Gcf Of 8 And 6
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 7 min read
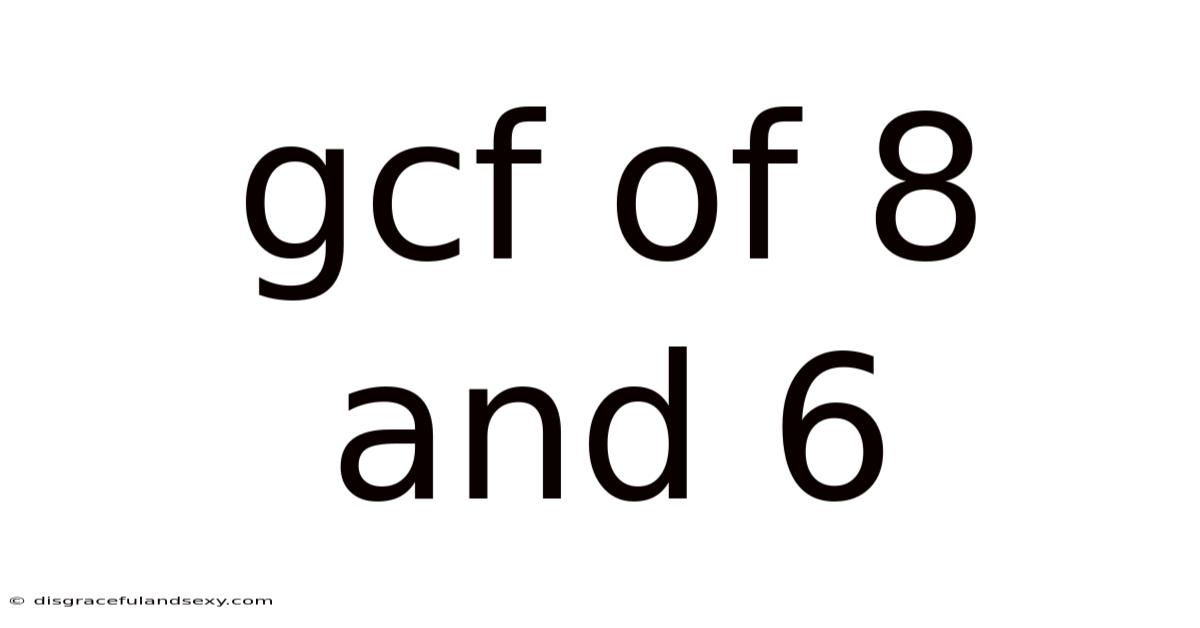
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 8 and 6: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications ranging from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic problems. This article will explore the GCF of 8 and 6 in detail, explaining various methods for finding it and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll go beyond a simple answer, providing a comprehensive understanding that will empower you to tackle similar problems with confidence.
Understanding the Concept of GCF
Before diving into the specifics of finding the GCF of 8 and 6, let's establish a clear understanding of the concept. The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more numbers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the numbers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that goes evenly into both numbers. This concept is crucial in simplifying fractions, factoring polynomials, and various other mathematical operations.
Method 1: Listing Factors
The most straightforward method for finding the GCF of relatively small numbers like 8 and 6 is to list all their factors and identify the largest common one.
Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8 Factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
By comparing the two lists, we can see that the common factors are 1 and 2. The largest of these common factors is 2. Therefore, the GCF of 8 and 6 is 2.
This method is simple and intuitive, making it ideal for teaching the concept to beginners. However, for larger numbers, this approach becomes less efficient and more prone to errors.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more powerful and efficient method for finding the GCF, especially when dealing with larger numbers. This method involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.).
Let's find the prime factorization of 8 and 6:
- 8 = 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³ (8 is expressed as the product of three 2's)
- 6 = 2 x 3 (6 is expressed as the product of 2 and 3)
Once we have the prime factorization of both numbers, we identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers. In this case, the only common prime factor is 2. The lowest power of 2 present in both factorizations is 2¹ (or simply 2). Therefore, the GCF of 8 and 6 is 2.
This method is more efficient than listing factors because it systematically breaks down the numbers into their fundamental components. It's particularly useful for larger numbers where listing all factors would be cumbersome.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers become equal, and that number is the GCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCF of 8 and 6:
- Start with the larger number (8) and the smaller number (6).
- Subtract the smaller number from the larger number: 8 - 6 = 2
- Replace the larger number with the result (2) and keep the smaller number (6). Now we have the numbers 6 and 2.
- Repeat the process: 6 - 2 = 4
- We now have 4 and 2.
- Repeat: 4 - 2 = 2
- We now have 2 and 2. Both numbers are equal, indicating that the GCF is 2.
The Euclidean algorithm is an elegant and efficient method that avoids the need for prime factorization or listing factors. It's especially beneficial for very large numbers where other methods would be impractical.
Mathematical Implications and Applications
The GCF is a fundamental concept in number theory with numerous applications across various mathematical fields. Some key applications include:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The GCF allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 8/6 can be simplified to 4/3 by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF (2).
-
Solving Diophantine Equations: Diophantine equations are algebraic equations where only integer solutions are sought. The GCF plays a crucial role in determining the solvability of certain types of Diophantine equations.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Modular arithmetic, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus), relies heavily on the GCF for various operations and theorems.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concept of GCF extends to abstract algebra, where it finds applications in the study of rings and ideals.
-
Cryptography: The GCF is also utilized in certain cryptographic algorithms and techniques, contributing to the security of digital communication.
Beyond the Basics: GCF of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the GCF of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, you would find the prime factorization of each number and then identify the common prime factors with the lowest powers. For the Euclidean algorithm, you would repeatedly apply the algorithm to pairs of numbers until you arrive at the GCF of all numbers. For example, to find the GCF of 8, 6, and 12:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 8 = 2³
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 12 = 2² x 3 The only common prime factor is 2, and its lowest power is 2¹. Therefore, the GCF of 8, 6, and 12 is 2.
-
Euclidean Algorithm (iterative approach): You could first find the GCF of 8 and 6 (which is 2), and then find the GCF of that result (2) and 12 (which is also 2).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if the GCF of two numbers is 1?
- A: If the GCF of two numbers is 1, it means the numbers are relatively prime or coprime. This signifies that they share no common factors other than 1.
-
Q: Is there a limit to the size of numbers for which the GCF can be found?
- A: Theoretically, there's no limit to the size of numbers for which the GCF can be found. However, the computational time required may increase significantly for extremely large numbers, making certain methods less practical. Sophisticated algorithms and software are available to handle very large numbers efficiently.
-
Q: Why is understanding GCF important?
- A: Understanding GCF is crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and developing a deeper understanding of number theory. It forms the foundation for many advanced mathematical concepts and applications.
-
Q: Can I use a calculator to find the GCF?
- A: Yes, many calculators and mathematical software packages have built-in functions to calculate the GCF of two or more numbers. However, understanding the underlying methods is essential for developing a strong mathematical foundation.
Conclusion
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of 8 and 6, which is 2, is a seemingly simple task, but it unveils a wealth of mathematical concepts and techniques. From the basic method of listing factors to the more efficient prime factorization and Euclidean algorithm, we've explored various approaches to determine the GCF. Understanding these methods not only allows you to solve GCF problems but also provides a foundational understanding of number theory, paving the way for exploring more complex mathematical concepts and their applications in various fields. Remember, the key is not just getting the answer (2 in this case), but grasping the underlying principles and methods that enable you to solve similar problems efficiently and confidently. This understanding empowers you to tackle more complex mathematical challenges with a solid foundation in number theory.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Gcf Of 8 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.