Factor X 2 6x 12
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
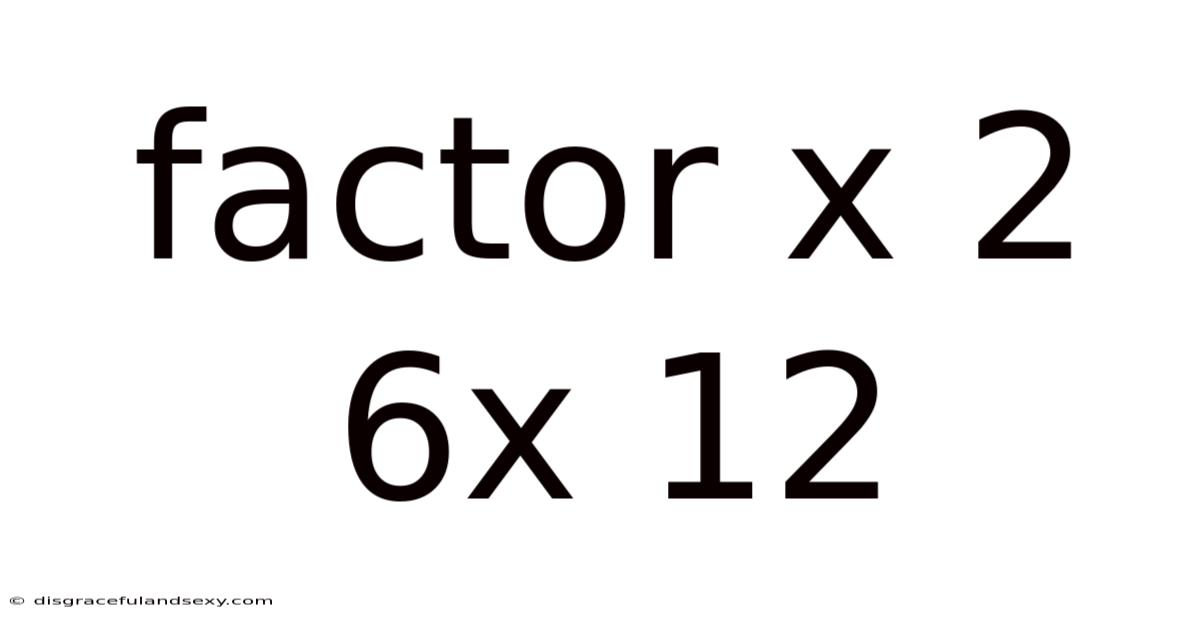
Table of Contents
Decoding the Quadratic Expression: x² + 6x + 12
This article delves into the quadratic expression x² + 6x + 12, exploring its properties, how to solve it, and its applications in various mathematical contexts. We'll move beyond simple solutions to understand the deeper meaning and implications of this seemingly straightforward equation. Understanding quadratics is crucial for various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and computer science. This exploration will equip you with a solid foundation in quadratic equations and their applications.
Introduction to Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and a is not equal to zero. Our focus, x² + 6x + 12, fits this form with a = 1, b = 6, and c = 12. However, unlike many quadratic equations, this one doesn't easily factor and requires a different approach to find its roots (solutions).
Understanding the Discriminant
Before we delve into solving methods, let's introduce the discriminant, a crucial element in understanding the nature of quadratic equation solutions. The discriminant (often represented by the Greek letter delta, Δ) is calculated using the formula: Δ = b² - 4ac. The discriminant tells us about the types of solutions a quadratic equation has:
- Δ > 0: The equation has two distinct real roots.
- Δ = 0: The equation has one real root (a repeated root).
- Δ < 0: The equation has two complex conjugate roots (involving imaginary numbers).
For our equation, x² + 6x + 12, let's calculate the discriminant:
Δ = (6)² - 4(1)(12) = 36 - 48 = -12
Since Δ = -12 < 0, we know that our quadratic equation, x² + 6x + 12 = 0, has two complex conjugate roots. This means the solutions will involve the imaginary unit, i, where i² = -1.
Solving the Quadratic Equation Using the Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula provides a direct method for finding the roots of any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it factors easily. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting the values from our equation (a = 1, b = 6, c = 12) into the quadratic formula, we get:
x = [-6 ± √(-12)] / 2
Since we have a negative number under the square root, we introduce the imaginary unit i:
√(-12) = √(12 * -1) = √12 * √(-1) = 2√3 * i
Therefore, the solutions are:
x = [-6 ± 2√3i] / 2
Simplifying, we get the two complex conjugate roots:
x₁ = -3 + √3i x₂ = -3 - √3i
Graphical Representation and the Parabola
Quadratic equations can be graphically represented as parabolas. The parabola's shape depends on the value of a. If a > 0, the parabola opens upwards (U-shaped), and if a < 0, it opens downwards (∩-shaped). The vertex of the parabola represents the minimum or maximum value of the quadratic function.
In our case (x² + 6x + 12), since a = 1 > 0, the parabola opens upwards. The x-coordinates of the roots (-3 + √3i and -3 - √3i) are complex, meaning the parabola does not intersect the x-axis. This is consistent with our discriminant analysis showing no real roots. The parabola's vertex can be found using the formula x = -b/2a = -6/2(1) = -3. Substituting this into the equation gives the y-coordinate of the vertex: y = (-3)² + 6(-3) + 12 = 3. Therefore, the vertex of the parabola is at (-3, 3).
Completing the Square: An Alternative Approach
Completing the square is another method to solve quadratic equations. This method involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial. Let's apply this to our equation:
x² + 6x + 12 = 0
-
Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 6x = -12
-
Take half of the coefficient of x (which is 6), square it (9), and add it to both sides: x² + 6x + 9 = -12 + 9
-
Factor the left side as a perfect square: (x + 3)² = -3
-
Take the square root of both sides: x + 3 = ±√(-3) = ±√3i
-
Solve for x: x = -3 ± √3i
This confirms the same complex conjugate roots we obtained using the quadratic formula.
Applications of Complex Numbers in Various Fields
While our initial equation may seem abstract, the complex roots it yields are crucial in various advanced applications. Complex numbers are indispensable in:
- Electrical Engineering: Analyzing alternating current circuits and signal processing heavily relies on complex numbers. Impedance, a measure of opposition to the flow of alternating current, is often represented as a complex number.
- Quantum Mechanics: The wave function in quantum mechanics is often a complex function, and its properties and operations utilize complex number arithmetic.
- Fluid Dynamics: Analyzing complex fluid flows requires the use of complex numbers and conformal mapping techniques.
- Signal Processing: Filtering and manipulating signals, especially in digital signal processing, utilizes complex numbers in the frequency domain (Fourier Transform).
- Control Systems Engineering: Designing and analyzing control systems often requires working with complex numbers to understand system stability and performance.
The fact that our simple quadratic equation yields complex solutions highlights the power and pervasiveness of complex numbers in advanced mathematical modelling across various scientific and engineering disciplines. Understanding the solution process, even if the roots are complex, provides a fundamental building block for approaching more complex mathematical problems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are complex numbers important?
A: Complex numbers extend the real number system, allowing us to solve equations that have no real solutions. They are crucial for many advanced mathematical concepts and applications in various fields of science and engineering.
Q: Can all quadratic equations be solved using the quadratic formula?
A: Yes, the quadratic formula works for all quadratic equations, whether they have real or complex roots.
Q: What does it mean when the discriminant is negative?
A: A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has two complex conjugate roots. These roots involve the imaginary unit i.
Q: Is there a graphical interpretation of complex roots?
A: While complex roots aren't directly represented on the standard x-y plane, they can be visualized using the complex plane, where the real and imaginary parts are plotted on separate axes.
Q: How are complex numbers used in real-world applications?
A: Complex numbers find widespread use in electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, fluid dynamics, signal processing, and control systems engineering, among other fields.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple quadratic equation x² + 6x + 12 = 0, despite yielding complex roots, offers a valuable lesson in the power and versatility of quadratic equations and complex numbers. While the parabola doesn't intersect the x-axis, its properties and the methods used to solve it provide a fundamental understanding of quadratic equations and their broader applications. Mastering these concepts lays a strong foundation for tackling more intricate mathematical problems in various scientific and engineering disciplines. The exploration of its solution process highlights the interconnectedness of different mathematical concepts and the importance of understanding not just the answers but also the underlying mathematical principles. The journey to understand this specific equation opens doors to a deeper understanding of a vast and fascinating mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 6x 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.