Factor 3x 2 7x 2
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
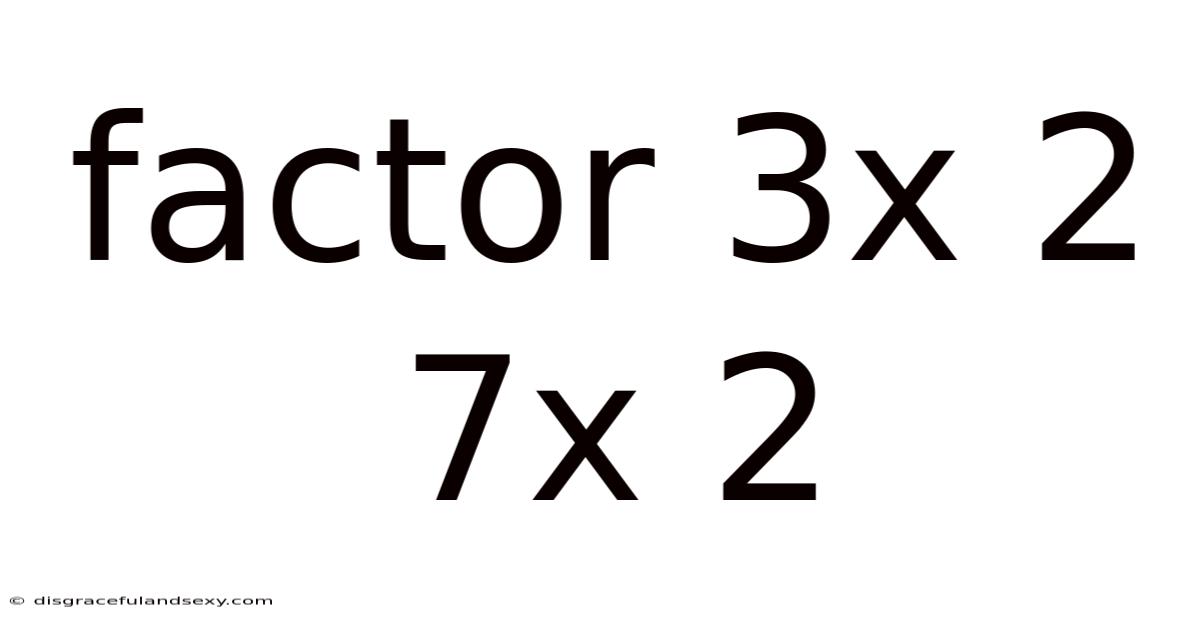
Table of Contents
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: 3x² + 7x + 2
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to factor the quadratic expression 3x² + 7x + 2. We will explore various methods, explain the underlying mathematical principles, and delve into the significance of factoring in algebra. This process is fundamental to solving quadratic equations, simplifying algebraic expressions, and understanding more advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding quadratic factoring will unlock many doors in your mathematical journey.
I. Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before diving into the factoring process, let's establish a solid understanding of what a quadratic expression is. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. In our specific case, 3x² + 7x + 2, a = 3, b = 7, and c = 2.
II. Methods for Factoring 3x² + 7x + 2
Several methods can be used to factor quadratic expressions. We will explore two common approaches:
A. The AC Method:
This method involves finding two numbers that add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 'ac' (the product of the coefficient of x² and the constant term).
-
Find the product 'ac': In our case, a = 3 and c = 2, so ac = 3 * 2 = 6.
-
Find two numbers that add up to 'b' and multiply to 'ac': We need two numbers that add up to 7 (our 'b' value) and multiply to 6. These numbers are 6 and 1 (6 + 1 = 7 and 6 * 1 = 6).
-
Rewrite the middle term: Rewrite the middle term (7x) as the sum of the two numbers we found, multiplied by x: 6x + 1x. Our expression now becomes: 3x² + 6x + 1x + 2.
-
Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair:
3x² + 6x + 1x + 2 = 3x(x + 2) + 1(x + 2)
-
Factor out the common binomial: Notice that (x + 2) is common to both terms. Factor it out:
3x(x + 2) + 1(x + 2) = (3x + 1)(x + 2)
Therefore, the factored form of 3x² + 7x + 2 is (3x + 1)(x + 2).
B. Trial and Error Method:
This method involves systematically trying different combinations of binomial factors until you find the correct one. It relies on understanding the distributive property (FOIL method).
-
Set up the binomial factors: Since the coefficient of x² is 3, we know that the first terms in our binomial factors must multiply to 3x². The possibilities are (3x _)(x _).
-
Consider the constant term: The constant term is 2. Its factors are 1 and 2, or -1 and -2.
-
Test combinations: Let's try different combinations:
-
(3x + 1)(x + 2): Using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last), this expands to 3x² + 6x + x + 2 = 3x² + 7x + 2. This is correct!
-
(3x + 2)(x + 1): This expands to 3x² + 3x + 2x + 2 = 3x² + 5x + 2. This is incorrect.
-
(3x - 1)(x - 2): This expands to 3x² - 6x - x + 2 = 3x² -7x + 2. This is incorrect.
-
(3x - 2)(x - 1): This expands to 3x² -3x -2x + 2 = 3x² -5x + 2. This is incorrect.
-
By testing these combinations, we confirm that (3x + 1)(x + 2) is the correct factorization.
III. Verification and Checking your Answer
It's crucial to verify your answer by expanding the factored form back into the original quadratic expression. Using the FOIL method on (3x + 1)(x + 2), we get:
- First: 3x * x = 3x²
- Outer: 3x * 2 = 6x
- Inner: 1 * x = x
- Last: 1 * 2 = 2
Adding these terms together: 3x² + 6x + x + 2 = 3x² + 7x + 2. This matches our original expression, confirming that our factorization is correct.
IV. The Significance of Factoring Quadratic Expressions
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra with wide-ranging applications:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring allows us to solve quadratic equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. Once factored, we can use the zero product property (if the product of two factors is zero, at least one of the factors must be zero) to find the solutions (roots) of the equation.
-
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions: Factoring can simplify complex algebraic expressions, making them easier to manipulate and understand.
-
Graphing Quadratic Functions: The factored form of a quadratic reveals the x-intercepts (where the graph crosses the x-axis) of the corresponding parabola.
-
Calculus: Factoring plays a crucial role in calculus, especially in techniques like finding derivatives and integrals.
-
Real-World Applications: Quadratic equations and their solutions are used to model many real-world phenomena, including projectile motion, area calculations, and optimization problems. Understanding factoring is therefore essential for solving these real-world problems.
V. Advanced Factoring Techniques (for more complex quadratics)
While the AC method and trial and error are sufficient for many quadratic expressions, more complex scenarios might require advanced techniques:
-
Completing the Square: This technique involves manipulating the quadratic expression to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored.
-
Quadratic Formula: This formula provides a direct solution for the roots of any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it can be easily factored. The formula is: x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a.
-
Difference of Squares: This technique applies to expressions of the form a² - b², which factors to (a + b)(a - b).
VI. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if the quadratic expression cannot be factored using integers?
A: Some quadratic expressions cannot be factored using integers. In such cases, the quadratic formula or completing the square can be used to find the roots, or the expression might be considered prime (cannot be factored).
-
Q: Is there only one way to factor a quadratic expression?
A: No. While the factored form is unique (disregarding the order of the factors), different methods might lead to the same result.
-
Q: What if the leading coefficient (a) is negative?
A: It's often helpful to factor out a -1 from the entire expression before applying the other factoring techniques. This simplifies the process.
VII. Conclusion
Factoring the quadratic expression 3x² + 7x + 2, which results in (3x + 1)(x + 2), is a fundamental algebraic skill. We explored two common methods – the AC method and trial and error – both leading to the same solution. Understanding this process extends beyond simple factorization; it unlocks the ability to solve quadratic equations, simplify complex expressions, and delve into more advanced mathematical concepts. Mastering quadratic factoring empowers you to tackle various mathematical challenges and opens doors to more complex and rewarding mathematical explorations. Remember to always check your answer by expanding the factored form to ensure accuracy. Practice regularly, and you will find this skill becoming increasingly intuitive and effortless.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor 3x 2 7x 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.