Factor X 2 8x 20
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
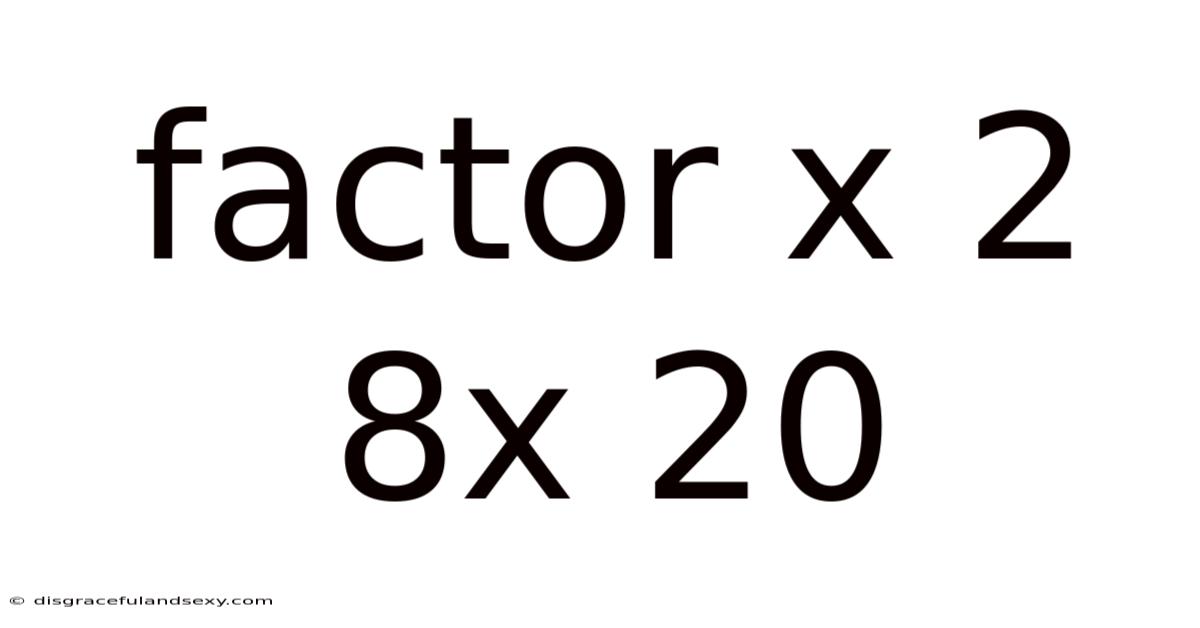
Table of Contents
Factoring Quadratic Expressions: A Deep Dive into x² + 8x + 20
Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. This comprehensive guide will explore the process of factoring the specific quadratic expression x² + 8x + 20, providing a step-by-step approach, examining different methods, and delving into the underlying mathematical concepts. We'll also address common questions and misconceptions surrounding quadratic factorization. By the end, you'll not only understand how to factor this particular expression but also possess a solid foundation for tackling similar problems.
Introduction: What is Factoring?
Factoring, in the context of algebra, is the process of breaking down a mathematical expression into simpler terms that, when multiplied together, result in the original expression. For quadratic expressions (expressions of the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants), factoring involves finding two binomial expressions whose product equals the original quadratic. This skill is crucial for solving quadratic equations, simplifying complex expressions, and understanding many mathematical concepts in higher-level courses.
Attempting to Factor x² + 8x + 20 Directly
Let's begin with our target expression: x² + 8x + 20. The standard approach to factoring quadratic expressions of the form x² + bx + c involves finding two numbers that add up to 'b' (in this case, 8) and multiply to 'c' (in this case, 20).
We need to find two numbers that satisfy these conditions:
- Sum: The two numbers must add up to 8.
- Product: The two numbers must multiply to 20.
Let's consider the factor pairs of 20:
- 1 and 20
- 2 and 10
- 4 and 5
None of these pairs add up to 8. This indicates that x² + 8x + 20 cannot be factored using integers. This doesn't mean the expression is unfactorable; it simply means it doesn't factor neatly into binomial expressions with integer coefficients.
Exploring Other Factoring Methods
Since direct factoring with integers failed, we need to explore other methods to understand the nature of this quadratic expression.
1. The Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a powerful tool for finding the roots (or zeros) of any quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
In our case, a = 1, b = 8, and c = 20. Substituting these values into the quadratic formula gives:
x = [-8 ± √(8² - 4 * 1 * 20)] / 2 * 1 x = [-8 ± √(64 - 80)] / 2 x = [-8 ± √(-16)] / 2 x = [-8 ± 4i] / 2 x = -4 ± 2i
Notice that the solutions are complex numbers involving the imaginary unit i (where i² = -1). This confirms that the quadratic expression cannot be factored into real binomial expressions.
2. Completing the Square
Completing the square is another method for solving quadratic equations and can provide insight into the structure of the quadratic expression. The process involves manipulating the expression to create a perfect square trinomial.
-
Focus on the x² + 8x terms: We want to transform x² + 8x into a perfect square. A perfect square trinomial has the form (x + a)² = x² + 2ax + a². In our case, 2a = 8, so a = 4. Therefore, the perfect square trinomial is (x + 4)². This expands to x² + 8x + 16.
-
Adjust for the constant term: To obtain x² + 8x + 20, we need to add 4 to the perfect square trinomial (16 + 4 = 20).
-
Rewrite the expression: We can rewrite x² + 8x + 20 as (x + 4)² + 4.
This form, (x + 4)² + 4, shows that the quadratic expression represents a parabola shifted 4 units to the left and 4 units up. This form is also known as the vertex form of a quadratic, where the vertex is located at (-4, 4). This method highlights the parabola's characteristics without factoring it into linear binomial terms.
Understanding the Implications of Non-Factorability
The fact that x² + 8x + 20 cannot be factored using real numbers has important consequences:
- No real roots: The quadratic equation x² + 8x + 20 = 0 has no real solutions. The roots are complex conjugates (-4 + 2i and -4 - 2i).
- No x-intercepts: The graph of the quadratic function y = x² + 8x + 20 does not intersect the x-axis. This is because the x-intercepts represent the real roots of the equation.
- Prime Polynomial: In the context of polynomial factorization, x² + 8x + 20 is considered a prime polynomial over the real numbers because it cannot be factored into polynomials of lower degree with real coefficients.
Graphical Representation
Plotting the graph of y = x² + 8x + 20 visually confirms these observations. The parabola opens upwards (because the coefficient of x² is positive), and its vertex lies above the x-axis, indicating no real x-intercepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is it important to know if a quadratic expression can be factored?
A1: Factoring is essential for solving quadratic equations, simplifying algebraic expressions, and understanding the behavior of quadratic functions. Knowing whether a quadratic is factorable helps determine the best approach to solving related problems.
Q2: What if I encounter a similar expression but with different coefficients?
A2: The same principles apply. Always attempt direct factoring first. If that fails, use the quadratic formula or completing the square to analyze the expression and determine its roots and characteristics.
Q3: Are there other methods for factoring quadratic expressions besides the ones discussed?
A3: Yes, there are other methods like the AC method (for factoring expressions where a ≠ 1), but the principles of finding factors that add up to 'b' and multiply to 'ac' remain the same.
Q4: What does it mean when the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is negative?
A4: A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has no real roots, only complex conjugate roots. This implies the parabola does not intersect the x-axis.
Q5: Is it possible to factor a quadratic expression that has irrational roots?
A5: Yes, it's possible, but the factors will likely involve irrational numbers. The quadratic formula will give you the irrational roots, and those roots can be used to form the factors.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Quadratic Factoring
While x² + 8x + 20 cannot be factored using integers or real numbers, exploring this expression has provided valuable insights into quadratic factorization techniques. We've learned that not all quadratic expressions factor neatly, and we've explored alternative methods like the quadratic formula and completing the square to analyze the expression. Understanding these methods and the concept of complex roots is crucial for mastering algebra and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. Remember, the inability to factor with integers doesn't diminish the expression's importance; it simply highlights the richer landscape of quadratic functions and their solutions. Through this in-depth exploration, we have moved beyond a simple factoring exercise and delved into a deeper understanding of quadratic expressions and their properties.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 2 8x 20 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.