9x2 + 18x + 8
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
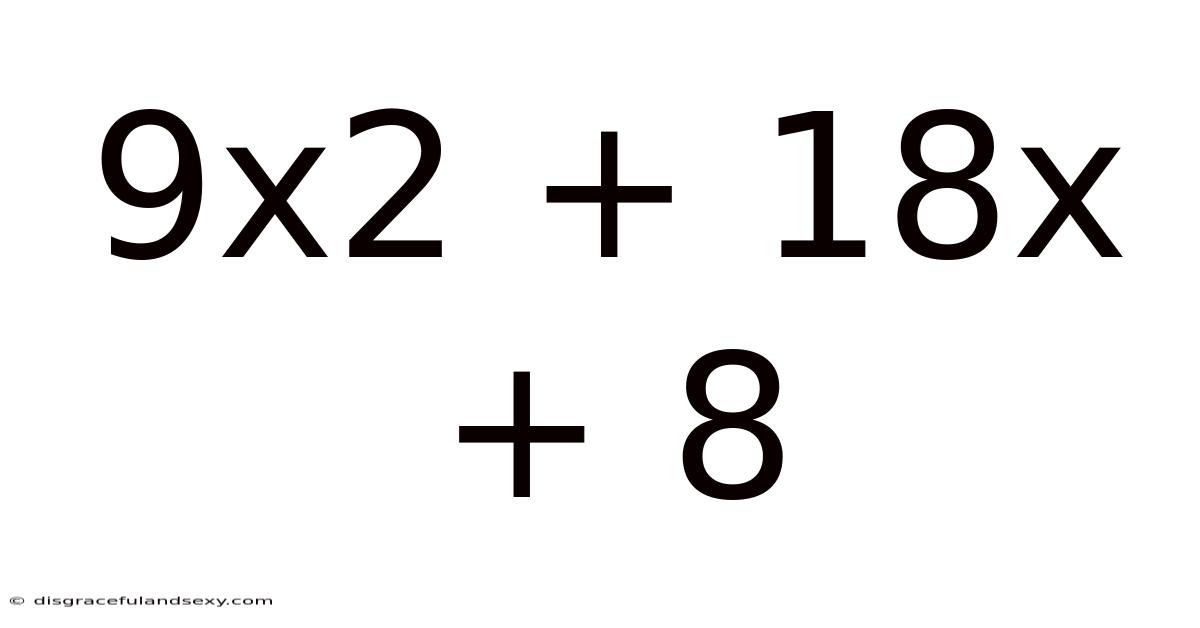
Table of Contents
Decoding the Quadratic Expression: 9x² + 18x + 8
This article delves deep into the quadratic expression 9x² + 18x + 8, exploring its various facets from basic simplification and factorization to its graphical representation and real-world applications. We'll unpack its components, understand its behavior, and learn how to solve equations involving this expression. Whether you're a high school student grappling with algebra or a math enthusiast looking to refresh your knowledge, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools to master this seemingly simple yet surprisingly rich quadratic expression.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we dive into the specifics of 9x² + 18x + 8, let's establish a foundation in quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial expression of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It takes the general form: ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a is not equal to zero. Our expression, 9x² + 18x + 8, perfectly fits this mold, with a = 9, b = 18, and c = 8.
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: Finding the Roots
Factoring a quadratic expression involves rewriting it as a product of two simpler expressions. This process is crucial for solving quadratic equations and understanding the expression's behavior. There are several methods for factoring, and we'll explore the most common ones in relation to 9x² + 18x + 8.
1. The AC Method:
This method is particularly useful when the coefficient of x² (a) is not 1. We multiply a and c (9 * 8 = 72). Then, we look for two numbers that add up to b (18) and multiply to 72. These numbers are 12 and 6. We rewrite the expression as follows:
9x² + 12x + 6x + 8
Now, we factor by grouping:
3x(3x + 4) + 2(3x + 4)
Notice that (3x + 4) is a common factor. We can factor it out:
(3x + 4)(3x + 2)
Therefore, the factored form of 9x² + 18x + 8 is (3x + 4)(3x + 2).
2. Quadratic Formula:
The quadratic formula provides a direct method for finding the roots (or zeros) of a quadratic equation, which are the values of x that make the expression equal to zero. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Plugging in the values from our expression (a = 9, b = 18, c = 8):
x = [-18 ± √(18² - 4 * 9 * 8)] / (2 * 9) x = [-18 ± √(324 - 288)] / 18 x = [-18 ± √36] / 18 x = [-18 ± 6] / 18
This gives us two solutions:
x = (-18 + 6) / 18 = -12/18 = -2/3 x = (-18 - 6) / 18 = -24/18 = -4/3
These roots correspond to the factors we found using the AC method: (3x + 4) and (3x + 2). Setting each factor equal to zero and solving for x yields the same roots: -4/3 and -2/3.
Graphical Representation: Parabolas
Quadratic expressions are graphically represented as parabolas. A parabola is a U-shaped curve. The parabola's vertex represents the minimum or maximum value of the expression, and its x-intercepts represent the roots of the corresponding quadratic equation (where the expression equals zero).
For 9x² + 18x + 8, the parabola opens upwards because the coefficient of x² (a = 9) is positive. The x-intercepts are at x = -4/3 and x = -2/3, which we found earlier. The vertex can be found using the formula x = -b/2a:
x = -18 / (2 * 9) = -1
Substituting x = -1 back into the expression gives the y-coordinate of the vertex:
9(-1)² + 18(-1) + 8 = -1
So the vertex of the parabola is at (-1, -1).
Completing the Square
Another method for solving quadratic equations and understanding the structure of a quadratic expression is completing the square. This involves manipulating the expression to create a perfect square trinomial. Let's apply this to 9x² + 18x + 8:
- Factor out the coefficient of x²:
9(x² + 2x) + 8
- Complete the square inside the parenthesis: To complete the square for x² + 2x, we take half of the coefficient of x (which is 1), square it (1² = 1), and add and subtract it inside the parenthesis:
9(x² + 2x + 1 - 1) + 8
- Rewrite as a perfect square:
9((x + 1)² - 1) + 8
- Simplify:
9(x + 1)² - 9 + 8
9(x + 1)² - 1
This form, 9(x + 1)² - 1, reveals the vertex form of the quadratic, making it easy to identify the vertex (-1, -1).
Real-World Applications
Quadratic expressions like 9x² + 18x + 8 are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields:
- Physics: Describing projectile motion, where the height of an object over time follows a parabolic path.
- Engineering: Modeling the curve of bridges, arches, and other structures.
- Economics: Analyzing profit maximization problems, where quadratic functions can represent revenue or cost.
- Computer Graphics: Creating curved lines and shapes in computer-generated images.
Solving Equations Involving 9x² + 18x + 8
Let's consider an example of solving an equation involving our quadratic expression:
9x² + 18x + 8 = 0
We've already solved this equation using the quadratic formula and factoring. The solutions are x = -4/3 and x = -2/3. These are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis.
Now consider a slightly more complex example:
9x² + 18x + 8 = 16
To solve this, we first set the equation to zero:
9x² + 18x - 8 = 0
Now we can use the quadratic formula or attempt to factor. In this case, factoring might be less straightforward. Applying the quadratic formula:
x = [-18 ± √(18² - 4 * 9 * -8)] / (2 * 9) x = [-18 ± √(324 + 288)] / 18 x = [-18 ± √612] / 18
This yields two irrational solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the discriminant of 9x² + 18x + 8?
A: The discriminant (b² - 4ac) is 36, indicating that the quadratic equation has two real and distinct roots.
-
Q: Is 9x² + 18x + 8 a prime polynomial?
A: No, it is not a prime polynomial because it can be factored into (3x + 4)(3x + 2).
-
Q: What is the axis of symmetry of the parabola represented by 9x² + 18x + 8?
A: The axis of symmetry is a vertical line passing through the vertex. Its equation is x = -1.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple quadratic expression 9x² + 18x + 8 unveils a wealth of mathematical concepts and practical applications. By understanding its factorization, graphical representation, and the methods for solving associated equations, we gain a deeper appreciation of its significance in various fields. From basic algebra to advanced applications in physics and engineering, mastering this expression forms a crucial foundation for further mathematical exploration. This exploration has not only provided solutions but also demonstrated diverse problem-solving techniques within the realm of quadratic equations. Remember, consistent practice and a deeper understanding of the underlying principles are key to mastering this fundamental aspect of algebra.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 9x2 + 18x + 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.