Factor 9x 2 24x 16
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 5 min read
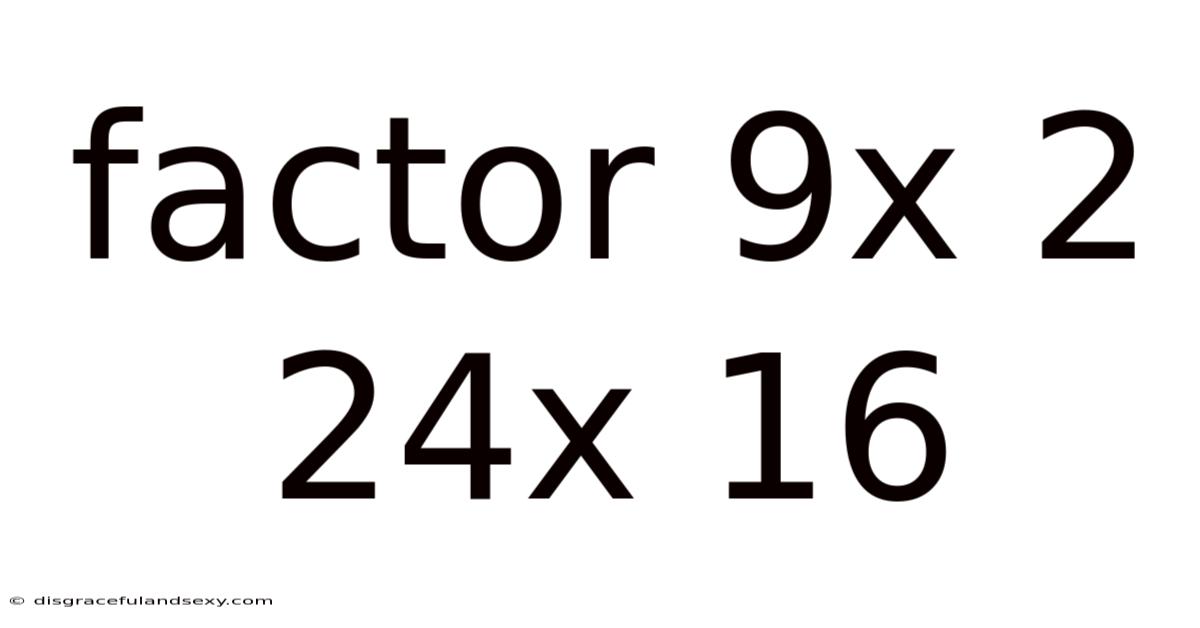
Table of Contents
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: 9x² + 24x + 16
This article will explore the process of factoring the quadratic expression 9x² + 24x + 16. We'll cover various methods, including the traditional factoring method, the AC method, and even consider the use of the quadratic formula (though not strictly necessary in this case). Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. We'll break down the steps in a clear and accessible way, making this process understandable for anyone with a basic grasp of algebra.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants. Factoring a quadratic expression involves rewriting it as a product of two linear expressions. This process essentially reverses the expansion of brackets (FOIL method).
Our target quadratic expression is 9x² + 24x + 16. Notice that a = 9, b = 24, and c = 16. The goal is to find two binomials (expressions with two terms) whose product equals this expression.
Method 1: Traditional Factoring (Trial and Error)
This method relies on recognizing factors of the leading coefficient (9) and the constant term (16). We're looking for two binomials of the form (px + q)(rx + s), where p, q, r, and s are constants. When we expand this using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last), we get:
prx² + (ps + qr)x + qs
We need to find values of p, q, r, and s such that:
- pr = 9 (the coefficient of x²)
- ps + qr = 24 (the coefficient of x)
- qs = 16 (the constant term)
Let's try some combinations. The factors of 9 are 1, 3, and 9. The factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16. Through trial and error, we might consider the following:
- (3x + 4)(3x + 4)
Let's expand this:
(3x + 4)(3x + 4) = 9x² + 12x + 12x + 16 = 9x² + 24x + 16
This works perfectly! Therefore, the factored form of 9x² + 24x + 16 is (3x + 4)(3x + 4), or (3x + 4)². This is a perfect square trinomial.
Method 2: The AC Method
The AC method is a systematic approach that works well for more complex quadratic expressions. It's particularly useful when the traditional trial-and-error method becomes cumbersome.
-
Identify a, b, and c: In our expression, a = 9, b = 24, and c = 16.
-
Calculate ac: ac = 9 * 16 = 144
-
Find two numbers that add up to b and multiply to ac: We need two numbers that add up to 24 and multiply to 144. These numbers are 12 and 12 (12 + 12 = 24 and 12 * 12 = 144).
-
Rewrite the expression: Rewrite the original expression, splitting the middle term (24x) using the two numbers we found:
9x² + 12x + 12x + 16
- Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair:
3x(3x + 4) + 4(3x + 4)
- Factor out the common binomial: Notice that both terms now share the common binomial (3x + 4). Factor this out:
(3x + 4)(3x + 4) = (3x + 4)²
Again, we arrive at the same factored form: (3x + 4)².
Method 3: Quadratic Formula (for completeness)
While the quadratic formula isn't strictly necessary for factoring this particular expression (since the traditional and AC methods are more efficient), it's a valuable tool for solving quadratic equations and can be used to find the roots, which can then help in factoring.
The quadratic formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting our values (a = 9, b = 24, c = 16):
x = [-24 ± √(24² - 4 * 9 * 16)] / (2 * 9) x = [-24 ± √(576 - 576)] / 18 x = -24 / 18 = -4/3
Since the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is 0, there's only one real root, x = -4/3. This indicates a perfect square trinomial. To find the factored form, we can use the root to construct the factors:
Since x = -4/3, then 3x = -4, so 3x + 4 = 0. Therefore, (3x + 4) is a factor. Because it's a perfect square trinomial, the factored form is (3x + 4)².
Understanding Perfect Square Trinomials
The expression 9x² + 24x + 16 is a perfect square trinomial. This means it can be factored into the square of a binomial. Perfect square trinomials have a specific pattern:
a² + 2ab + b² = (a + b)²
or
a² - 2ab + b² = (a - b)²
In our case, a = 3x and b = 4. Notice that:
- a² = (3x)² = 9x²
- 2ab = 2 * (3x) * 4 = 24x
- b² = 4² = 16
This confirms that 9x² + 24x + 16 is indeed a perfect square trinomial.
Applications of Factoring Quadratic Expressions
Factoring quadratic expressions is a crucial skill with wide-ranging applications in algebra and beyond:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Setting a quadratic expression equal to zero creates a quadratic equation. Factoring allows you to find the roots (solutions) of the equation.
-
Simplifying Expressions: Factoring can simplify complex algebraic expressions, making them easier to manipulate and analyze.
-
Calculus: Factoring plays a significant role in calculus, particularly in finding derivatives and integrals.
-
Physics and Engineering: Quadratic equations are frequently used to model physical phenomena, and factoring is essential for solving these equations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What if the quadratic expression doesn't factor easily? If the traditional method or AC method proves difficult, the quadratic formula always provides a solution, even if the roots are irrational or complex numbers.
-
Why is factoring important? Factoring is a fundamental algebraic technique that simplifies expressions, solves equations, and is a cornerstone for more advanced mathematical concepts.
-
Are there other methods for factoring quadratic expressions? Yes, there are other methods, including completing the square and using graphical techniques, but the methods discussed here are generally the most efficient and widely used.
Conclusion
Factoring the quadratic expression 9x² + 24x + 16 yields the result (3x + 4)². We explored three different methods to arrive at this solution: the traditional factoring method (trial and error), the AC method, and the quadratic formula (though less efficient in this specific case). Understanding these methods provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex algebraic problems. Remember to practice regularly to build your proficiency in factoring quadratic expressions and to appreciate the elegance and power of this fundamental algebraic technique. The ability to factor efficiently will significantly enhance your understanding and mastery of algebra and related mathematical fields.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor 9x 2 24x 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.