Factor 6x 2 5x 4
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
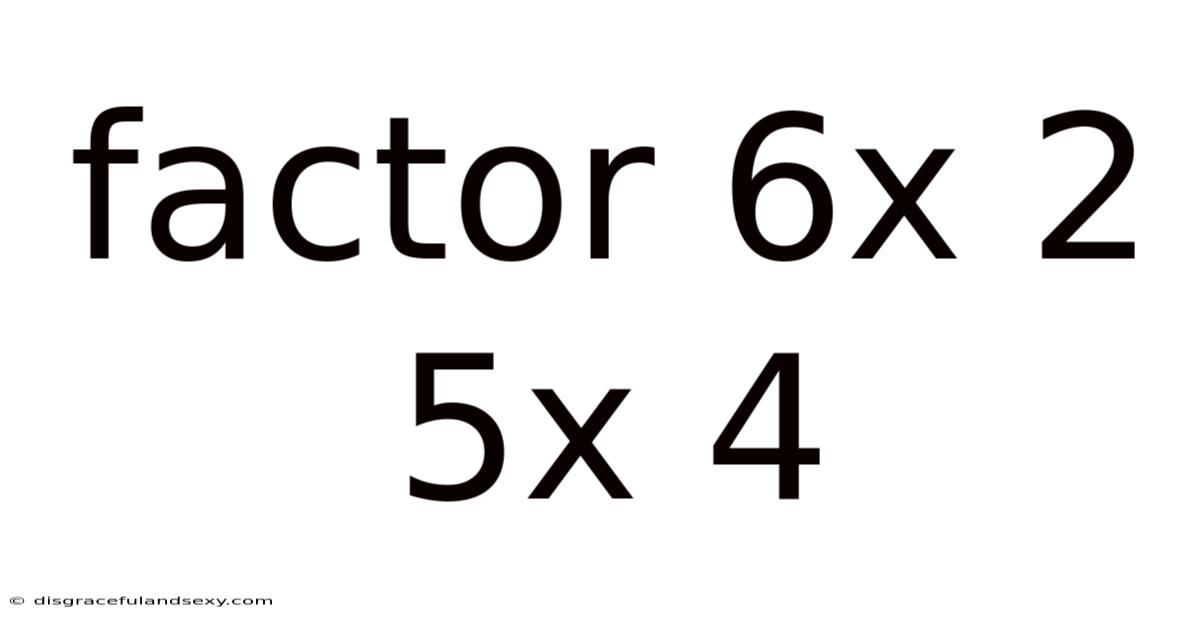
Table of Contents
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: 6x² + 5x - 4
This article will guide you through the process of factoring the quadratic expression 6x² + 5x - 4. We'll explore various methods, delve into the underlying mathematical principles, and provide a clear, step-by-step approach suitable for students of all levels. Understanding quadratic factoring is crucial for solving quadratic equations and tackling more advanced algebraic concepts. By the end of this article, you'll not only be able to factor this specific expression but also gain a comprehensive understanding of the techniques involved.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before diving into the factoring process, let's refresh our understanding of quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. In our case, the quadratic expression is 6x² + 5x - 4, where a = 6, b = 5, and c = -4.
Factoring a quadratic expression involves rewriting it as a product of two simpler expressions, usually linear binomials. This process is essential for solving quadratic equations, finding roots, and simplifying algebraic expressions.
Method 1: AC Method (Product-Sum Method)
The AC method, also known as the product-sum method, is a widely used technique for factoring quadratic expressions. It involves finding two numbers that satisfy specific conditions related to the coefficients a and c.
Steps:
-
Find the product AC: Multiply the coefficient of the x² term (a) by the constant term (c). In our case, AC = 6 * (-4) = -24.
-
Find two numbers whose product is AC and whose sum is B: We need to find two numbers that multiply to -24 and add up to 5 (the coefficient of the x term, b). These numbers are 8 and -3 because 8 * (-3) = -24 and 8 + (-3) = 5.
-
Rewrite the middle term: Rewrite the middle term (5x) using the two numbers found in step 2. Our expression becomes: 6x² + 8x - 3x - 4.
-
Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair:
2x(3x + 4) - 1(3x + 4)
-
Factor out the common binomial: Notice that (3x + 4) is a common factor in both terms. Factor it out:
(3x + 4)(2x - 1)
Therefore, the factored form of 6x² + 5x - 4 is (3x + 4)(2x - 1).
Method 2: Trial and Error
This method involves systematically testing different combinations of binomial factors until you find the correct pair. While it might seem less structured, it can be efficient once you gain experience.
Steps:
-
Consider factors of the leading coefficient (a): The coefficient of x² is 6. Its factors are (1, 6), (2, 3), (3,2), and (6,1).
-
Consider factors of the constant term (c): The constant term is -4. Its factors are (1, -4), (-1, 4), (2, -2), (-2, 2), (4,-1), (-4,1).
-
Test combinations: We systematically try different combinations of these factors to find the pair that produces the correct middle term (5x) when expanded. For example, let's try (2x + 1)(3x - 4): Expanding this gives 6x² - 8x + 3x - 4 = 6x² - 5x - 4, which is close but not quite right. The signs are incorrect.
-
Adjust signs: Let's try adjusting the signs. If we try (3x + 4)(2x - 1), expanding this gives 6x² -3x + 8x - 4 = 6x² + 5x - 4. This is correct.
Therefore, the factored form of 6x² + 5x - 4 is again (3x + 4)(2x - 1).
Method 3: Quadratic Formula (Indirect Factoring)
While not a direct factoring method, the quadratic formula can be used to find the roots of the quadratic equation 6x² + 5x - 4 = 0. These roots can then be used to construct the factored form.
The quadratic formula is given by:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For our equation, a = 6, b = 5, and c = -4. Substituting these values into the formula, we get:
x = [-5 ± √(5² - 4 * 6 * -4)] / (2 * 6) x = [-5 ± √(25 + 96)] / 12 x = [-5 ± √121] / 12 x = [-5 ± 11] / 12
This gives us two roots:
x₁ = (-5 + 11) / 12 = 6/12 = 1/2 x₂ = (-5 - 11) / 12 = -16/12 = -4/3
The factored form can then be constructed using these roots:
(x - x₁)(x - x₂) = (x - 1/2)(x + 4/3)
To eliminate fractions, we can multiply each factor by the denominator of the fraction:
(2x - 1)(3x + 4)
This again yields the factored form (3x + 4)(2x - 1).
A Deeper Dive into the Mathematics
The success of the AC method relies on the distributive property of multiplication. When we expand (3x + 4)(2x - 1), we get:
3x(2x - 1) + 4(2x - 1) = 6x² - 3x + 8x - 4 = 6x² + 5x - 4
This demonstrates how the factored form accurately represents the original quadratic expression. The trial and error method also relies on this principle, though it involves a more intuitive approach. The quadratic formula, on the other hand, provides a direct route to the roots, which are then used to reconstruct the factored form. This connection between roots and factors is a fundamental concept in algebra.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Is there only one correct factored form? A: While there might be variations in the order of the factors, the essential factors remain the same. (3x + 4)(2x - 1) is essentially the same as (2x - 1)(3x + 4).
-
Q: What if I can't find the two numbers in the AC method? A: If you cannot find two numbers whose product is AC and whose sum is B, it's possible that the quadratic expression is not factorable using integers. In such cases, other methods, such as the quadratic formula, may be necessary.
-
Q: Which method is the best? A: The best method depends on individual preference and the specific quadratic expression. The AC method provides a systematic approach, while trial and error can be quicker for simpler expressions. The quadratic formula is a reliable method for all quadratic expressions, even those that are not easily factored.
-
Q: What if the leading coefficient (a) is 1? A: If a = 1, factoring becomes simpler. You just need to find two numbers that add up to b and multiply to c.
Conclusion
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. We have explored three effective methods – the AC method, trial and error, and the indirect approach using the quadratic formula. Each method offers a different perspective on the underlying mathematical principles. Mastering these methods will greatly enhance your ability to solve quadratic equations, simplify algebraic expressions, and progress to more advanced mathematical concepts. Remember to practice regularly to build confidence and fluency in factoring quadratic expressions. The more you practice, the easier it will become to recognize patterns and choose the most efficient method for each problem. Understanding the underlying mathematics will help you not just solve problems but truly grasp the concepts involved.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor 6x 2 5x 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.