Integral Of Xsin 2x Dx
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
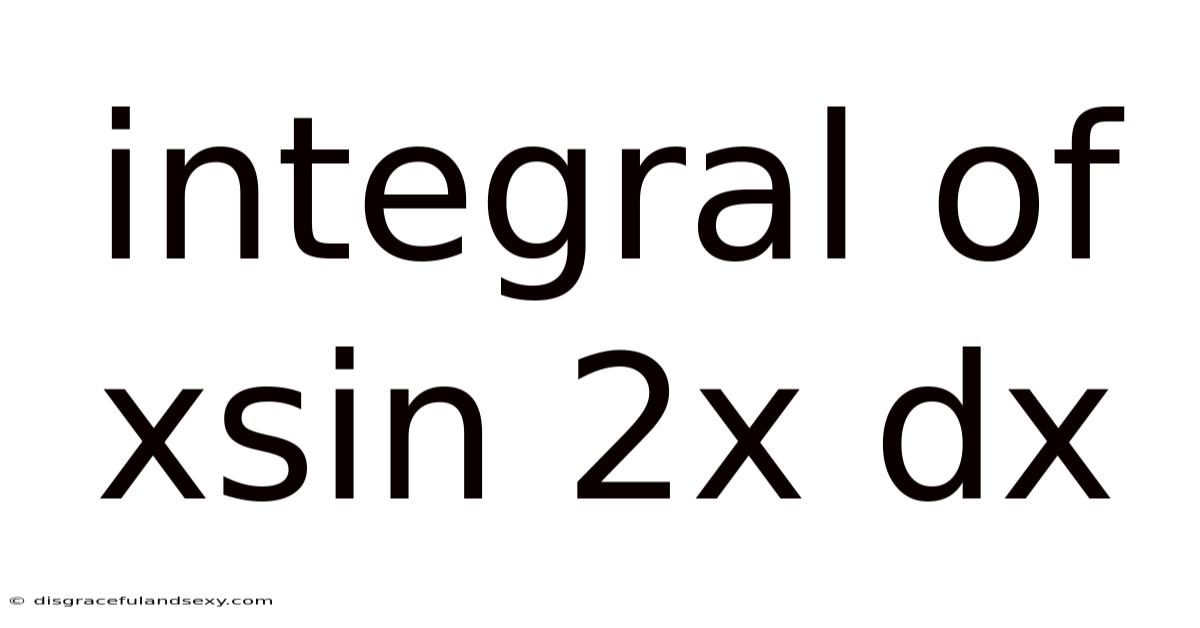
Table of Contents
Solving the Integral of x sin(2x) dx: A Comprehensive Guide
This article provides a detailed explanation of how to solve the integral ∫x sin(2x) dx. We'll explore the process step-by-step, clarifying the underlying mathematical concepts and offering insights to help you master integration by parts. Understanding this integral is crucial for students studying calculus and its various applications in physics, engineering, and other scientific fields. This guide aims to be a complete resource, covering not only the solution but also the theoretical background and frequently asked questions.
Introduction: Understanding Integration by Parts
The integral ∫x sin(2x) dx cannot be solved using simple substitution. Instead, we employ a powerful technique called integration by parts, which is derived from the product rule for differentiation. The product rule states that the derivative of a product of two functions, u(x) and v(x), is given by:
d/dx [u(x)v(x)] = u'(x)v(x) + u(x)v'(x)
Integrating both sides with respect to x, we get:
∫d/dx [u(x)v(x)] dx = ∫u'(x)v(x) dx + ∫u(x)v'(x) dx
This simplifies to:
u(x)v(x) = ∫u'(x)v(x) dx + ∫u(x)v'(x) dx
Rearranging this equation, we arrive at the formula for integration by parts:
∫u(x)v'(x) dx = u(x)v(x) - ∫v(x)u'(x) dx
This formula allows us to solve integrals of products of functions by strategically choosing u(x) and v'(x). The key is to select u(x) such that its derivative, u'(x), is simpler than u(x) itself, and v'(x) such that its integral, v(x), is easily calculable.
Step-by-Step Solution: ∫x sin(2x) dx
Let's apply integration by parts to solve ∫x sin(2x) dx.
Step 1: Choosing u(x) and v'(x)
We need to carefully select u(x) and v'(x). A good rule of thumb is to choose u(x) as the function that simplifies when differentiated. In this case:
- u(x) = x (Its derivative is simply 1)
- v'(x) = sin(2x) (Its integral is readily available)
Step 2: Finding u'(x) and v(x)
Now we find the derivative of u(x) and the integral of v'(x):
- u'(x) = 1
- v(x) = ∫sin(2x) dx = -1/2 cos(2x) (Remember to apply the chain rule for integration)
Step 3: Applying the Integration by Parts Formula
Substitute u(x), v(x), u'(x), and v'(x) into the integration by parts formula:
∫x sin(2x) dx = x(-1/2 cos(2x)) - ∫(-1/2 cos(2x))(1) dx
Step 4: Simplifying and Solving the Remaining Integral
This simplifies to:
∫x sin(2x) dx = -1/2 x cos(2x) + 1/2 ∫cos(2x) dx
The remaining integral is straightforward:
∫cos(2x) dx = 1/2 sin(2x) + C (where C is the constant of integration)
Step 5: Final Solution
Substituting this back into our equation gives the final solution:
∫x sin(2x) dx = -1/2 x cos(2x) + 1/4 sin(2x) + C
A Deeper Dive: The Rationale Behind the Choice of u(x) and v'(x)
The choice of u(x) and v'(x) is crucial for the success of integration by parts. While other choices might work, they often lead to more complex integrals, potentially requiring multiple applications of integration by parts or leading to circular reasoning. In our example, choosing u(x) = x and v'(x) = sin(2x) was advantageous because:
- Differentiating u(x) = x simplifies it to u'(x) = 1, a constant, making the second integral much easier to handle.
- Integrating v'(x) = sin(2x) is a standard integral, resulting in a relatively simple expression for v(x).
Had we chosen the opposite – u(x) = sin(2x) and v'(x) = x – we would have ended up with a significantly more challenging integral to solve. This highlights the importance of strategic thinking when selecting u(x) and v'(x).
Mathematical Proof and Verification
We can verify our solution through differentiation. Let's differentiate the result we obtained:
d/dx [-1/2 x cos(2x) + 1/4 sin(2x) + C]
Applying the product rule and chain rule:
= [-1/2 cos(2x) + x sin(2x)] + 1/2 cos(2x)
The terms cancel, leaving us with:
= x sin(2x)
This confirms that our solution for the integral is correct.
Applications of this Integral in Various Fields
The integral ∫x sin(2x) dx, and similar integrals involving trigonometric functions and polynomials, appear frequently in various fields:
- Physics: Solving problems related to simple harmonic motion, oscillations, and wave phenomena often involves integrals of this type. For example, calculating the work done by a sinusoidal force.
- Engineering: Analysis of electrical circuits with sinusoidal signals, mechanical vibrations, and signal processing all utilize similar integral techniques.
- Signal Processing: Fourier analysis, a fundamental tool in signal processing, relies heavily on the integration of trigonometric functions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if I choose u(x) and v'(x) differently? Will I still get the correct answer?
A1: You might still get the correct answer, but the process will likely be significantly more complex and potentially involve multiple applications of integration by parts. The choice of u(x) and v'(x) directly influences the complexity of the calculations. Choosing wisely simplifies the solution process.
Q2: Can this integral be solved using any other method besides integration by parts?
A2: No, there's no simpler or more direct method to solve this specific integral. Integration by parts is the most efficient and standard approach.
Q3: What is the significance of the constant of integration, C?
A3: The constant of integration, C, accounts for the fact that the derivative of a constant is zero. Therefore, there are infinitely many antiderivatives of x sin(2x), all differing by a constant. The constant C represents this family of antiderivatives.
Q4: How do I know when to use integration by parts?
A4: Integration by parts is typically used when dealing with integrals involving the product of two functions, especially when one function simplifies upon differentiation, and the other has a readily available integral.
Conclusion
Solving the integral ∫x sin(2x) dx provides a practical demonstration of the integration by parts technique. Understanding this process is fundamental for mastering calculus and its various applications in science and engineering. Remember that strategic selection of u(x) and v'(x) is key to efficient problem-solving. By carefully following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently tackle similar integrals and build a stronger foundation in integral calculus. The detailed explanation, accompanied by the mathematical proof and verification, aims to provide a comprehensive understanding, fostering a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of integration by parts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of Xsin 2x Dx . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.