Factor X 2 13x 40
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 5 min read
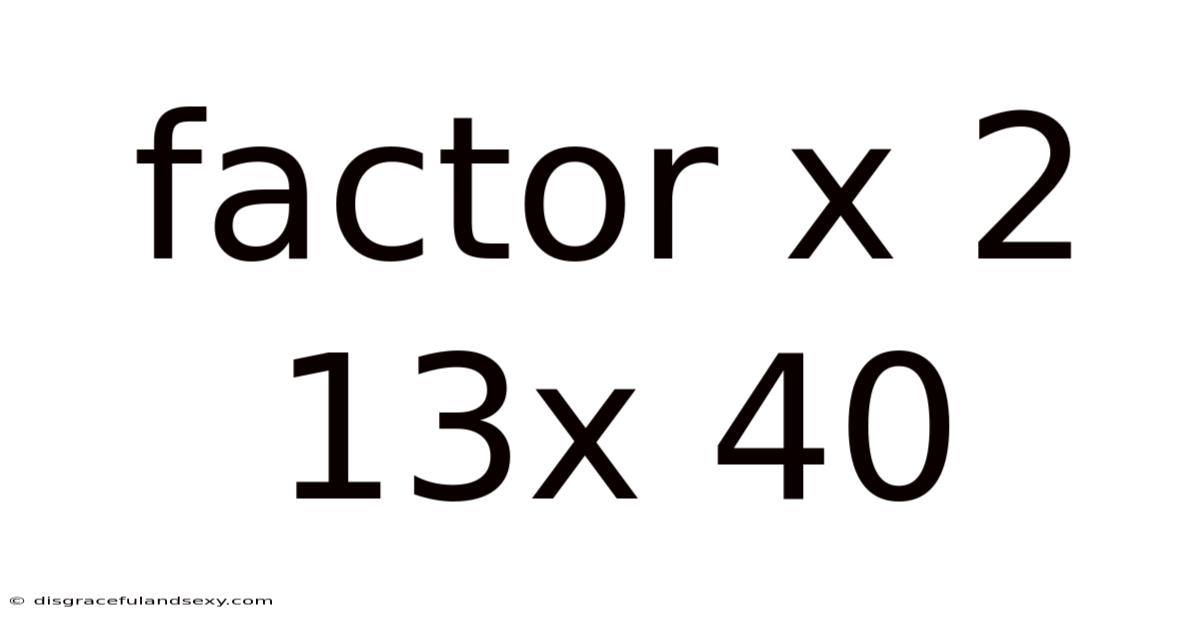
Table of Contents
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: x² + 13x + 40
This article will delve into the process of factoring the quadratic expression x² + 13x + 40. We'll explore various methods, providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. This process is fundamental to algebra and is crucial for solving quadratic equations and simplifying algebraic expressions. Understanding quadratic factoring will build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Introduction to Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. Factoring a quadratic expression involves rewriting it as a product of two simpler expressions, usually two binomials. This process is the reverse of expanding binomials using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last).
Our specific expression, x² + 13x + 40, fits this standard form with a = 1, b = 13, and c = 40. The goal is to find two binomials (x + p) and (x + q) such that their product equals x² + 13x + 40. In other words, we're looking for p and q such that (x + p)(x + q) = x² + 13x + 40.
Method 1: The AC Method (for more complex quadratics)
While the AC method is generally used for quadratics where 'a' is not equal to 1, it's still a valuable approach to understand for this problem. The AC method systematically finds the factors.
- Identify a, b, and c: In our expression, a = 1, b = 13, and c = 40.
- Find the product ac: ac = 1 * 40 = 40
- Find two numbers that add up to b and multiply to ac: We need two numbers that add to 13 and multiply to 40. These numbers are 5 and 8 (5 + 8 = 13 and 5 * 8 = 40).
- Rewrite the middle term: Rewrite the original expression using the two numbers found in step 3: x² + 5x + 8x + 40.
- Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair: x(x + 5) + 8(x + 5)
- Factor out the common binomial: Notice that (x + 5) is a common factor. Factor it out: (x + 5)(x + 8).
Therefore, the factored form of x² + 13x + 40 is (x + 5)(x + 8).
Method 2: Trial and Error (for simpler quadratics)
Since 'a' is 1 in our expression, the trial and error method is straightforward and efficient. We directly look for two numbers that add up to the coefficient of x (13) and multiply to the constant term (40).
We list the factor pairs of 40:
- 1 and 40
- 2 and 20
- 4 and 10
- 5 and 8
The pair 5 and 8 adds up to 13. Therefore, the factored form is (x + 5)(x + 8).
Method 3: Using the Quadratic Formula (for a more general approach)
The quadratic formula provides a way to find the roots (or zeros) of a quadratic equation, ax² + bx + c = 0. While it doesn't directly factor the expression, it provides valuable information that can lead to the factored form. The quadratic formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For our expression, a = 1, b = 13, and c = 40. Substituting these values:
x = [-13 ± √(13² - 4 * 1 * 40)] / 2 * 1 x = [-13 ± √(169 - 160)] / 2 x = [-13 ± √9] / 2 x = [-13 ± 3] / 2
This gives us two solutions:
x₁ = (-13 + 3) / 2 = -5 x₂ = (-13 - 3) / 2 = -8
Since the roots are -5 and -8, the factored form is (x + 5)(x + 8). The roots are the opposite of the constants in the binomial factors because setting each factor to zero leads to these solutions.
Checking the Factored Form
It's crucial to check if the factored form is correct by expanding it using the FOIL method:
(x + 5)(x + 8) = x² + 8x + 5x + 40 = x² + 13x + 40
This confirms that (x + 5)(x + 8) is the correct factored form of x² + 13x + 40.
Solving Quadratic Equations using Factoring
Factoring is a powerful technique for solving quadratic equations. If we have the equation x² + 13x + 40 = 0, we can use the factored form:
(x + 5)(x + 8) = 0
This equation is true if either (x + 5) = 0 or (x + 8) = 0. Solving these gives us x = -5 and x = -8, which are the roots of the quadratic equation.
Applications of Quadratic Factoring
Quadratic factoring has extensive applications across various fields:
- Physics: Calculating projectile motion, analyzing oscillations, and modeling parabolic trajectories.
- Engineering: Designing structures, optimizing systems, and solving problems related to curves and shapes.
- Economics: Modeling cost functions, revenue functions, and profit maximization.
- Computer Science: Developing algorithms and solving optimization problems.
- Statistics: Analyzing data distributions and performing statistical modeling.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the quadratic expression cannot be factored easily?
A1: If the quadratic expression doesn't factor easily using the methods described above, the quadratic formula is always reliable. Alternatively, completing the square can also be employed to solve the quadratic equation.
Q2: Are there other methods for factoring quadratics?
A2: Yes, besides the methods discussed, there are other advanced techniques like using the difference of squares, perfect square trinomials, and grouping when dealing with more complex quadratic expressions.
Q3: What happens if 'a' is not equal to 1?
A3: When 'a' is not 1, the AC method becomes more essential. It systematically handles the complexities introduced by a non-unit leading coefficient. Trial and error becomes significantly more challenging in this case.
Q4: Why is factoring important in mathematics?
A4: Factoring is a fundamental algebraic skill with wide-ranging applications in simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding mathematical relationships. It's a building block for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Conclusion
Factoring the quadratic expression x² + 13x + 40 is a straightforward process once you understand the underlying principles. This article presented three methods – the AC method, trial and error, and using the quadratic formula – offering flexibility based on the complexity of the expression. Mastering these techniques will significantly enhance your algebraic skills and provide a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems in various fields. Remember to always check your factored form by expanding it to ensure accuracy. The ability to factor quadratics is an essential tool for success in algebra and beyond. Practice consistently, and you'll find factoring quadratic expressions becomes increasingly intuitive and efficient.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 13x 40 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.