Factor X 2 6x 5
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 7 min read
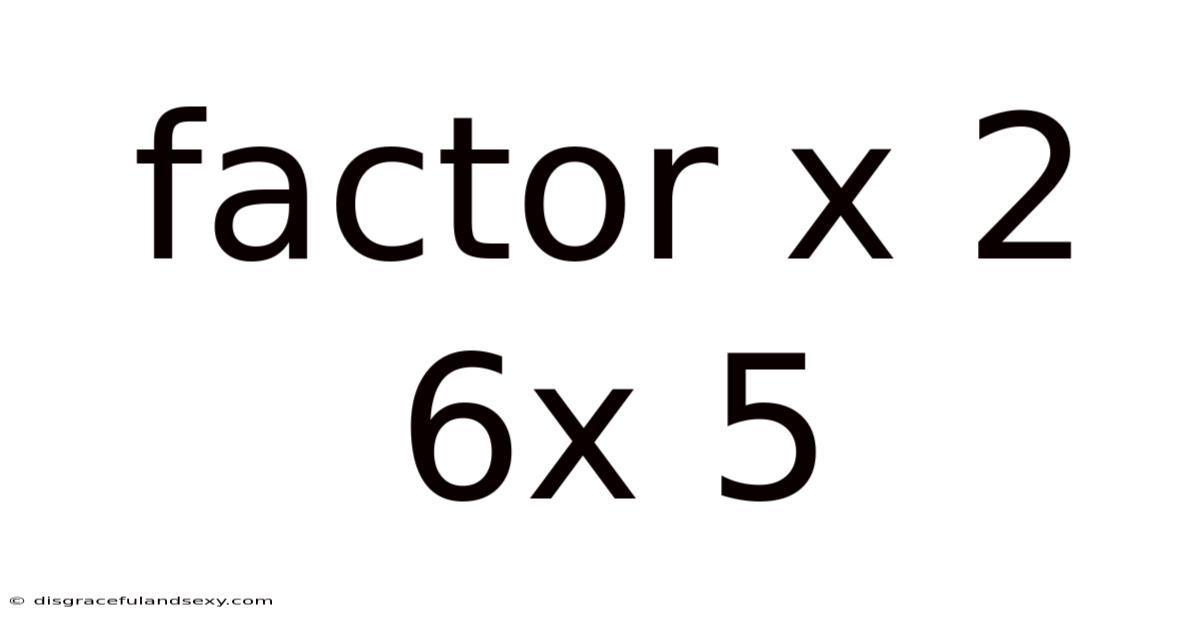
Table of Contents
Understanding the Quadratic Expression: x² + 6x + 5
This article delves into the quadratic expression x² + 6x + 5, exploring its various aspects, from factorization and solving for its roots to its graphical representation and real-world applications. We will cover this topic comprehensively, ensuring a thorough understanding for students and anyone interested in learning more about quadratic equations. Understanding quadratic expressions is fundamental to algebra and has wide-ranging applications in various fields like physics, engineering, and economics.
Introduction: What is a Quadratic Expression?
A quadratic expression is a mathematical expression of the form ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. The highest power of the variable 'x' is 2, which defines it as a quadratic. Our focus is on the specific expression x² + 6x + 5. This seemingly simple expression holds a wealth of mathematical concepts that we will unpack step-by-step.
1. Factorization of x² + 6x + 5
Factorization is the process of breaking down a mathematical expression into simpler components that, when multiplied together, give the original expression. Factoring quadratic expressions is a crucial skill in algebra. There are several methods to factor x² + 6x + 5. Let's explore the most common approach:
- Method 1: Finding Factors
We need to find two numbers that add up to 6 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 5 (the constant term). Those two numbers are 1 and 5. Therefore, we can factor the expression as follows:
x² + 6x + 5 = (x + 1)(x + 5)
This means that the quadratic expression can be represented as the product of two linear expressions: (x + 1) and (x + 5). This factorization is crucial for solving the quadratic equation and understanding its roots.
- Method 2: Completing the Square
Completing the square is another powerful method for factoring and solving quadratic equations. While it might seem more complex for this specific equation, understanding the method is valuable for more challenging quadratics.
To complete the square for x² + 6x + 5, we follow these steps:
-
Focus on the x² and x terms: x² + 6x
-
Take half of the coefficient of x and square it: (6/2)² = 9
-
Add and subtract this value: x² + 6x + 9 - 9
-
Factor the perfect square trinomial: (x + 3)² - 9
-
Combine the remaining terms: (x + 3)² - 9 + 5 = (x + 3)² - 4
-
Rewrite as a difference of squares: (x + 3)² - 2² = (x + 3 + 2)(x + 3 - 2) = (x + 5)(x + 1)
This method demonstrates the same factorization as Method 1, highlighting the versatility of algebraic techniques.
2. Solving the Quadratic Equation: x² + 6x + 5 = 0
Once we have factored the quadratic expression, we can solve the corresponding quadratic equation, x² + 6x + 5 = 0. The solutions to this equation are called the roots or zeros of the equation.
Since we have factored the expression as (x + 1)(x + 5) = 0, we can use the zero product property, which states that if the product of two factors is zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero. Therefore:
- x + 1 = 0 => x = -1
- x + 5 = 0 => x = -5
The roots of the quadratic equation x² + 6x + 5 = 0 are x = -1 and x = -5. These are the values of x that make the equation true.
3. Graphical Representation: Parabola
Quadratic equations graphically represent a parabola, a U-shaped curve. The parabola's vertex (the turning point) and its intercepts (where the parabola crosses the x-axis and y-axis) are important features.
-
x-intercepts: The x-intercepts are the points where the parabola crosses the x-axis. These points correspond to the roots of the quadratic equation. In our case, the x-intercepts are (-1, 0) and (-5, 0).
-
y-intercept: The y-intercept is the point where the parabola crosses the y-axis. This occurs when x = 0. Substituting x = 0 into the equation gives: y = 0² + 6(0) + 5 = 5. The y-intercept is (0, 5).
-
Vertex: The vertex of the parabola can be found using the formula x = -b/2a, where a and b are the coefficients from the standard form ax² + bx + c. In our case, a = 1 and b = 6, so the x-coordinate of the vertex is x = -6/(2*1) = -3. Substituting x = -3 into the equation gives y = (-3)² + 6(-3) + 5 = -4. The vertex is (-3, -4).
The parabola opens upwards because the coefficient of x² (a = 1) is positive.
4. The Discriminant and Nature of Roots
The discriminant of a quadratic equation, denoted by Δ (delta), is given by the formula Δ = b² - 4ac. The discriminant helps determine the nature of the roots of the quadratic equation:
-
Δ > 0: The equation has two distinct real roots. This is the case for our equation, x² + 6x + 5 = 0, as Δ = 6² - 4(1)(5) = 16 > 0.
-
Δ = 0: The equation has one real root (a repeated root).
-
Δ < 0: The equation has no real roots; the roots are complex conjugates.
5. Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations have many real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
-
Projectile Motion: The path of a projectile (like a ball thrown in the air) can be modeled using a quadratic equation. The equation describes the height of the projectile as a function of time.
-
Area Calculations: Finding the dimensions of a rectangular area given its area and perimeter often involves solving a quadratic equation.
-
Engineering and Physics: Quadratic equations are frequently used in various engineering and physics problems, including calculating the trajectory of objects, analyzing circuits, and modeling oscillations.
-
Economics: Quadratic functions can model cost, revenue, and profit functions in economic models, helping to determine optimal production levels.
6. Further Exploration: Completing the Square and the Quadratic Formula
We've already touched upon completing the square as a factorization method. It's also a powerful technique for deriving the quadratic formula, which provides a general solution for any quadratic equation:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
This formula allows us to find the roots of any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it's easily factorable. For x² + 6x + 5 = 0, applying the quadratic formula yields the same roots we obtained through factorization: x = -1 and x = -5.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between a quadratic expression and a quadratic equation?
A: A quadratic expression is a mathematical expression of the form ax² + bx + c. A quadratic equation is formed when a quadratic expression is set equal to zero: ax² + bx + c = 0.
-
Q: Can all quadratic expressions be factored easily?
A: No. While some quadratic expressions factor easily, others may require more advanced techniques like completing the square or the quadratic formula to find their roots.
-
Q: What does it mean when a quadratic equation has no real roots?
A: It means that the parabola representing the quadratic equation does not intersect the x-axis. The roots are complex numbers involving the imaginary unit i (where i² = -1).
-
Q: Why is understanding quadratic equations important?
A: Quadratic equations are fundamental to algebra and have broad applications across various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and computer science. Understanding them is crucial for solving many real-world problems.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Understanding
This article provided a detailed examination of the quadratic expression x² + 6x + 5, covering its factorization, solving the corresponding quadratic equation, its graphical representation, and its real-world applications. We explored various methods for factoring and solving quadratic equations, emphasizing the importance of understanding both the algebraic manipulation and the graphical interpretation. By understanding quadratic expressions and equations, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for tackling a wide range of mathematical and real-world problems. The principles discussed here form the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and their applications in diverse fields. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and build confidence in solving quadratic equations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 6x 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.