E 2 E 2 2
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
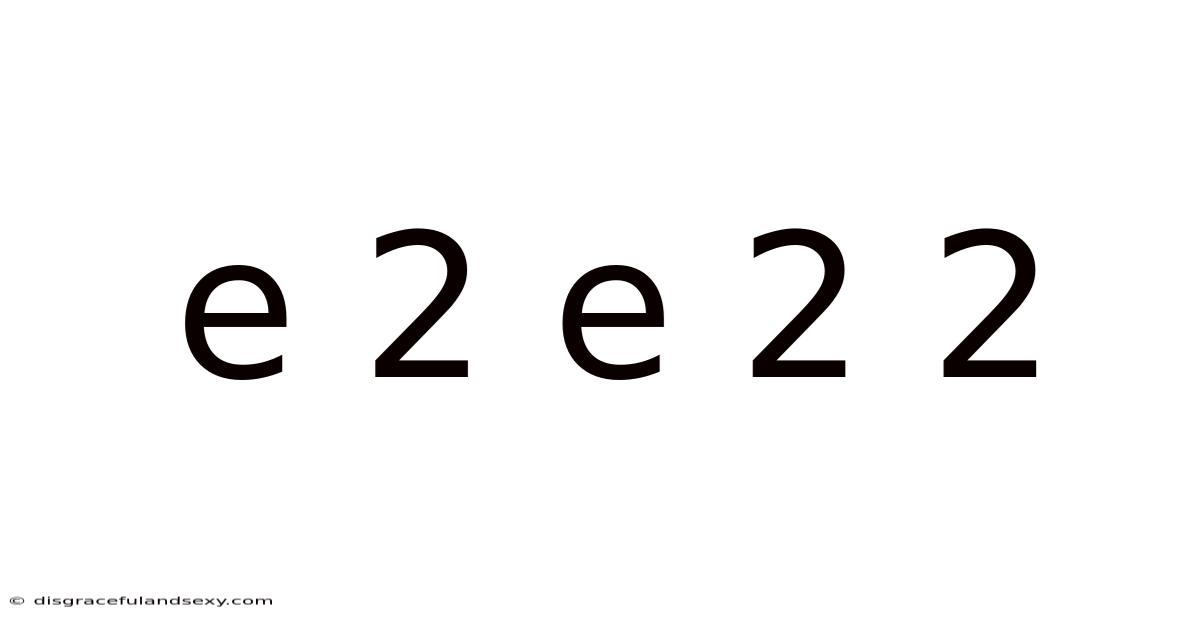
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: A Deep Dive into e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup>
The expression e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup>, at first glance, appears daunting. It's a tower of exponents, a seemingly endless climb of mathematical operations. This article aims to demystify this expression, exploring its nature, calculating its approximate value, and understanding the mathematical concepts underpinning its complexity. We'll delve into the properties of the exponential function, e, and how repeated exponentiation leads to astonishingly large numbers. This exploration will provide a solid understanding of this intriguing mathematical construct and highlight the power and elegance of mathematical notation.
Understanding the Exponential Function and e
Before we tackle the colossal e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup>, let's lay a firm foundation by understanding the exponential function and its base, e. The exponential function, often written as f(x) = a<sup>x</sup>, describes exponential growth or decay. The base, a, determines the rate of growth or decay. When a is greater than 1, we have exponential growth; when a is between 0 and 1, we have exponential decay.
The number e, approximately equal to 2.71828, holds a special place in mathematics. It's an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and it's also a transcendental number, meaning it's not a root of any non-zero polynomial with rational coefficients. e arises naturally in various areas of mathematics, including calculus, probability, and complex analysis. Its importance stems from its unique properties related to exponential growth and its connection to the natural logarithm.
One of the defining characteristics of e is its role in the derivative of the exponential function. The derivative of e<sup>x</sup> is simply e<sup>x</sup> itself – a remarkable property that simplifies many calculations in calculus. This self-replicating nature is a key reason why e appears frequently in models describing natural phenomena, such as population growth, radioactive decay, and compound interest.
Breaking Down the Tower of Exponents
Now, let's dissect our main subject: e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup>. This expression represents a tetration, which is a repeated exponentiation. Tetration is an extension of the basic arithmetic operations: addition, multiplication, and exponentiation. While addition is repeated counting, multiplication is repeated addition, and exponentiation is repeated multiplication, tetration is repeated exponentiation.
The expression can be understood as a nested series of exponentiations. We start with the innermost exponent: e<sup>2</sup>. This is approximately 7.389. Next, we have 2<sup>(e<sup>2</sup>)</sup> ≈ 2<sup>7.389</sup>, which is approximately 161.8. Then, we calculate e<sup>(2<sup>(e<sup>2</sup>)</sup>)</sup> ≈ e<sup>161.8</sup>. Finally, we have 2<sup>(e<sup>(2<sup>(e<sup>2</sup>)</sup>)</sup>)</sup> ≈ 2<sup>(e<sup>161.8</sup>)</sup>. This last step leads to an astronomically large number.
Approximating the Value
Calculating the precise value of e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup> is computationally challenging due to the sheer magnitude of the number. Even high-precision calculators will struggle. However, we can get a reasonable approximation using logarithmic properties and step-by-step calculations with increasingly precise values for e.
Let's break down the approximation:
- e<sup>2</sup> ≈ 7.389
- 2<sup>e<sup>2</sup></sup> ≈ 2<sup>7.389</sup> ≈ 161.8
- e<sup>2<sup>e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup> ≈ e<sup>161.8</sup> ≈ 1.24 × 10<sup>70</sup>
- 2<sup>e<sup>2<sup>e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup></sup> ≈ 2<sup>1.24 × 10<sup>70</sup></sup>
The final step involves a number so large that it's difficult to comprehend or even express in standard scientific notation. The number of digits in this result would be astronomical. This highlights the immense growth potential of repeated exponentiation.
The Significance of Tetration and Hyperoperations
The expression e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup> demonstrates the power and complexity of tetration. Tetration is just one example of hyperoperations, which extend beyond the familiar operations of addition, multiplication, and exponentiation. These hyperoperations provide a framework for understanding increasingly complex mathematical structures.
Tetration, represented by the notation a↑↑b or <sup>b</sup>a, is defined as repeatedly exponentiating a to itself b times. For example:
- a↑↑1 = a
- a↑↑2 = a<sup>a</sup>
- a↑↑3 = a<sup>a<sup>a</sup></sup>
- and so on.
Beyond tetration lies pentation (repeated tetration), hexation (repeated pentation), and so on. These hyperoperations quickly lead to numbers of unimaginable magnitude.
Practical Applications (Limited)
While the expression e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup> itself doesn't have direct, easily identifiable practical applications in everyday life or most scientific fields, its study illuminates important concepts. Understanding tetration and hyperoperations contributes to our understanding of:
- Computational Complexity: Algorithms dealing with extremely large numbers, as encountered in cryptography and computer science, benefit from the study of these concepts.
- Mathematical Foundations: Investigating hyperoperations helps in developing a deeper understanding of mathematical structures and their properties.
- Number Theory: The exploration of such large numbers can lead to new insights into number theory, particularly concerning the distribution and properties of large numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is there a closed-form solution for e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup>?
A: No, there's no known closed-form solution that expresses this value in a concise, easily calculable form. The sheer magnitude of the number necessitates approximation methods.
Q: What are the limitations in calculating this value?
A: The primary limitation is computational. The number is so large that it exceeds the capacity of most standard calculators and even many high-performance computers. Storing and manipulating such a large number presents significant challenges.
Q: What other mathematical concepts relate to this expression?
A: Besides tetration and hyperoperations, related concepts include:
- Exponential Growth: This expression is a prime example of extremely rapid exponential growth.
- Logarithms: Logarithms are crucial in simplifying and approximating the calculation of such large numbers.
- Limits and Calculus: Calculus provides the tools for understanding the behavior of exponential functions and their derivatives, which are essential in analyzing this expression.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple expression e<sup>2e<sup>2e<sup>2</sup></sup></sup> unveils a world of mathematical complexity and profound implications. While its precise value remains computationally elusive, exploring its structure and attempting to approximate its value provides valuable insights into the nature of exponential functions, tetration, and the limits of our computational capabilities. The journey to understanding this expression is a testament to the power and elegance of mathematics, highlighting the boundless potential for exploration within even seemingly simple mathematical constructs. The vastness of this number serves as a reminder of the incredible scale and complexity that exists within the seemingly infinite realm of mathematics. Further exploration into tetration and related hyperoperations promises even more exciting discoveries and a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about E 2 E 2 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.