9 Square Root Of 3
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
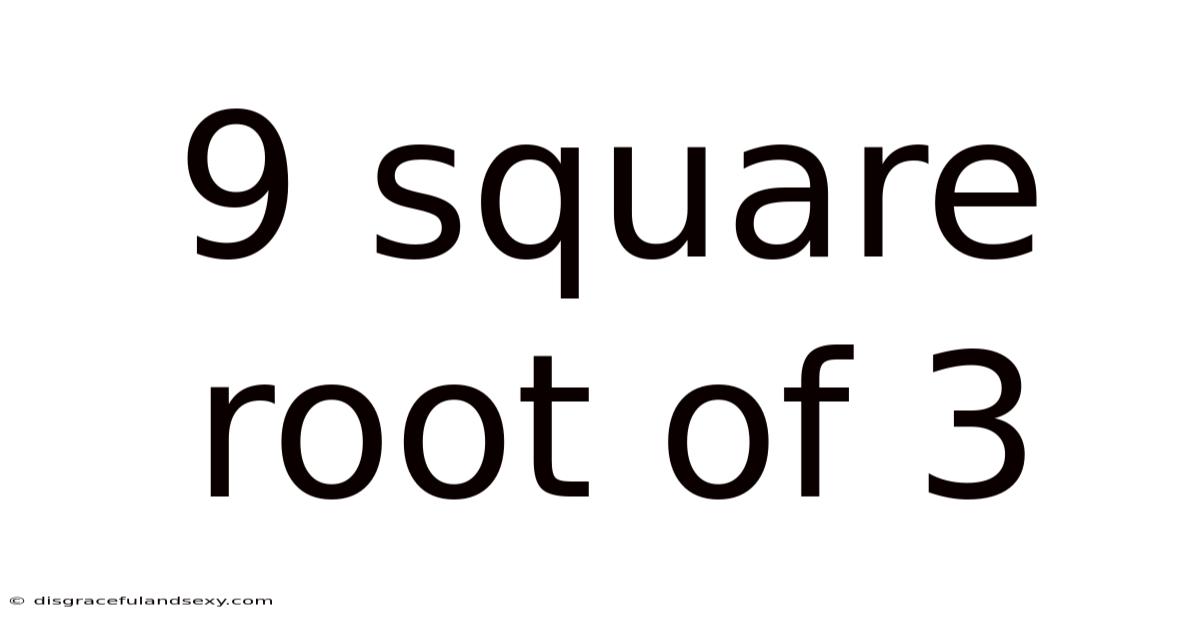
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of 9√3: A Deep Dive into its Mathematical Significance and Applications
The expression "9√3" might seem daunting at first glance, but understanding its components unlocks a world of mathematical possibilities. This article delves into the intricacies of 9√3, exploring its fundamental properties, practical applications, and its significance within broader mathematical contexts. We'll journey from the basics of square roots and simplifying expressions to more advanced applications in geometry, trigonometry, and even physics. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate this seemingly simple expression, revealing its surprising depth and relevance.
Understanding the Basics: Square Roots and Simplification
Before we embark on our exploration of 9√3, let's solidify our understanding of the core components: square roots and radical simplification. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. The number under the square root symbol (√) is called the radicand.
Now, let's consider 9√3. This expression represents 9 multiplied by the square root of 3. We can't simplify √3 further because 3 is not a perfect square (it's not the result of squaring a whole number). However, we can understand its approximate value. √3 is approximately 1.732. Therefore, 9√3 is approximately 9 * 1.732 = 15.588. This approximation is useful for practical applications, but it's crucial to remember that √3 is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
Geometric Applications: Triangles and Their Properties
One of the most common applications of 9√3 lies within geometry, particularly in the realm of triangles. Consider an equilateral triangle. All its sides are equal in length, and all its angles measure 60 degrees. The height (or altitude) of an equilateral triangle with side length 's' is given by the formula: height = (s√3)/2.
Let's say we have an equilateral triangle with a side length of 6 units. Using the formula, the height would be (6√3)/2 = 3√3. Now, imagine we have three such equilateral triangles forming a larger equilateral triangle. The height of this larger triangle would be 3 * 3√3 = 9√3. This demonstrates the direct link between 9√3 and the geometric properties of equilateral triangles. This relationship extends to other geometric figures derived from equilateral triangles.
Furthermore, 9√3 appears frequently in calculations involving special right-angled triangles, specifically 30-60-90 triangles. These triangles have angles of 30, 60, and 90 degrees, and their side lengths are in a specific ratio. Understanding this ratio allows us to quickly calculate various lengths and areas involving these triangles, often leading to expressions containing 9√3.
Trigonometric Connections: Sine, Cosine, and Tangent
Trigonometry provides another avenue for exploring the significance of 9√3. The trigonometric functions—sine, cosine, and tangent—relate the angles of a right-angled triangle to the ratios of its sides. In a 30-60-90 triangle, the ratios involving these functions often lead to expressions with √3.
For example, in a 30-60-90 triangle, the sine of 60 degrees (sin 60°) is √3/2. Similarly, the cosine of 30 degrees (cos 30°) is also √3/2. Understanding these relationships allows us to solve numerous problems related to angles and side lengths in triangles, and calculations can easily incorporate 9√3 in various scenarios involving multiple triangles or scaled versions of these special right triangles.
Advanced Applications: Vector Analysis and Physics
The applications of 9√3 extend beyond basic geometry and trigonometry. In physics and engineering, vector analysis frequently involves calculations that lead to expressions containing √3. Vectors are quantities with both magnitude and direction, and they are crucial for representing forces, velocities, and other physical quantities.
Consider, for instance, a scenario involving the resolution of forces. If a force is acting at an angle of 60 degrees, resolving this force into its horizontal and vertical components might involve calculations that result in terms containing √3. Similarly, in analyzing the motion of projectiles, the calculations related to velocity and displacement frequently involve trigonometric functions, thus incorporating √3 in the resulting equations. A more complex problem might incorporate multiples of these simpler scenarios, culminating in a result that could include 9√3.
Illustrative Examples: Real-World Applications
Let's consider a few real-world scenarios where 9√3 might appear:
-
Civil Engineering: Designing a bridge structure or a supporting framework for a building might involve calculations involving equilateral triangles or 30-60-90 triangles, which directly lead to expressions involving √3 and potentially multiples such as 9√3.
-
Electrical Engineering: In analyzing alternating current circuits, calculations involving phase angles and impedance can lead to expressions containing trigonometric functions, often resulting in terms like 9√3, especially in scenarios involving complex impedance analysis with specific angular relationships.
-
Computer Graphics: Generating realistic images requires extensive use of geometry and trigonometry, making 9√3 a potentially relevant value in algorithms for rendering three-dimensional shapes and calculating lighting effects, especially when dealing with regular polygons and their rotational symmetries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: How can I calculate the exact value of 9√3? A: You cannot calculate the exact value of 9√3 because √3 is an irrational number with an infinite, non-repeating decimal representation. You can obtain an approximation using a calculator or by using numerical methods.
-
Q: Is 9√3 a rational or irrational number? A: 9√3 is an irrational number because it is the product of a rational number (9) and an irrational number (√3). The product of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational.
-
Q: What are some alternative ways to represent 9√3? A: While there isn't a simpler exact representation, you can express it as 9 * ³√27 (since 3 cubed is 27). However, this doesn't fundamentally simplify the expression.
-
Q: Are there any other mathematical contexts where 9√3 arises? A: Yes, many areas within advanced mathematics, such as complex analysis and abstract algebra, might involve expressions that simplify to or incorporate multiples of √3. However, these are generally far more advanced mathematical contexts beyond the scope of this introductory explanation.
Conclusion: The Broader Significance of 9√3
While seemingly simple, the expression 9√3 holds significant mathematical weight. Its appearances in geometry, trigonometry, and physics highlight its fundamental role within a wide range of applications. Understanding its properties and connections to other mathematical concepts provides a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of different mathematical fields. This exploration emphasizes the importance of mastering fundamental concepts like square roots and trigonometric functions, which serve as building blocks for more complex mathematical endeavors. From simple geometric calculations to advanced physics problems, 9√3 proves to be a surprisingly pervasive and significant mathematical constant, far exceeding its initial apparent simplicity. The ability to recognize and manipulate such expressions is crucial for anyone pursuing further studies in mathematics, engineering, and related fields.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 9 Square Root Of 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.