Factor X 2 14x 49
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
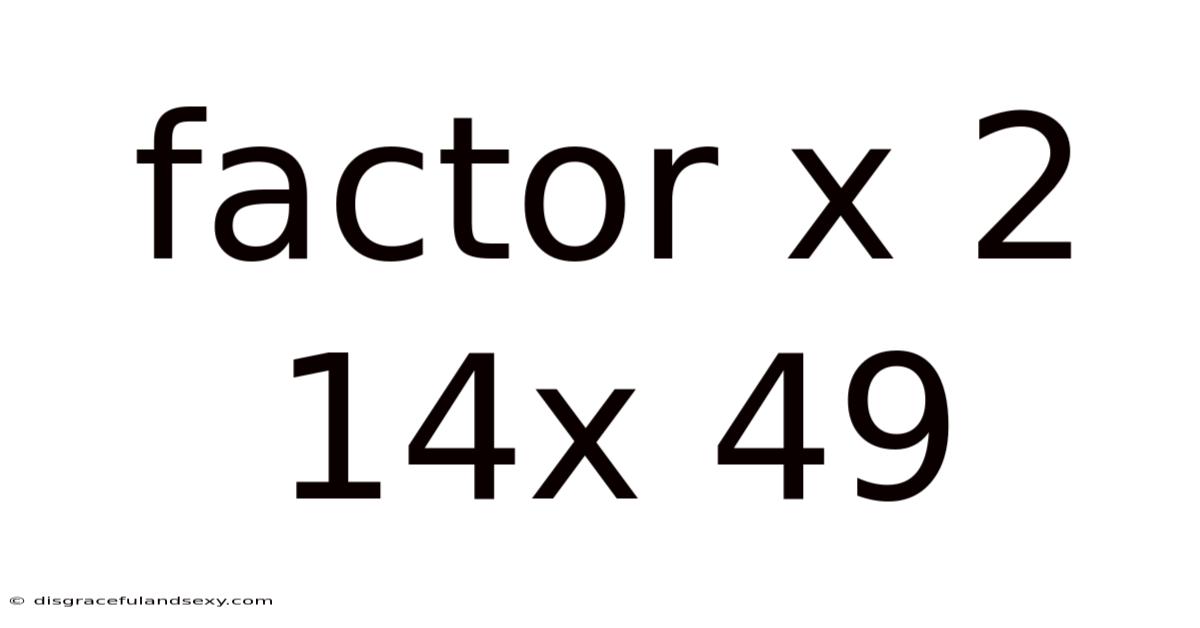
Table of Contents
Factoring x² + 14x + 49: A Deep Dive into Quadratic Expressions
This article will explore the factoring of the quadratic expression x² + 14x + 49. We'll delve into the process step-by-step, explaining the underlying mathematical principles and providing examples to solidify your understanding. This process is fundamental to algebra and crucial for solving quadratic equations and understanding various mathematical concepts. We will cover different approaches to factoring, including recognizing perfect square trinomials and using the quadratic formula (though not strictly necessary in this specific case). By the end, you'll not only be able to factor this specific expression but also understand the broader context of factoring quadratic expressions.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before diving into the factoring process, let's briefly review what a quadratic expression is. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. Our expression, x² + 14x + 49, fits this form perfectly, with a = 1, b = 14, and c = 49.
Method 1: Recognizing a Perfect Square Trinomial
The quickest and easiest way to factor x² + 14x + 49 is to recognize that it's a perfect square trinomial. A perfect square trinomial is a quadratic expression that can be factored into the square of a binomial. This means it can be written in the form (px + q)², where p and q are constants.
The key to identifying a perfect square trinomial lies in observing the relationship between the coefficients. Notice that:
- The first term, x², is the square of x (x² = x * x).
- The last term, 49, is the square of 7 (49 = 7 * 7).
- The middle term, 14x, is twice the product of x and 7 (14x = 2 * x * 7).
Therefore, x² + 14x + 49 fits the pattern of a perfect square trinomial and can be factored as:
(x + 7)²
This means (x + 7)(x + 7) = x² + 7x + 7x + 49 = x² + 14x + 49.
Method 2: Factoring by Finding Two Numbers
If you don't immediately recognize the perfect square trinomial pattern, you can use a more general factoring method. This involves finding two numbers that add up to the coefficient of the x term (b = 14) and multiply to the constant term (c = 49).
In our case, we need two numbers that add up to 14 and multiply to 49. These numbers are 7 and 7 (7 + 7 = 14 and 7 * 7 = 49).
Once we've found these numbers, we can rewrite the quadratic expression as:
x² + 7x + 7x + 49
Now, we can factor by grouping:
x(x + 7) + 7(x + 7)
Notice that (x + 7) is a common factor in both terms. We can factor it out:
(x + 7)(x + 7) = (x + 7)²
This again confirms that the factored form of x² + 14x + 49 is (x + 7)².
Method 3: Using the Quadratic Formula (for broader understanding)
While not strictly necessary for this specific problem because of its straightforward nature as a perfect square trinomial, understanding the quadratic formula provides a broader perspective on solving quadratic equations and factoring. The quadratic formula solves for the roots (or zeros) of a quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For our expression x² + 14x + 49, a = 1, b = 14, and c = 49. Substituting these values into the quadratic formula gives:
x = [-14 ± √(14² - 4 * 1 * 49)] / (2 * 1) x = [-14 ± √(196 - 196)] / 2 x = [-14 ± √0] / 2 x = -14 / 2 x = -7
This gives us a single root, x = -7. Since the quadratic formula yields only one root, it indicates that the quadratic expression is a perfect square, confirming our earlier findings. The factored form is then (x - (-7))(x - (-7)) = (x + 7)².
This demonstrates the connection between finding the roots of a quadratic equation and factoring the corresponding quadratic expression.
Applications of Factoring
Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions like x² + 14x + 49 is crucial for many mathematical applications, including:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring allows us to find the solutions (roots) of quadratic equations. For example, if x² + 14x + 49 = 0, then (x + 7)² = 0, which implies x = -7.
-
Graphing Quadratic Functions: The factored form helps determine the x-intercepts (where the graph crosses the x-axis) of a quadratic function. In this case, the graph of y = x² + 14x + 49 touches the x-axis at x = -7.
-
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions: Factoring can simplify more complex algebraic expressions, making them easier to manipulate and solve.
-
Calculus: Factoring is used extensively in calculus, particularly in finding derivatives and integrals.
-
Physics and Engineering: Quadratic equations and their solutions appear frequently in physics and engineering problems involving projectile motion, energy, and other phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if the quadratic expression cannot be factored easily?
A: If the quadratic expression doesn't factor easily using the methods described above (i.e., it's not a perfect square trinomial and you can't find two numbers that satisfy the conditions), you can use the quadratic formula to find the roots and then express the quadratic in factored form using those roots. Alternatively, you can leave it in its original unfactored form.
Q: Are there other types of quadratic expressions?
A: Yes, there are various types of quadratic expressions, including those with a leading coefficient other than 1 (e.g., 2x² + 5x + 2), those that result in complex roots (involving imaginary numbers), and those that are prime (cannot be factored).
Q: Why is factoring important?
A: Factoring is a fundamental algebraic skill that simplifies expressions, helps solve equations, and provides insights into the behavior of functions. It is a building block for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Q: Can I use a calculator or software to factor quadratic expressions?
A: Yes, many calculators and mathematical software packages can factor quadratic expressions. However, understanding the underlying principles and methods is essential for solving more complex problems and building a strong foundation in algebra.
Conclusion
Factoring x² + 14x + 49 is straightforward due to its nature as a perfect square trinomial. The factored form is (x + 7)². This article detailed various methods to achieve this factorization, highlighting the importance of recognizing patterns and understanding the underlying mathematical principles. Mastering the techniques presented here will greatly improve your algebraic skills and provide a solid foundation for tackling more advanced mathematical concepts in the future. Remember that while tools like calculators can assist, a thorough understanding of the process remains paramount for true mathematical proficiency.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 14x 49 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.