Factor 4x 2 4x 1
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
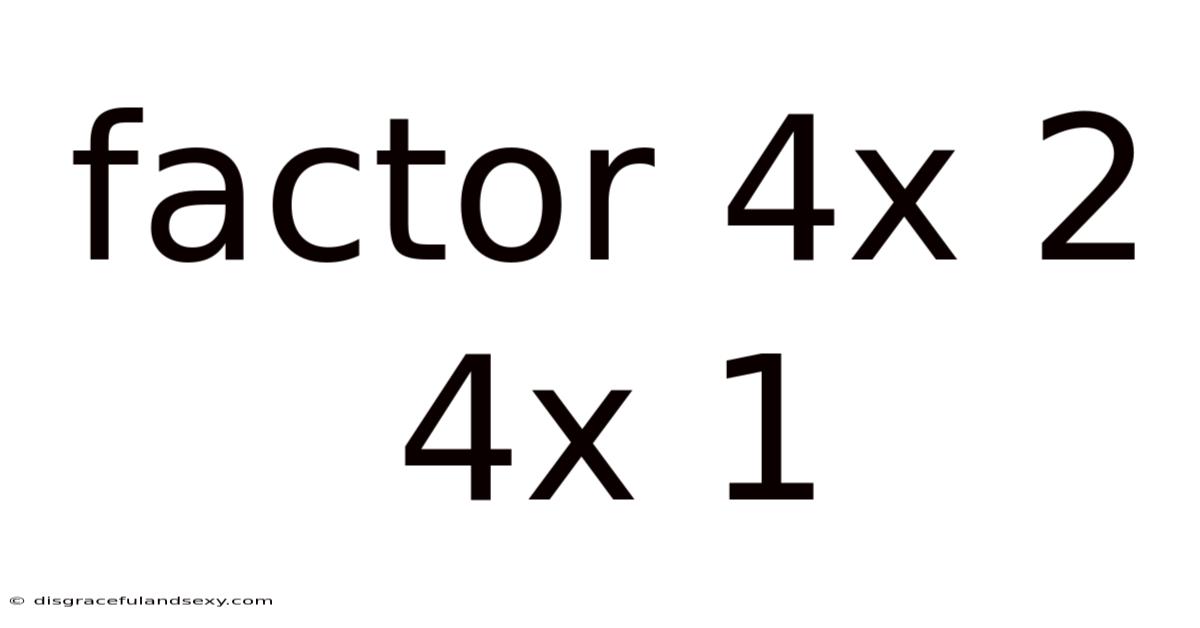
Table of Contents
Decoding the Expression: 4x² + 4x + 1 – A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding quadratic expressions is fundamental in algebra and forms the basis for many advanced mathematical concepts. This article will delve into the specifics of the expression 4x² + 4x + 1, exploring its factorization, its graphical representation, its applications, and answering frequently asked questions. We'll break down the process step-by-step, making it accessible to learners of all levels. This exploration will cover topics including quadratic equations, perfect square trinomials, and the connection between algebraic expressions and their geometric interpretations.
I. Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a mathematical expression of the form ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. The term 'quadratic' refers to the highest power of the variable 'x', which is 2. Our focus, 4x² + 4x + 1, is a specific example of a quadratic expression. Understanding how to manipulate and solve these expressions is crucial for many areas of mathematics and its real-world applications, from physics to finance. This particular expression holds a special significance as it represents a perfect square trinomial, a concept we will explore in detail.
II. Factorization: Unveiling the Hidden Structure
Factorization is the process of breaking down a mathematical expression into simpler components that, when multiplied together, produce the original expression. This is akin to finding the building blocks of a structure. For 4x² + 4x + 1, factorization reveals its inherent symmetry and allows us to simplify it significantly.
There are several methods to factor this quadratic expression. One common method is to look for patterns. Notice that:
- The first term (4x²) is a perfect square: (2x)² = 4x²
- The last term (1) is a perfect square: 1² = 1
- The middle term (4x) is twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms: 2 * (2x) * 1 = 4x
This pattern indicates that 4x² + 4x + 1 is a perfect square trinomial. This means it can be factored into the form (a + b)², where 'a' and 'b' are expressions. In our case:
4x² + 4x + 1 = (2x + 1)²
To verify this factorization, we can expand (2x + 1)² using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last):
(2x + 1)(2x + 1) = 4x² + 2x + 2x + 1 = 4x² + 4x + 1
This confirms our factorization.
III. Alternative Factorization Methods
While recognizing the perfect square trinomial pattern is the quickest method, let's explore other factorization techniques applicable to quadratic expressions in general, which can be valuable for more complex examples.
1. Factoring by Grouping: This method is useful when you have four or more terms. While not directly applicable to our simple trinomial, it's a valuable tool for more complex quadratic expressions.
2. Using the Quadratic Formula: The quadratic formula provides a general solution for solving quadratic equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. While it doesn't directly factor the expression, it can help find the roots (the values of x that make the expression equal to zero). The roots are related to the factors. For our expression, the quadratic formula would give us a repeated root, indicating the perfect square trinomial nature.
3. Trial and Error: This method involves systematically testing different combinations of factors until you find the correct combination. It can be time-consuming for complex expressions, but it's a good way to build intuition about factorization.
IV. Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Expression
The quadratic expression 4x² + 4x + 1 represents a parabola, a U-shaped curve. The graph of y = 4x² + 4x + 1 will be a parabola that opens upwards (because the coefficient of x² is positive). The vertex of the parabola, which is the lowest point, will be located at x = -b/2a = -4/(2*4) = -1/2. When x = -1/2, y = 0. This means the parabola touches the x-axis at x = -1/2, indicating a repeated root. The y-intercept (where the parabola crosses the y-axis) occurs when x = 0, resulting in y = 1.
Understanding the graphical representation provides a visual interpretation of the algebraic expression, connecting abstract concepts to concrete visuals. This is particularly useful for analyzing the behavior of the function, identifying its minimum value, and understanding its relationship to the roots.
V. Applications: Real-World Connections
Quadratic expressions and their related equations have numerous applications across various disciplines:
- Physics: Describing the trajectory of projectiles (e.g., the path of a ball thrown in the air).
- Engineering: Modeling the shape of curves in bridges and other structures.
- Economics: Analyzing cost functions and profit maximization in business.
- Computer Graphics: Creating curved shapes and animations.
- Mathematics: Solving problems in calculus, optimization, and other advanced mathematical areas.
The specific expression 4x² + 4x + 1, being a perfect square trinomial, simplifies calculations and analyses in these applications, often leading to more elegant solutions.
VI. Solving Quadratic Equations: Putting it into Practice
If we set our expression equal to zero, we have a quadratic equation: 4x² + 4x + 1 = 0. Solving this equation means finding the values of 'x' that satisfy the equation. Since we already factored the expression, we can easily solve the equation:
(2x + 1)² = 0
Taking the square root of both sides:
2x + 1 = 0
Solving for x:
x = -1/2
This indicates that the equation has a repeated root at x = -1/2. This means the parabola touches the x-axis at only one point.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is a perfect square trinomial?
A: A perfect square trinomial is a quadratic expression that can be factored into the square of a binomial. It follows the pattern (a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b² or (a - b)² = a² - 2ab + b².
Q2: How can I tell if a quadratic expression is a perfect square trinomial?
A: Check if the first and last terms are perfect squares, and if the middle term is twice the product of the square roots of the first and last terms.
Q3: What if the coefficient of x² is not a perfect square?
A: You can still factor the quadratic expression using other methods, such as the quadratic formula or factoring by grouping. Completing the square is another technique that can be employed.
Q4: Are there any other significant types of quadratic expressions besides perfect square trinomials?
A: Yes, there are also quadratic expressions that factor into two distinct linear factors (e.g., x² - 1 = (x-1)(x+1)) and those that cannot be factored using real numbers (these have complex roots).
Q5: What are the real-world applications of solving quadratic equations?
A: Quadratic equations are used extensively in various fields, such as physics (projectile motion), engineering (structural design), economics (optimization problems), and computer science (graphics and animation).
VIII. Conclusion: Mastering Quadratic Expressions
The expression 4x² + 4x + 1, although seemingly simple, provides a rich platform for understanding key concepts in algebra. By exploring its factorization, graphical representation, and applications, we’ve gained a deeper appreciation for the power and versatility of quadratic expressions. Mastering this type of expression builds a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and real-world problems. The ability to recognize perfect square trinomials and apply various factorization methods is invaluable for success in algebra and beyond. Remember to practice consistently and explore different approaches to deepen your understanding of these essential mathematical tools.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor 4x 2 4x 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.