Factor X 2 6x 7
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
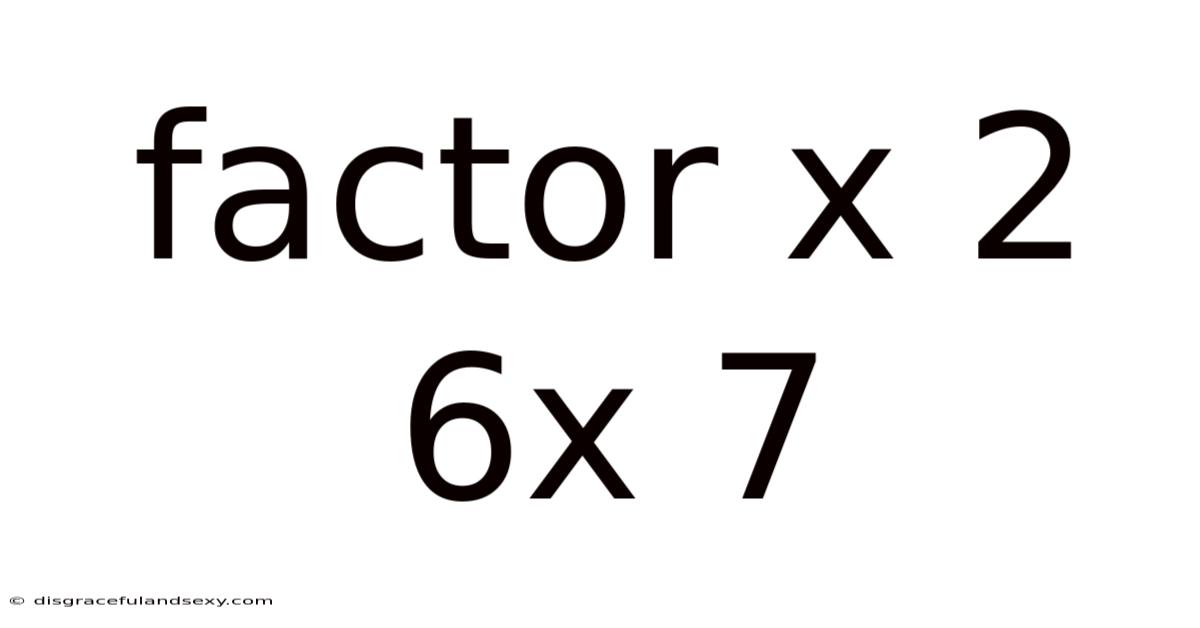
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Quadratic Expression: x² + 6x + 7
This article delves into the fascinating world of quadratic expressions, specifically focusing on the expression x² + 6x + 7. We'll explore its properties, how to solve it, and its applications in various mathematical contexts. Understanding this seemingly simple expression provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex algebraic problems. We'll cover everything from factoring and finding roots to graphing and interpreting its meaning. This comprehensive guide is perfect for anyone looking to strengthen their understanding of quadratic equations.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. Our specific expression, x² + 6x + 7, fits this form perfectly, with a = 1, b = 6, and c = 7.
Why are quadratic expressions important? They model many real-world phenomena, from the trajectory of a projectile to the area of a rectangular shape. Understanding how to manipulate and solve them is crucial in various fields like physics, engineering, and economics.
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: x² + 6x + 7
Factoring a quadratic expression means rewriting it as a product of two simpler expressions. This is often the first step in solving quadratic equations. For our expression, x² + 6x + 7, finding factors isn't as straightforward as some others. Let's explore why.
We look for two numbers that add up to the coefficient of the x term (6) and multiply to the constant term (7). However, there are no two integers that satisfy both conditions simultaneously. The factors of 7 are only 1 and 7, and their sum is 8, not 6.
This means that x² + 6x + 7 is a prime quadratic expression, meaning it cannot be factored easily into integers. However, this doesn't mean we can't solve it. We have other methods at our disposal.
Solving the Quadratic Equation: x² + 6x + 7 = 0
To find the roots (or zeros) of the quadratic equation x² + 6x + 7 = 0, which are the values of x that make the equation true, we can use the quadratic formula:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Plugging in the values from our equation (a = 1, b = 6, c = 7), we get:
x = [-6 ± √(6² - 4 * 1 * 7)] / (2 * 1) x = [-6 ± √(36 - 28)] / 2 x = [-6 ± √8] / 2 x = [-6 ± 2√2] / 2 x = -3 ± √2
Therefore, the two roots of the equation x² + 6x + 7 = 0 are x = -3 + √2 and x = -3 - √2. These are irrational roots, meaning they cannot be expressed as simple fractions.
Graphing the Quadratic Function: y = x² + 6x + 7
The quadratic expression can be represented graphically as a parabola. The parabola's shape is determined by the coefficient of the x² term (which is positive in this case, resulting in a parabola that opens upwards).
The vertex of the parabola, which is the lowest point, can be found using the formula:
x = -b / 2a = -6 / (2 * 1) = -3
Substituting this x value back into the equation, we find the y-coordinate of the vertex:
y = (-3)² + 6(-3) + 7 = 9 - 18 + 7 = -2
So, the vertex of the parabola is at the point (-3, -2). The parabola intersects the y-axis at the point (0, 7) (because when x = 0, y = 7). The x-intercepts are the roots we calculated earlier: (-3 + √2, 0) and (-3 - √2, 0).
Completing the Square: An Alternative Method
Completing the square is another technique to solve quadratic equations. It involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial. Let's apply this to our equation:
x² + 6x + 7 = 0
-
Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 6x = -7
-
Take half of the coefficient of the x term (6/2 = 3), square it (3² = 9), and add it to both sides: x² + 6x + 9 = -7 + 9 x² + 6x + 9 = 2
-
Factor the left side as a perfect square: (x + 3)² = 2
-
Take the square root of both sides: x + 3 = ±√2
-
Solve for x: x = -3 ± √2
This confirms the roots we found using the quadratic formula.
The Discriminant: Understanding the Nature of Roots
The expression b² - 4ac within the quadratic formula is called the discriminant. It tells us about the nature of the roots of the quadratic equation:
- If b² - 4ac > 0: The equation has two distinct real roots.
- If b² - 4ac = 0: The equation has one real root (a repeated root).
- If b² - 4ac < 0: The equation has two complex roots (involving imaginary numbers).
In our case, b² - 4ac = 36 - 28 = 8, which is greater than 0. This confirms that our equation has two distinct real roots, as we found earlier.
Applications of Quadratic Expressions
Quadratic expressions have numerous real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
-
Projectile Motion: The path of a projectile (like a ball thrown in the air) can be modeled using a quadratic equation. The equation describes the height of the projectile as a function of time.
-
Area Calculations: Finding the dimensions of a rectangle with a given area and relationship between the sides often involves solving a quadratic equation.
-
Optimization Problems: Quadratic functions can be used to find the maximum or minimum value of a quantity, such as maximizing the area of a field with a fixed perimeter.
-
Engineering and Physics: Quadratic equations appear frequently in various physical phenomena, such as the behavior of springs, the motion of pendulums, and electrical circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can all quadratic expressions be factored easily?
A: No, not all quadratic expressions can be factored easily into integers. Some, like x² + 6x + 7, are prime and require other methods like the quadratic formula or completing the square to solve.
Q: What if 'a' is not equal to 1 in the quadratic expression?
A: The methods described still apply, but you'll need to adjust the calculations accordingly. The quadratic formula works regardless of the value of 'a'. For factoring, it might become more challenging.
Q: What are complex roots?
A: Complex roots are solutions to quadratic equations that involve the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1. They occur when the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is negative.
Q: Why is completing the square a useful method?
A: Completing the square is useful because it helps rewrite the quadratic expression in a form that allows us to easily find the roots and also provides insights into the vertex of the parabola.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple quadratic expression x² + 6x + 7 reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts. While it cannot be factored easily, understanding methods like the quadratic formula and completing the square allows us to find its roots and understand its graphical representation as a parabola. The discriminant provides valuable information about the nature of the roots, and the expression itself finds applications in various real-world scenarios. Mastering the manipulation and solution of quadratic expressions is fundamental to success in numerous areas of mathematics and its applications. This exploration serves as a solid foundation for further study into more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 6x 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.