Factor X 2 5x 36
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
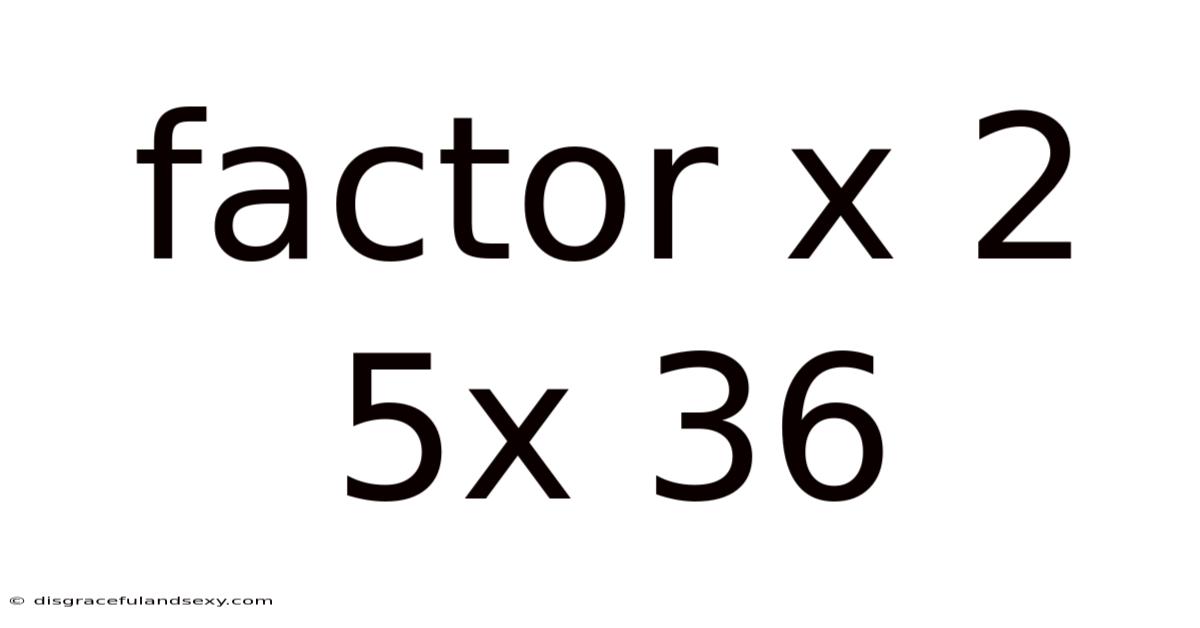
Table of Contents
Factoring Quadratic Expressions: A Deep Dive into x² + 5x + 36
This article provides a comprehensive guide to factoring the quadratic expression x² + 5x + 36. We'll explore various methods, delve into the underlying mathematical principles, and address common misconceptions. Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, graphing parabolas, and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. We will uncover why this particular quadratic is unique and what strategies are most effective when dealing with similar expressions.
I. Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants (numbers). Factoring a quadratic expression means rewriting it as a product of two simpler expressions, typically two binomials. This process is essential for solving quadratic equations and simplifying algebraic expressions. Our target expression, x² + 5x + 36, fits this general form with a = 1, b = 5, and c = 36.
II. Attempting Traditional Factoring Methods
The most common method for factoring quadratic expressions is to look for two numbers that add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 'c' (the constant term). Let's try this approach with x² + 5x + 36:
We need two numbers that add up to 5 and multiply to 36. Let's list the factor pairs of 36:
- 1 and 36
- 2 and 18
- 3 and 12
- 4 and 9
- 6 and 6
None of these pairs add up to 5. This means that x² + 5x + 36 cannot be factored using the simple method of finding factors that sum to the coefficient of x and multiply to the constant term.
III. Exploring the Discriminant and the Nature of Roots
When a quadratic expression cannot be factored using integer coefficients, it doesn't necessarily mean it's unfactorable. The discriminant helps determine the nature of the roots (solutions) of the corresponding quadratic equation (ax² + bx + c = 0). The discriminant is calculated as:
Δ = b² - 4ac
For our expression, x² + 5x + 36:
Δ = (5)² - 4(1)(36) = 25 - 144 = -119
Since the discriminant is negative, the quadratic equation x² + 5x + 36 = 0 has no real roots. This implies that the quadratic expression itself cannot be factored using real numbers. The roots are complex numbers involving the imaginary unit i (where i² = -1).
IV. Factoring with Complex Numbers
To factor x² + 5x + 36, we need to use the quadratic formula to find its roots, which will then allow us to express the quadratic as a product of two binomials. The quadratic formula is:
x = (-b ± √Δ) / 2a
Substituting the values from our expression:
x = (-5 ± √-119) / 2
This gives us two complex roots:
x₁ = (-5 + i√119) / 2 x₂ = (-5 - i√119) / 2
Now we can write the factored form using these roots:
x² + 5x + 36 = (x - x₁)(x - x₂) = (x - [(-5 + i√119) / 2])(x - [(-5 - i√119) / 2])
This is the complete factorization of x² + 5x + 36 using complex numbers. Note that this factored form involves complex conjugates (roots that are complex numbers with opposite imaginary parts).
V. Completing the Square
Another method to approach this problem is completing the square. This method involves manipulating the quadratic expression to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored. Let's see how it works:
-
Focus on the x² and x terms: We have x² + 5x.
-
Find half of the coefficient of x and square it: Half of 5 is 2.5, and 2.5² = 6.25.
-
Add and subtract this value: We add and subtract 6.25 to the expression: x² + 5x + 6.25 - 6.25 + 36
-
Create a perfect square trinomial: The first three terms (x² + 5x + 6.25) form a perfect square trinomial: (x + 2.5)².
-
Simplify: The expression becomes (x + 2.5)² + 29.75
This method demonstrates that the expression represents a parabola shifted and scaled, but it does not factor neatly into binomial form with real numbers. This reinforces the finding from the discriminant that real number factorization isn't possible.
VI. Graphical Representation
Graphing the quadratic function y = x² + 5x + 36 reveals a parabola that opens upwards and lies entirely above the x-axis. This visually confirms that there are no x-intercepts (real roots), supporting our previous conclusions about the impossibility of factoring with real numbers. The parabola's vertex represents the minimum value of the function, which is a real number, even if the roots are complex.
VII. Applications and Significance
While x² + 5x + 36 doesn't factor nicely using real numbers, the methods used to analyze it are crucial in various mathematical contexts. Understanding the discriminant allows us to predict the nature of solutions to quadratic equations without actually solving them. Completing the square is a useful technique in calculus and other advanced areas of mathematics. Working with complex numbers expands our mathematical toolkit, allowing us to solve problems that are otherwise unsolvable within the realm of real numbers. The concept of complex roots is fundamental in fields like electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, and signal processing.
VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why is it important to know if a quadratic expression can be factored?
A: Factoring is essential for solving quadratic equations, simplifying algebraic expressions, and understanding the behavior of quadratic functions. Being able to determine if factoring is possible (with real numbers) guides our approach to problem-solving.
-
Q: What if 'a' is not equal to 1?
A: If 'a' is not 1, factoring becomes more challenging. Methods like grouping or the AC method can be employed. These involve finding factors that satisfy both the sum of 'b' and the product of 'a' and 'c'.
-
Q: Can all quadratic expressions be factored?
A: All quadratic expressions can be factored, but not necessarily using real numbers. If the discriminant is negative, the roots will be complex numbers, leading to a factorization involving complex numbers as demonstrated with our example.
-
Q: Are there any other methods for factoring quadratic expressions?
A: Yes, there are other advanced techniques like using the sum and product of roots directly, which are particularly useful when dealing with certain types of quadratic equations. However, the methods discussed above (simple factorization, discriminant analysis, completing the square, and quadratic formula) provide a comprehensive approach to factoring quadratic expressions.
IX. Conclusion
While x² + 5x + 36 cannot be factored using real numbers, analyzing this expression has provided a valuable opportunity to review and solidify key algebraic concepts. We've explored various factoring techniques, learned the significance of the discriminant, and expanded our understanding to include complex numbers. This journey highlights the importance of having a range of tools in your mathematical toolbox, allowing you to tackle a variety of problems, regardless of their complexity. The inability to factor this quadratic with real numbers isn't a limitation; rather, it's an opportunity to appreciate the richness and depth of mathematics beyond the realm of readily apparent solutions. Remember, the process of attempting factorization and understanding why it's not possible with real numbers is just as important as successful factorization.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 5x 36 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.