Factor 6x 2 7x 3
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
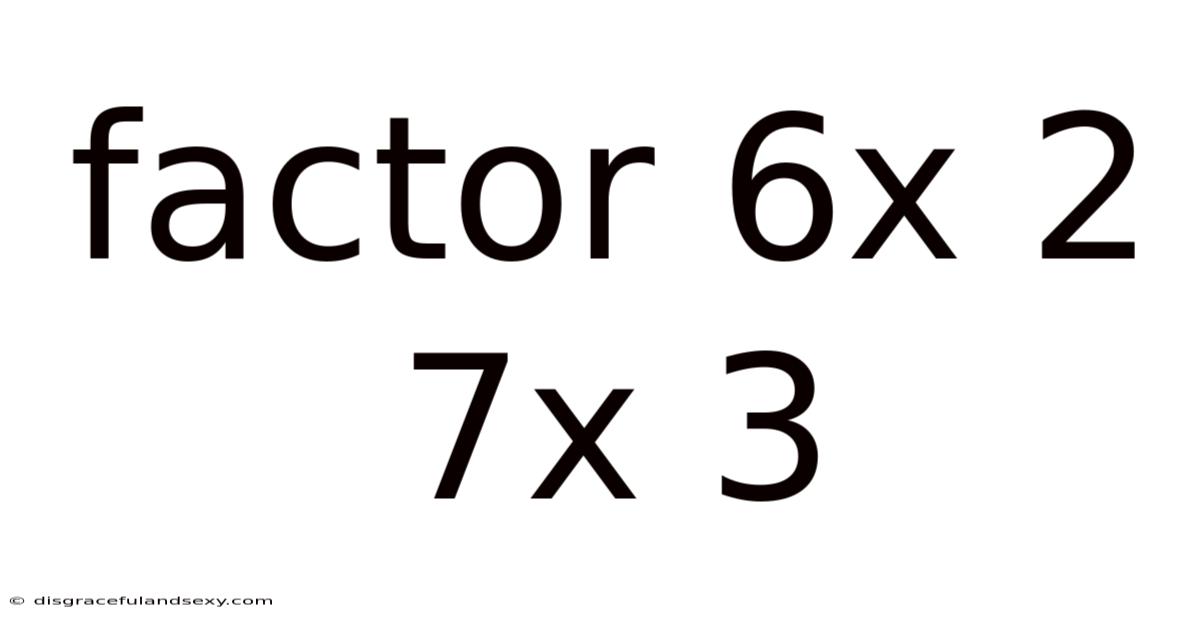
Table of Contents
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: 6x² + 7x - 3
Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on factoring the specific quadratic expression 6x² + 7x - 3, explaining the process step-by-step and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll cover various methods, explore why this particular expression presents a good example of factoring challenges, and answer frequently asked questions to solidify your understanding. This detailed approach ensures you not only solve this problem but also develop a strong foundation for tackling similar quadratic equations.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we dive into factoring 6x² + 7x - 3, let's briefly review what a quadratic expression is. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a is not equal to zero. Factoring a quadratic expression means rewriting it as a product of two simpler expressions, usually two binomials.
Our example, 6x² + 7x - 3, fits this general form with a = 6, b = 7, and c = -3. The presence of a leading coefficient (a) other than 1 makes the factoring process slightly more complex than simpler cases.
Method 1: AC Method (Factoring by Grouping)
The AC method, also known as factoring by grouping, is a systematic approach to factoring quadratic expressions, particularly useful when the leading coefficient (a) is not 1. Here's how it works for 6x² + 7x - 3:
-
Find the product AC: Multiply the coefficient of the x² term (a = 6) and the constant term (c = -3). This gives us AC = 6 * (-3) = -18.
-
Find two numbers that add up to B and multiply to AC: We need to find two numbers that add up to the coefficient of the x term (b = 7) and multiply to -18. These numbers are 9 and -2 (9 + (-2) = 7 and 9 * (-2) = -18).
-
Rewrite the middle term: Replace the middle term (7x) with the sum of the two numbers we found, multiplied by x: 9x - 2x. This gives us: 6x² + 9x - 2x - 3.
-
Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair:
3x(2x + 3) - 1(2x + 3)
-
Factor out the common binomial: Notice that both terms now share the common binomial (2x + 3). Factor this out:
(2x + 3)(3x - 1)
Therefore, the factored form of 6x² + 7x - 3 is (2x + 3)(3x - 1).
Method 2: Trial and Error
This method involves systematically trying different combinations of binomial factors until you find the correct one. It's more intuitive but can be time-consuming, especially for expressions with larger coefficients. For 6x² + 7x - 3:
-
Consider the factors of the leading coefficient (6): The possible pairs are (1, 6), (2, 3), (3,2), (6,1).
-
Consider the factors of the constant term (-3): The possible pairs are (1, -3), (-1, 3), (3, -1), (-3, 1).
-
Test different combinations: We need to find a combination that, when multiplied using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last), gives us the original expression. After testing various combinations, we find that (2x + 3)(3x - 1) works:
- First: (2x)(3x) = 6x²
- Outer: (2x)(-1) = -2x
- Inner: (3)(3x) = 9x
- Last: (3)(-1) = -3
Adding the Outer and Inner terms (-2x + 9x = 7x), we get the original expression: 6x² + 7x - 3.
Therefore, the factored form, again, is (2x + 3)(3x - 1).
Why is Factoring Important?
Factoring quadratic expressions is crucial for several reasons:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Setting a quadratic expression equal to zero creates a quadratic equation. Factoring the expression allows you to find the roots (or solutions) of the equation using the zero-product property (if ab = 0, then a = 0 or b = 0).
-
Simplifying Expressions: Factoring can simplify complex algebraic expressions, making them easier to manipulate and understand.
-
Graphing Quadratic Functions: The factored form of a quadratic expression reveals the x-intercepts (where the graph crosses the x-axis) of the corresponding quadratic function.
-
Further Algebraic Manipulations: Factoring is a prerequisite for many advanced algebraic techniques, such as solving rational equations and working with polynomial functions.
Explanation of the Mathematical Principles
The success of both methods hinges on the distributive property of multiplication and the concept of finding factors. The AC method cleverly uses the distributive property in reverse to break down the quadratic expression into a form that allows easy factoring by grouping. The trial and error method relies on a deep understanding of how the distributive property works in expanding binomials. Both approaches exploit the fundamental relationships between the coefficients and the factors of the quadratic expression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if I can't find the factors easily using the AC method or trial and error?
A: If you struggle to find suitable factors, you can use the quadratic formula to solve for the roots of the equation 6x² + 7x - 3 = 0. The roots will then help you construct the factored form. The quadratic formula is: x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a.
Q: Is there only one correct factored form?
A: While the order of the factors might differ (e.g., (3x - 1)(2x + 3) is equivalent to (2x + 3)(3x - 1)), there's essentially only one unique factorization for a given quadratic expression.
Q: Can all quadratic expressions be factored?
A: No, not all quadratic expressions can be factored using integer coefficients. Some quadratic expressions require the use of irrational or complex numbers to be completely factored. The discriminant (b² - 4ac) in the quadratic formula helps determine the nature of the roots and whether factoring with integers is possible.
Conclusion
Factoring the quadratic expression 6x² + 7x - 3 effectively demonstrates the power and versatility of algebraic techniques. Both the AC method and the trial and error method provide valid pathways to the solution (2x + 3)(3x - 1). Mastering these methods not only helps you solve specific problems but also strengthens your understanding of fundamental algebraic concepts, paving the way for success in more advanced mathematical studies. Remember to practice regularly; the more you practice, the more proficient you'll become in factoring quadratic expressions and tackling other algebraic challenges. By understanding the underlying principles and employing these systematic methods, you can confidently approach and solve various quadratic factoring problems.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor 6x 2 7x 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.