Integrate 2x 1 X 2
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
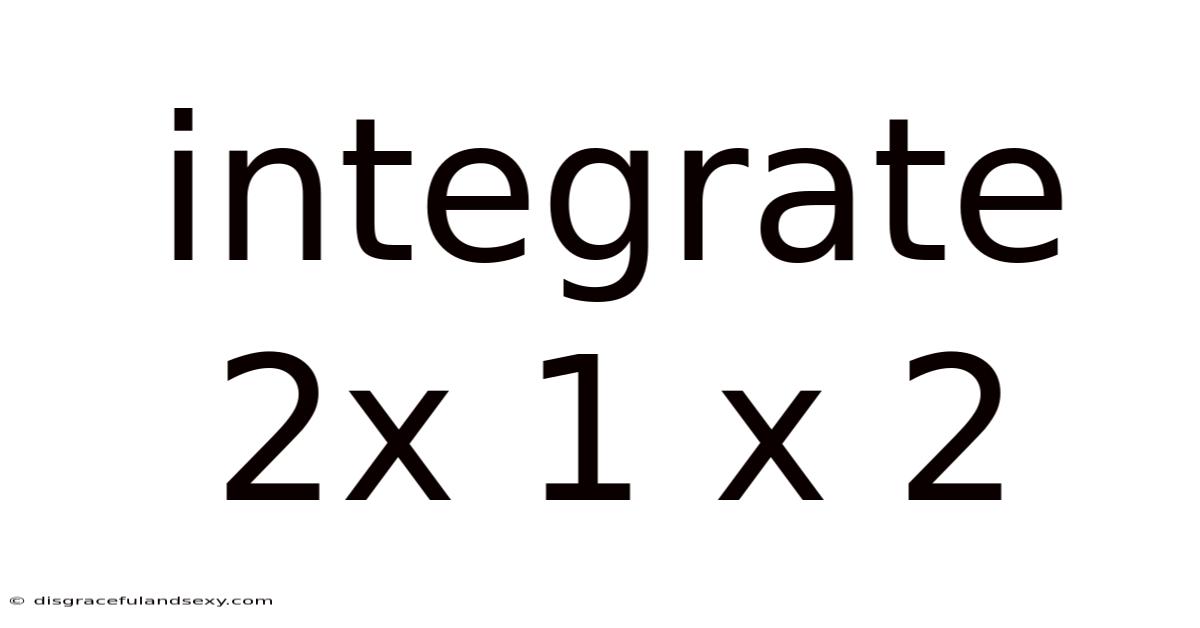
Table of Contents
Integrating 2 x 1 x 2: A Deep Dive into Matrix Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical operation of integrating, or rather, multiplying, the matrices represented by 2 x 1 and 1 x 2. While the numerical result might seem straightforward, understanding the underlying principles of matrix multiplication opens up a world of applications across various fields, from computer graphics and machine learning to quantum physics and economics. We'll delve into the mechanics of the operation, explore its significance, and unravel its broader implications.
Introduction: Beyond Simple Multiplication
The expression "integrate 2 x 1 x 2" is slightly misleading in a strict mathematical sense. Integration is a calculus concept related to finding areas under curves. What we are actually dealing with here is matrix multiplication. We have two matrices: a column vector (2 x 1) and a row vector (1 x 2). Understanding how these matrices interact reveals fundamental concepts in linear algebra.
The matrices can be represented as follows:
Matrix A (2 x 1):
[ a ]
[ b ]
Matrix B (1 x 2):
[ c d ]
Where a, b, c, and d are any real numbers.
The Mechanics of Matrix Multiplication: A Step-by-Step Guide
Matrix multiplication isn't simply element-wise multiplication. It involves a systematic process of row-column multiplication and summation. The resulting matrix's dimensions are determined by the outer dimensions of the original matrices. In this case, the resulting matrix will be a 2 x 2 matrix.
Here's a breakdown of the multiplication:
-
Determining the Dimensions: The number of columns in the first matrix (A) must equal the number of rows in the second matrix (B). In our case, A has 1 column and B has 1 row, fulfilling this condition. The resulting matrix will have the number of rows of A and the number of columns of B, leading to a 2 x 2 matrix.
-
Performing the Multiplication: Each element in the resulting matrix is calculated by multiplying the corresponding row of matrix A with the corresponding column of matrix B and summing the products.
Let's calculate the elements of the resulting 2 x 2 matrix (C):
- C<sub>11</sub> (Row 1, Column 1): (a * c) = ac
- C<sub>12</sub> (Row 1, Column 2): (a * d) = ad
- C<sub>21</sub> (Row 2, Column 1): (b * c) = bc
- C<sub>22</sub> (Row 2, Column 2): (b * d) = bd
Therefore, the resulting matrix C (2 x 2) is:
[ ac ad ]
[ bc bd ]
Illustrative Example: Putting it into Practice
Let's assign numerical values to a, b, c, and d:
Matrix A (2 x 1):
[ 2 ]
[ 3 ]
Matrix B (1 x 2):
[ 4 5 ]
Following the steps above:
- C<sub>11</sub>: (2 * 4) = 8
- C<sub>12</sub>: (2 * 5) = 10
- C<sub>21</sub>: (3 * 4) = 12
- C<sub>22</sub>: (3 * 5) = 15
The resulting matrix C (2 x 2) is:
[ 8 10 ]
[ 12 15 ]
The Significance of Matrix Multiplication: Beyond Simple Numbers
This seemingly simple operation has profound implications in various fields:
-
Linear Transformations: Matrix multiplication is the fundamental mechanism for representing linear transformations in vector spaces. Imagine transforming a point in 2D space – a matrix multiplication can rotate, scale, or shear the point.
-
Computer Graphics: Rendering images on a screen involves complex transformations of points and vectors. Matrix multiplication is the engine that drives these transformations, allowing for rotations, scaling, projections, and more.
-
Machine Learning: Many machine learning algorithms, particularly those involving neural networks, rely heavily on matrix multiplication. Training a neural network involves repeatedly performing matrix multiplications to update the network's weights and biases.
-
Physics and Engineering: Matrix multiplication finds extensive use in solving systems of linear equations, which are common in physics and engineering problems. For example, analyzing stress and strain in materials often involves solving large systems of linear equations using matrix methods.
-
Economics and Finance: Matrix algebra is used extensively in econometrics, for example, in the construction and analysis of input-output models that describe the interdependencies between various sectors of an economy. Portfolio optimization in finance also involves matrix calculations.
-
Quantum Mechanics: Quantum systems are often described using matrices and vectors. The evolution of a quantum state is governed by matrix multiplication, making it a cornerstone of quantum computation.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The 2 x 1 and 1 x 2 matrix multiplication example is a foundational building block. More complex scenarios involve larger matrices and more intricate calculations:
-
Higher Dimensional Matrices: The principles of matrix multiplication extend seamlessly to matrices of any dimension (provided the dimensions are compatible for multiplication). Consider a 3 x 3 matrix multiplied by a 3 x 1 matrix – the resulting matrix will be 3 x 1.
-
Matrix Transpose: The transpose of a matrix is created by swapping its rows and columns. The transpose of a 2 x 1 matrix is a 1 x 2 matrix, and vice versa. Understanding transposes is crucial in many matrix operations.
-
Identity Matrix: The identity matrix is a square matrix (same number of rows and columns) with 1s on the main diagonal and 0s elsewhere. Multiplying any matrix by the identity matrix leaves the original matrix unchanged.
-
Inverse Matrices: The inverse of a matrix, when it exists, is a matrix that, when multiplied by the original matrix, results in the identity matrix. Finding inverse matrices is essential in solving linear equations and performing various transformations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What happens if the number of columns in the first matrix doesn't match the number of rows in the second matrix?
A: Matrix multiplication is undefined in this case. The matrices are incompatible for multiplication.
-
Q: Is matrix multiplication commutative? (i.e., is A * B = B * A?)
A: No, matrix multiplication is generally not commutative. The order of multiplication matters. A * B is usually different from B * A, even if both multiplications are defined.
-
Q: Are there any software tools that can help with matrix calculations?
A: Yes, many software packages, such as MATLAB, Python (with libraries like NumPy), R, and others, provide robust functions for performing matrix operations, including multiplication.
-
Q: Why is understanding matrix multiplication important?
A: Matrix multiplication is a fundamental operation in linear algebra, a powerful mathematical tool with wide-ranging applications in science, engineering, computer science, and other fields. Understanding it unlocks the door to understanding many complex systems and phenomena.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Advanced Mathematical Concepts
The seemingly simple integration (or rather, multiplication) of a 2 x 1 and a 1 x 2 matrix serves as a springboard for understanding the broader world of matrix operations. Mastering these foundational concepts unlocks the ability to tackle more complex problems and appreciate the elegance and power of linear algebra. From computer graphics to quantum physics, matrix multiplication is a fundamental building block upon which many advanced mathematical concepts and applications are built. Further exploration of these topics will reveal the far-reaching implications of this seemingly simple operation. Its pervasive nature underscores the importance of understanding this core mathematical tool in a variety of disciplines.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integrate 2x 1 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.