 kilobyte).
-
Factors and Divisibility: Understanding the factors of 8, 16, and 2 helps analyze the divisibility of 256. This is crucial in areas like resource allocation, data chunking, and array indexing in programming.
-
Geometric Interpretations: While less direct, we can consider geometric interpretations. If we think of 8, 16, and 2 as dimensions (length, width, height), then 8 x 16 x 2 could represent the volume of a rectangular prism. This opens avenues for visualizing the numerical sequence in spatial terms.
Applications in Computer Science and Technology
The sequence 8 x 16 x 2 and its product, 256, appear frequently in computer science and related technologies due to the prevalence of powers of two in binary systems.
-
Data Representation: 256 is directly related to the number of possible values represented by an 8-bit byte (2⁸ = 256). This is fundamental to how computers store and process information, from characters to colors to memory addresses. An 8 x 16 matrix, for instance, might be a way to represent data structures, particularly images or other types of visual information. The '2' might represent a depth or layer to such a structure.
-
Memory Addressing: In computer architecture, memory is often organized in blocks of sizes that are powers of two. 256 (and its multiples) is a common size for memory allocation and management units.
-
Image Resolution: While not directly related to 8 x 16 x 2 specifically, it's relevant to consider the use of powers of two in image resolution (e.g., 256 x 256 pixels, 512 x 512 pixels). The sequence might be part of a larger system defining image properties or data storage.
-
Network Protocols: Network protocols often utilize binary structures for efficient data transmission and handling. The powers of two inherent in 8 x 16 x 2 may appear in packet sizes, data structures within protocols, or other system configurations.
-
Game Development: In game development, using powers of two for texture sizes and other data structures is common for performance optimization. The sequence might be a part of calculations related to game assets or world design.
Applications in Engineering and Physics
While less prominent than in computer science, the sequence 8 x 16 x 2 can find applications in engineering and physics, primarily through its mathematical properties.
-
Dimensional Analysis: As mentioned earlier, the numbers can represent dimensions of an object. In engineering design, calculations involving volumes, surface areas, or other geometric properties might involve similar numerical relationships.
-
Signal Processing: In digital signal processing, binary representation and powers of two are essential. The sequence could potentially relate to sampling rates, data quantization, or signal transformations.
-
Control Systems: Certain control systems might use binary signals or data structures where powers of two play a significant role. The sequence could be relevant in specific control system configurations or data representations.
Beyond the Technical: Everyday Interpretations
While the primary focus has been on the technical aspects, let's consider potential interpretations outside specialized fields.
-
Scheduling and Organization: The numbers could represent units of time or tasks in a project management scenario. For example, 8 tasks of 16 units each, repeated twice.
-
Resource Allocation: The sequence could model resource distribution. 8 resources, each capable of handling 16 units, deployed in two phases.
-
Inventory Management: The numbers might represent inventory counts or order sizes. 8 items of type A, 16 items of type B, and 2 lots of each.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the most common application of 8 x 16 x 2?
A: In computer science, the most common application revolves around its connection to 256, which is 2⁸, representing an 8-bit byte. This is fundamental to data storage and manipulation in computers.
Q: Are there other number sequences similar to 8 x 16 x 2?
A: Yes, many other number sequences utilize powers of two, reflecting binary system logic. Examples include 4 x 8 x 2, 16 x 32 x 2, and so on. These often indicate similar uses in data representation or memory management.
Q: Can the sequence be interpreted differently based on context?
A: Absolutely. The interpretation depends heavily on the context in which the sequence is encountered. In a mathematical context, it's a simple multiplication. In computer science, it relates to data representation and memory. In other fields, it might relate to resource allocation, scheduling, or other organizational systems.
Conclusion: Unpacking the Significance of 8 x 16 x 2
The seemingly simple sequence "8 x 16 x 2" unveils a wealth of interpretations and applications across diverse fields. From its fundamental mathematical properties connected to powers of two to its significant role in computer science, engineering, and even everyday organizational tasks, this numerical combination showcases the interconnectedness of seemingly disparate areas of knowledge. Understanding this sequence not only involves solving a simple multiplication problem but also deciphering its underlying principles and their wide-ranging implications. Its prevalence highlights the pervasive influence of binary systems and power-of-two structures in modern technology and beyond. Further investigation into similar numerical sequences could reveal further patterns and applications across various disciplines.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8 X 16 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.