Derivative Of 5 Sin X
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
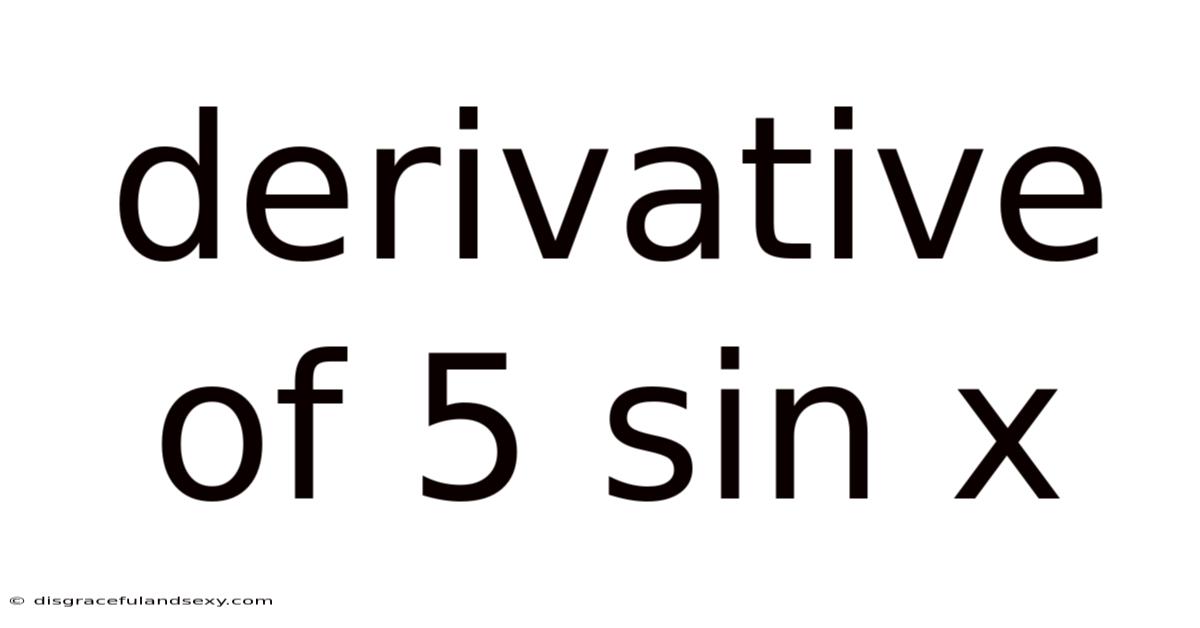
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mystery: Finding the Derivative of 5sin(x)
Understanding derivatives is fundamental to calculus, a powerful tool used across numerous fields, from physics and engineering to economics and finance. This article delves into finding the derivative of 5sin(x), a seemingly simple yet crucial concept that forms the bedrock of more complex calculations. We will explore the process step-by-step, explain the underlying principles, and address common questions, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for all readers, regardless of their mathematical background. By the end, you'll not only know the answer but also understand why it's the answer.
Introduction: Derivatives and Their Significance
Before diving into the specifics of 5sin(x), let's establish a foundational understanding of derivatives. In simple terms, the derivative of a function represents its instantaneous rate of change. Imagine a car traveling along a road; its speed at any given moment is its instantaneous rate of change of position. Similarly, the derivative of a function at a specific point tells us the slope of the tangent line to the function's graph at that point.
Derivatives are crucial because they allow us to analyze how functions change. This analysis has widespread applications:
- Physics: Calculating velocity and acceleration from position functions.
- Engineering: Optimizing designs and predicting system behavior.
- Economics: Modeling marginal cost and revenue.
- Machine Learning: Developing algorithms for optimization and prediction.
The derivative of a function f(x) is often denoted as f'(x), df/dx, or d/dx[f(x)].
Finding the Derivative of 5sin(x): A Step-by-Step Guide
The process of finding the derivative of 5sin(x) involves applying several key rules of differentiation:
-
The Constant Multiple Rule: This rule states that the derivative of a constant times a function is equal to the constant times the derivative of the function. Mathematically:
d/dx[cf(x)] = c * d/dx[f(x)]
where 'c' is a constant. In our case, c = 5 and f(x) = sin(x).
-
The Derivative of sin(x): This is a fundamental derivative that you'll need to memorize:
d/dx[sin(x)] = cos(x)
Now, let's combine these rules to find the derivative of 5sin(x):
d/dx[5sin(x)] = 5 * d/dx[sin(x)] (Applying the Constant Multiple Rule)
d/dx[5sin(x)] = 5 * cos(x) (Applying the derivative of sin(x))
Therefore, the derivative of 5sin(x) is 5cos(x).
A Deeper Dive: Understanding the Underlying Principles
The derivative of sin(x) being cos(x) might seem arbitrary, but it stems from the geometrical definition of the trigonometric functions and the concept of limits. While a full derivation is beyond the scope of this introductory article, understanding the intuition behind it is beneficial.
Imagine the unit circle. The sine of an angle x represents the y-coordinate of the point on the circle corresponding to that angle. As x changes (the angle increases), the y-coordinate changes as well. The rate at which this y-coordinate changes is the derivative. This rate is precisely the x-coordinate, which is defined as the cosine of the angle. This geometric relationship translates into the derivative d/dx[sin(x)] = cos(x).
Extending the Concepts: Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions
Understanding the derivative of 5sin(x) paves the way for understanding derivatives of other trigonometric functions. Here's a quick summary:
-
d/dx[cos(x)] = -sin(x): The negative sign reflects the fact that the cosine function decreases as the angle increases in the first quadrant.
-
d/dx[tan(x)] = sec²(x): The derivative of tangent is the square of the secant function.
-
d/dx[cot(x)] = -csc²(x): Similar to the cosine derivative, the cotangent derivative is negative.
-
d/dx[sec(x)] = sec(x)tan(x)
-
d/dx[csc(x)] = -csc(x)cot(x)
These derivatives are essential for solving more complex calculus problems involving trigonometric functions.
Applications: Real-World Examples
The derivative of 5sin(x), and more broadly, derivatives of trigonometric functions, have numerous real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
-
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM): Many physical systems, such as pendulums and mass-spring systems, exhibit SHM. The position of an object undergoing SHM can be described using a sine or cosine function. The derivative gives us the velocity and the second derivative gives us the acceleration.
-
Wave Phenomena: Waves, including sound waves and light waves, can be modeled using trigonometric functions. Derivatives are essential for analyzing wave properties, such as speed, frequency, and wavelength.
-
Electrical Circuits: In alternating current (AC) circuits, voltage and current often vary sinusoidally. Derivatives allow us to analyze the rate of change of voltage and current, which is crucial for understanding circuit behavior.
-
Signal Processing: Derivatives are used extensively in signal processing to analyze and manipulate signals, such as audio and images.
These are just a few examples demonstrating the far-reaching significance of derivatives in understanding and modeling real-world phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the derivative of sin(x) cos(x)?
A: This relationship is fundamentally geometric. The rate of change of the y-coordinate (sin(x)) on the unit circle is equal to the x-coordinate (cos(x)). This geometric relationship is formalized using the concept of limits in calculus.
Q: Can I use a calculator to find the derivative?
A: While calculators can perform numerical calculations, they don't directly provide symbolic derivatives. Understanding the rules of differentiation is crucial for solving problems involving derivatives. However, computer algebra systems (CAS) like Mathematica or Maple can symbolically calculate derivatives.
Q: What if the function was 5sin(2x)?
A: This requires the chain rule. The derivative would be 10cos(2x). The chain rule states that the derivative of a composite function is the derivative of the outer function (with the inside function left alone) times the derivative of the inner function.
Q: Are there other ways to find the derivative besides using the rules?
A: Yes, numerical methods can approximate the derivative using finite differences. However, these methods are approximations and don't provide the exact symbolic expression for the derivative.
Q: What is the second derivative of 5sin(x)?
A: The second derivative is obtained by differentiating the first derivative. The first derivative of 5sin(x) is 5cos(x). Differentiating this again gives us -5sin(x).
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of Derivatives
Understanding the derivative of 5sin(x) is not merely about obtaining the answer 5cos(x). It's about grasping the fundamental principles of calculus, appreciating the power of derivatives in analyzing change, and building a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical concepts. This knowledge opens doors to a deeper understanding of numerous scientific and engineering disciplines, equipping you with valuable tools for problem-solving and innovation. By mastering these fundamentals, you embark on a journey into the fascinating world of calculus and its endless applications. Remember to practice regularly, applying these rules to various functions to solidify your understanding and build confidence in your abilities. The journey may seem challenging at times, but the rewards are immense.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Derivative Of 5 Sin X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.