Factor X 2 7x 2
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
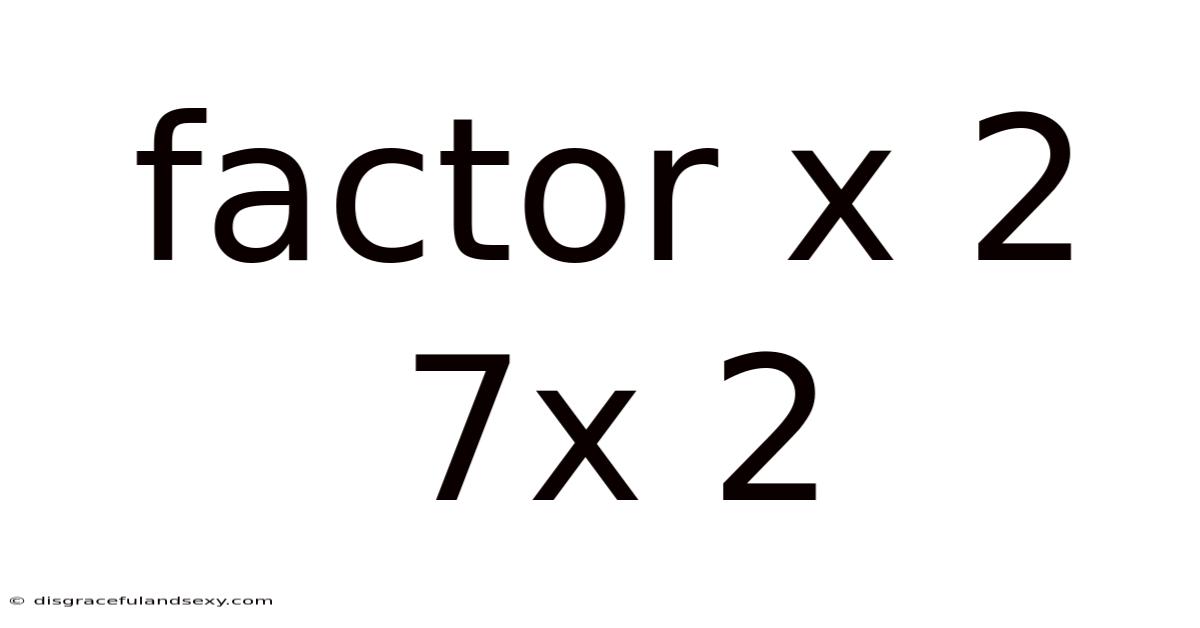
Table of Contents
Decoding the Quadratic: A Deep Dive into x² + 7x + 2
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the quadratic expression x² + 7x + 2, covering its analysis, solutions, graphing, and practical applications. We'll delve into the different methods for solving quadratic equations, emphasizing understanding over rote memorization. Whether you're a student struggling with algebra or a curious learner wanting to refresh your math skills, this guide offers a detailed and accessible explanation of this seemingly simple yet rich mathematical concept.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, 'x') is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. Our focus, x² + 7x + 2, perfectly fits this mold, with a = 1, b = 7, and c = 2. Understanding quadratic expressions is fundamental to various fields, including physics (projectile motion), engineering (designing parabolic structures), and economics (modeling growth and decay).
Method 1: Solving by Factoring
Factoring involves expressing the quadratic expression as a product of two simpler expressions. Unfortunately, x² + 7x + 2 cannot be factored easily using integers. To see why, we look for two numbers that add up to 7 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 2 (the constant term). No such integer pair exists. This doesn't mean the equation has no solutions; it simply means factoring isn't the most straightforward approach in this case. Let's explore other methods.
Method 2: The Quadratic Formula – A Universal Solver
The quadratic formula is a powerful tool that provides solutions for any quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Let's apply this to our expression, x² + 7x + 2 = 0:
- a = 1
- b = 7
- c = 2
Substituting these values into the quadratic formula:
x = [-7 ± √(7² - 4 * 1 * 2)] / (2 * 1) x = [-7 ± √(49 - 8)] / 2 x = [-7 ± √41] / 2
This gives us two distinct solutions:
- x₁ = (-7 + √41) / 2 ≈ -0.298
- x₂ = (-7 - √41) / 2 ≈ -6.702
These are the roots or zeros of the quadratic equation, representing the x-intercepts of the parabola when the equation is graphed. The quadratic formula always provides a solution, even when factoring fails.
Method 3: Completing the Square – A Geometric Approach
Completing the square is a method that transforms the quadratic expression into a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve. The process involves manipulating the equation to create a square of a binomial.
-
Move the constant term: Start with x² + 7x + 2 = 0. Subtract 2 from both sides: x² + 7x = -2
-
Find the value to complete the square: Take half of the coefficient of x (which is 7/2), square it ((7/2)² = 49/4), and add it to both sides: x² + 7x + 49/4 = -2 + 49/4
-
Factor the perfect square trinomial: The left side is now a perfect square: (x + 7/2)² = 41/4
-
Solve for x: Take the square root of both sides: x + 7/2 = ±√(41/4)
-
Isolate x: x = -7/2 ± √41/2
This yields the same solutions as the quadratic formula: x₁ = (-7 + √41) / 2 and x₂ = (-7 - √41) / 2. Completing the square offers a deeper understanding of the geometric representation of the quadratic.
Graphing the Quadratic: Visualizing the Solutions
The graph of a quadratic equation is a parabola. The parabola opens upwards if 'a' (the coefficient of x²) is positive, and downwards if 'a' is negative. In our case, a = 1 (positive), so the parabola opens upwards. The x-intercepts of the parabola are the solutions we calculated using the quadratic formula or completing the square (-0.298 and -6.702). The y-intercept is found by setting x = 0 in the original equation, giving us y = 2. The vertex of the parabola (the lowest point) can be found using the formula x = -b/2a = -7/2 = -3.5. Substituting this x-value back into the original equation gives the y-coordinate of the vertex.
The Discriminant: Unveiling the Nature of Solutions
The expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula (b² - 4ac) is called the discriminant. It reveals the nature of the solutions:
- b² - 4ac > 0: Two distinct real solutions (as in our case).
- b² - 4ac = 0: One real solution (a repeated root).
- b² - 4ac < 0: Two complex solutions (involving imaginary numbers).
In our equation, the discriminant is 49 - 8 = 41, which is positive, confirming the two distinct real solutions we found.
Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations have numerous real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
- Projectile motion: The trajectory of a projectile (like a ball thrown in the air) follows a parabolic path, described by a quadratic equation.
- Area calculations: Finding the dimensions of a rectangular area given its perimeter and area often involves solving a quadratic equation.
- Optimization problems: Quadratic equations are used to find the maximum or minimum values in various optimization problems in engineering and business.
- Modeling growth and decay: Certain growth and decay processes can be modeled using quadratic functions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why can't I factor x² + 7x + 2 easily?
- A: Because there are no two integers that add up to 7 and multiply to 2. This often happens, and it's why the quadratic formula is so valuable.
-
Q: What does it mean when the discriminant is negative?
- A: It means the quadratic equation has no real solutions; the solutions are complex numbers involving the imaginary unit 'i' (√-1).
-
Q: Is there a way to solve quadratic equations without the quadratic formula?
- A: Yes, completing the square and factoring are alternative methods, though factoring isn't always possible.
-
Q: What is the significance of the vertex of the parabola?
- A: The vertex represents the minimum (or maximum) value of the quadratic function. It's a crucial point in optimization problems.
Conclusion: Mastering Quadratic Expressions
This in-depth analysis of x² + 7x + 2 demonstrates the multifaceted nature of quadratic expressions. While seemingly straightforward, they offer a rich foundation for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts and solving problems across numerous disciplines. By mastering the techniques of factoring, using the quadratic formula, and completing the square, you gain powerful tools for tackling quadratic equations and their diverse applications. Remember, the key is not just to find the answer but to understand the underlying principles and how they connect to the bigger picture of mathematics and its real-world implications. Keep practicing, and you'll become confident in your ability to decode the world of quadratics!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 7x 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.