Derivative Of E 3x 2
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 5 min read
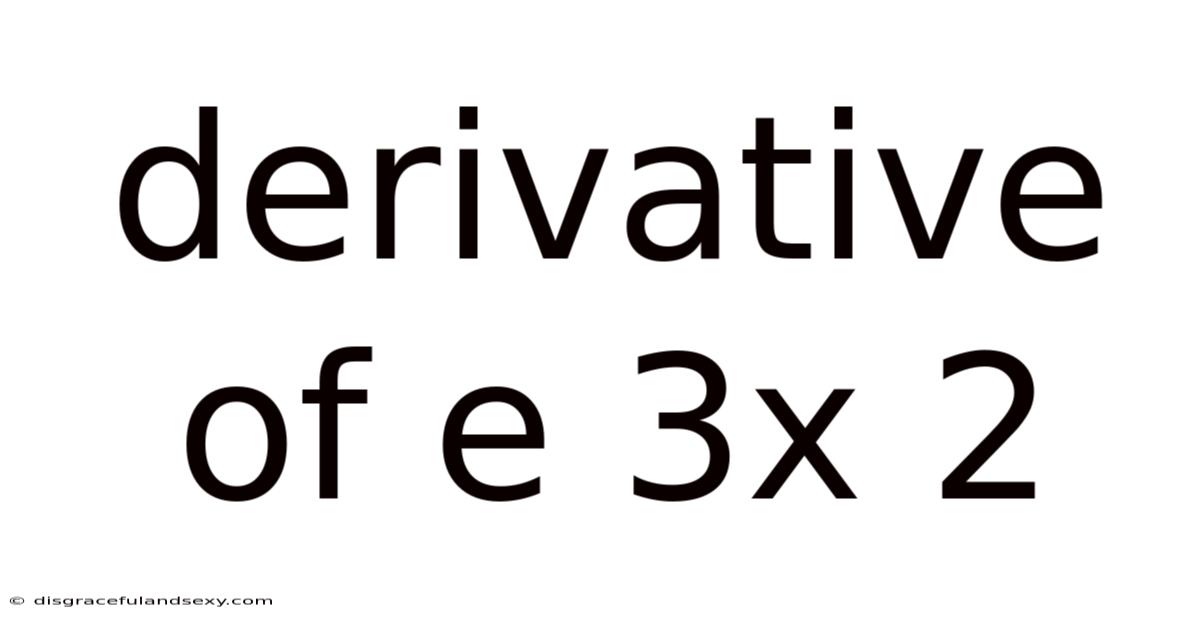
Table of Contents
Understanding the Derivative of e^(3x²): A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the derivative of exponential functions is a fundamental concept in calculus. This article provides a comprehensive explanation of how to derive the function e^(3x²), covering the underlying principles, step-by-step calculations, and addressing frequently asked questions. We will explore the chain rule, a crucial technique for differentiating composite functions like this one. Mastering this will solidify your understanding of calculus and its applications.
Introduction: Unveiling the Power of the Chain Rule
The function e^(3x²) is a composite function, meaning it's a function within a function. The outer function is the exponential function, e^u, and the inner function is u = 3x². To find its derivative, we'll utilize the chain rule, a powerful tool in calculus. The chain rule states that the derivative of a composite function is the derivative of the outer function (with the inner function left alone) multiplied by the derivative of the inner function. Mathematically, if y = f(g(x)), then dy/dx = f'(g(x)) * g'(x). This seemingly complex rule will become clear as we work through the example of e^(3x²).
Step-by-Step Differentiation of e^(3x²)
Let's break down the differentiation process step-by-step:
-
Identify the Outer and Inner Functions:
- Outer function: f(u) = e^u
- Inner function: g(x) = 3x²
-
Find the Derivative of the Outer Function:
The derivative of e^u with respect to u is simply e^u. Therefore, f'(u) = e^u.
-
Find the Derivative of the Inner Function:
The derivative of 3x² with respect to x is found using the power rule: d/dx (ax^n) = nax^(n-1). Applying this, we get g'(x) = 6x.
-
Apply the Chain Rule:
Now, we combine the derivatives according to the chain rule:
dy/dx = f'(g(x)) * g'(x) = e^(3x²) * 6x
-
Final Result:
The derivative of e^(3x²) is 6xe^(3x²).
Detailed Explanation and Illustrative Examples
Let's delve deeper into the reasoning behind each step and consider some related examples.
-
The Exponential Function e^x: The exponential function e^x is unique because its derivative is itself. This property makes it fundamental in many areas of mathematics and science, particularly in modeling exponential growth and decay.
-
The Power Rule: The power rule, as used in step 3, is a cornerstone of differentiation. It allows us to efficiently find the derivatives of functions involving powers of x. Understanding its application is crucial for mastering differentiation.
-
The Chain Rule's Intuition: Imagine a chain of gears. The rate at which the final gear turns depends on the rate at which each individual gear turns. Similarly, the rate of change of a composite function depends on the rate of change of its inner and outer functions. The chain rule elegantly captures this relationship.
-
Illustrative Examples:
-
Let's consider a slightly modified function: e^(x²). Following the same steps:
- Outer function: e^u
- Inner function: u = x²
- Derivative of outer function: e^u
- Derivative of inner function: 2x
- Applying the chain rule: dy/dx = e^(x²) * 2x = 2xe^(x²)
-
Now, let's analyze e^(5x). This simplifies the process somewhat:
- Outer function: e^u
- Inner function: u = 5x
- Derivative of outer function: e^u
- Derivative of inner function: 5
- Applying the chain rule: dy/dx = e^(5x) * 5 = 5e^(5x)
-
Practical Applications and Real-World Relevance
The derivative of exponential functions, such as e^(3x²), has wide-ranging applications across numerous fields. Here are a few examples:
-
Physics: Describing radioactive decay, the cooling of objects, or the movement of damped oscillations often involves exponential functions and their derivatives. Understanding these derivatives is critical for analyzing and predicting these phenomena.
-
Biology: Population growth, particularly in bacterial cultures, often follows an exponential pattern. The derivative helps to determine the rate of population growth at any given time.
-
Finance: Compound interest calculations, options pricing models, and other financial instruments rely heavily on exponential functions and their derivatives.
-
Engineering: Many engineering problems, especially those involving heat transfer, fluid dynamics, and electrical circuits, involve solving differential equations where exponential functions are a key component.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for various tasks, such as machine learning and simulations, often make use of exponential functions, and their derivatives play a crucial role in optimization and efficiency improvements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the exponent was more complex, say, e^(3x² + 2x + 1)?
A1: The process remains the same. The inner function becomes u = 3x² + 2x + 1. Its derivative is g'(x) = 6x + 2. Applying the chain rule, the derivative of e^(3x² + 2x + 1) is (6x + 2)e^(3x² + 2x + 1).
Q2: Is there a shortcut for differentiating e^(ax²)?
A2: There isn’t a formal “shortcut”, but with practice, you can quickly identify the pattern. For e^(ax²), the derivative will always be 2axe^(ax²).
Q3: Can I use logarithmic differentiation for this problem?
A3: Yes, logarithmic differentiation is an alternative method. Take the natural logarithm of both sides, then differentiate implicitly. This method can be particularly useful for more complex exponential functions, but for e^(3x²), the chain rule is more straightforward.
Q4: What is the significance of the constant 'e'?
A4: The constant e, approximately equal to 2.71828, is the base of the natural logarithm. It arises naturally in many mathematical and scientific contexts, primarily due to its unique property that its derivative is itself. This makes it the most convenient base for exponential functions in calculus.
Q5: How can I practice more problems like this?
A5: Practice is key! Work through various examples involving composite functions and the chain rule. Start with simpler examples and gradually increase the complexity. Online resources and textbooks offer numerous problems to hone your skills.
Conclusion: Mastering Differentiation of Exponential Functions
Understanding the derivative of e^(3x²) and similar functions is essential for anyone pursuing a deeper understanding of calculus and its applications. By mastering the chain rule and practicing various examples, you will build a solid foundation in differentiation and become more confident in tackling complex mathematical problems. Remember, practice is the key to unlocking the power of calculus and realizing its wide-ranging applications in diverse fields. Continue to explore more complex functions and refine your skills; the journey of mastering calculus is both rewarding and challenging.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Derivative Of E 3x 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.