C 2pir Solve For R
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
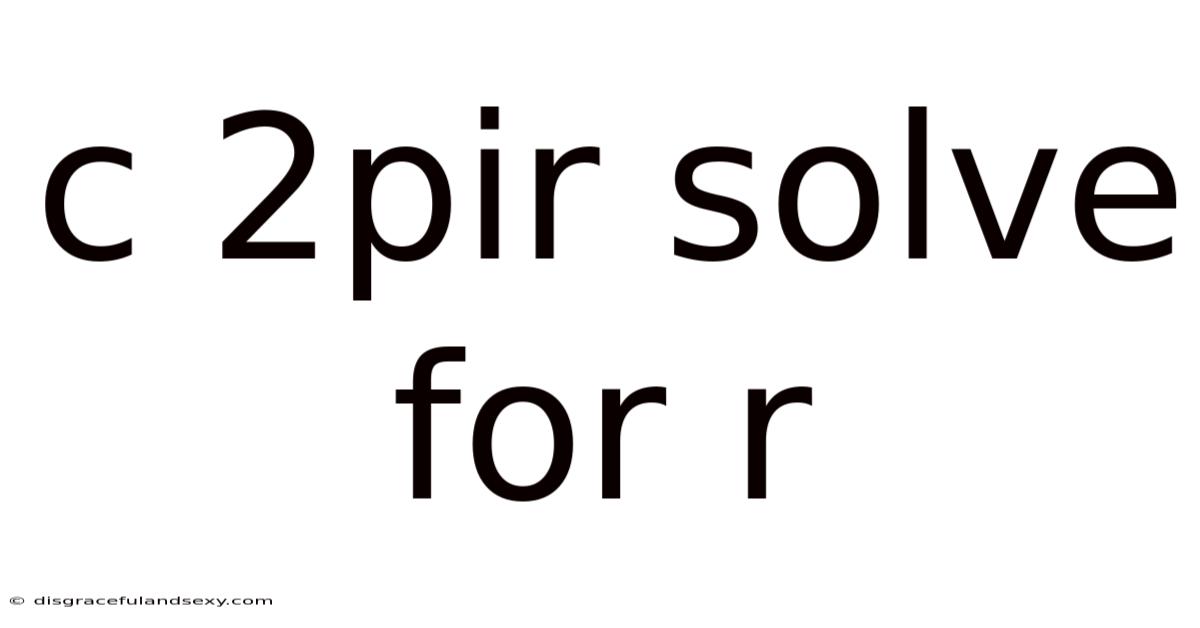
Table of Contents
Solving for Radius: Understanding and Applying C = 2πr
The formula C = 2πr represents a fundamental concept in geometry: the circumference of a circle. Understanding this equation and how to manipulate it to solve for different variables, particularly the radius (r), is crucial for various applications in mathematics, science, and engineering. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to solve for 'r' in the equation C = 2πr, including step-by-step instructions, explanations of the underlying principles, real-world applications, and frequently asked questions.
Understanding the Formula: C = 2πr
Before diving into the solution, let's solidify our understanding of the formula itself. The equation C = 2πr states that the circumference (C) of a circle is equal to twice the product of pi (π) and its radius (r).
- C: Represents the circumference, which is the distance around the circle.
- π (Pi): An irrational mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
- r: Represents the radius, which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
This formula is derived from the fundamental properties of circles and the relationship between their circumference and diameter. The diameter (d) of a circle is twice its radius (d = 2r). Since the ratio of circumference to diameter is π (C/d = π), we can substitute 2r for d, leading to the equation C = 2πr.
Solving for r: A Step-by-Step Guide
To solve for the radius (r), we need to isolate 'r' on one side of the equation. Here's a step-by-step guide:
1. Start with the formula:
C = 2πr
2. Divide both sides by 2π:
To isolate 'r', we need to eliminate the '2π' that's multiplying it. We achieve this by dividing both sides of the equation by 2π. This maintains the equality of the equation.
C / (2π) = (2πr) / (2π)
3. Simplify:
The '2π' on the right-hand side cancels out, leaving us with:
r = C / (2π)
This is our solution. The radius (r) is equal to the circumference (C) divided by 2π.
Practical Applications: Using the Formula in Real-World Scenarios
The ability to solve for the radius using C = 2πr has numerous practical applications:
-
Engineering and Construction: Calculating the radius is vital in designing circular structures, such as pipes, roads, and building foundations. Knowing the radius allows engineers to determine the amount of materials needed and ensure structural integrity. For instance, calculating the radius of a water pipe is essential to determine its flow capacity.
-
Manufacturing and Design: In manufacturing processes, precise measurements are crucial. Solving for the radius is essential in creating circular components for machinery, automotive parts, or other products requiring circular shapes. Determining the radius ensures the correct size and functionality of these parts.
-
Cartography and Geography: Calculating the radius is important in understanding the Earth’s dimensions and in map projections. For example, determining the radius of the Earth at different latitudes is crucial for accurate geographic calculations.
-
Astronomy: In astronomy, understanding the radii of celestial bodies (planets, stars, etc.) helps scientists model their behavior and understand their properties. This includes calculating orbital paths and estimating the sizes of distant objects.
Understanding Pi (π) and its Role
The constant π (pi) plays a central role in the formula C = 2πr. Its value is approximately 3.14159, but it's an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. This means we often use approximations of π in calculations, depending on the required level of accuracy.
The significance of π lies in its fundamental relationship between a circle's circumference and diameter. No matter the size of the circle, the ratio of its circumference to its diameter always equals π. This consistency makes π a crucial constant in various mathematical and scientific calculations.
Illustrative Examples: Solving for Radius
Let's work through some examples to illustrate the application of the formula r = C / (2π):
Example 1:
A circular garden has a circumference of 25 meters. What is its radius?
Using the formula:
r = C / (2π) = 25 meters / (2 * 3.14159) ≈ 3.98 meters
Therefore, the radius of the garden is approximately 3.98 meters.
Example 2:
A circular track has a circumference of 400 meters. Find the radius of the track.
Using the formula:
r = C / (2π) = 400 meters / (2 * 3.14159) ≈ 63.66 meters
The radius of the circular track is approximately 63.66 meters.
Advanced Considerations: Dealing with Units and Precision
Remember to always pay attention to the units of measurement. If the circumference is given in meters, the radius will also be in meters. Similarly, if the circumference is in feet, the radius will be in feet.
The precision of your answer depends on the precision of the value of π used in your calculation. For most practical applications, using π ≈ 3.14 is sufficient. However, for more accurate results, use a more precise value of π, such as 3.14159 or even more decimal places depending on the requirements of the problem. Many calculators have a dedicated π button for increased accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if I need to solve for the circumference (C) instead of the radius (r)?
A1: If you know the radius (r), you simply substitute its value into the original formula: C = 2πr. Multiply 2, π, and the radius to find the circumference.
Q2: Can I use this formula for any type of circle?
A2: Yes, this formula applies to all circles, regardless of their size or location. The relationship between circumference and radius remains constant for all circles.
Q3: How does the formula relate to the diameter?
A3: The diameter (d) of a circle is twice its radius (d = 2r). You can substitute 'd' into the formula to obtain another form of the circumference equation: C = πd.
Q4: What if I'm given the area of the circle instead of the circumference? Can I still find the radius?
A4: Yes, the area of a circle is given by A = πr². You can solve this equation for r by dividing both sides by π and then taking the square root: r = √(A/π).
Conclusion
Solving for the radius (r) in the equation C = 2πr is a fundamental skill in mathematics and has numerous practical applications across various fields. By understanding the steps involved in isolating 'r' and by applying the formula correctly, you can accurately calculate the radius of any circle given its circumference. Remember to pay attention to units and the precision of your calculations to ensure accurate results. This understanding provides a foundation for tackling more complex geometrical problems and enhances your ability to solve real-world challenges involving circular shapes.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about C 2pir Solve For R . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.