Negative 3 Divided By 3
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 6 min read
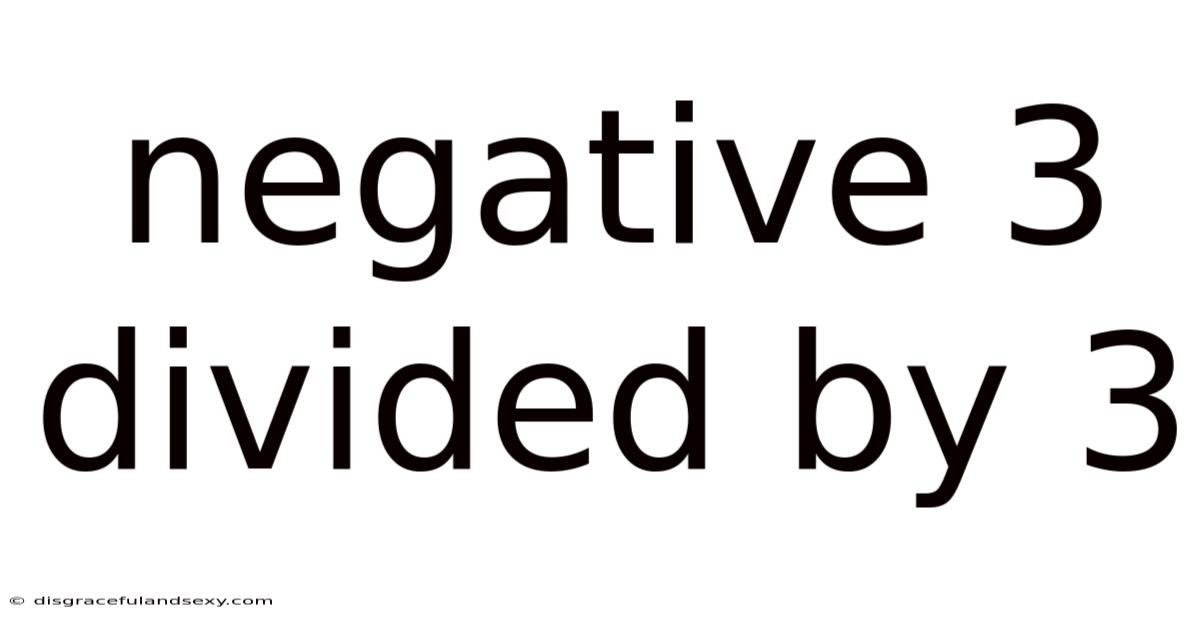
Table of Contents
Decoding -3 ÷ 3: A Deep Dive into Negative Division
Understanding division, especially when negative numbers are involved, can sometimes feel like navigating a mathematical maze. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the seemingly simple calculation of -3 ÷ 3, exploring the underlying principles, providing practical examples, and addressing common misconceptions. We'll journey beyond the answer to grasp the core concepts that govern division with negative integers, making this seemingly basic operation crystal clear.
Introduction: Why This Matters
The seemingly simple problem of -3 ÷ 3 might appear trivial at first glance. However, it acts as a gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts crucial for higher-level mathematics, particularly algebra. Mastering the rules of division with negative numbers is essential for solving equations, interpreting graphs, and tackling complex problems in various fields like physics, engineering, and finance. This article aims to demystify the process, providing a solid foundation for anyone struggling with this type of calculation.
Understanding Division: A Conceptual Overview
Before diving into the specifics of negative division, let's establish a firm understanding of what division represents. Division is essentially the inverse operation of multiplication. When we say "a ÷ b = c," we're asking, "What number (c) multiplied by b equals a?" For example, 6 ÷ 2 = 3 because 3 multiplied by 2 equals 6.
This fundamental relationship will be crucial in understanding how division works with negative numbers. The key is to consistently apply the rules of multiplication involving positive and negative integers.
The Rules of Multiplying with Negative Numbers
The rules for multiplying with negative numbers are as follows:
- Positive × Positive = Positive: A positive number multiplied by a positive number always results in a positive number (e.g., 2 × 3 = 6).
- Positive × Negative = Negative: A positive number multiplied by a negative number always results in a negative number (e.g., 2 × -3 = -6).
- Negative × Positive = Negative: A negative number multiplied by a positive number always results in a negative number (e.g., -2 × 3 = -6).
- Negative × Negative = Positive: A negative number multiplied by a negative number always results in a positive number (e.g., -2 × -3 = 6).
These rules are paramount to understanding division involving negative numbers, as division is directly linked to multiplication.
Solving -3 ÷ 3: Step-by-Step
Now, let's tackle the problem at hand: -3 ÷ 3. Using the inverse relationship between division and multiplication, we're looking for a number that, when multiplied by 3, equals -3.
Following the rules of multiplication, we can see that:
-1 × 3 = -3
Therefore, -3 ÷ 3 = -1.
Visualizing the Division: The Number Line
Using a number line can provide a visual representation to reinforce the concept. Imagine the number line, with zero in the center. To represent -3 ÷ 3, start at -3 on the number line. Then, divide this distance into three equal parts. Each part represents a movement of -1. Thus, each of the three equal parts is -1, confirming that -3 ÷ 3 = -1.
Applying the Rules to Other Examples
Let's extend our understanding by looking at other examples involving negative numbers and division:
- -6 ÷ 2 = -3: Because -3 × 2 = -6
- -9 ÷ 3 = -3: Because -3 × 3 = -9
- 12 ÷ -4 = -3: Because -3 × -4 = 12
- -15 ÷ 5 = -3: Because -3 × 5 = -15
Notice the pattern: when dividing a negative number by a positive number, the result is always negative. When dividing a positive number by a negative number, the result is also negative.
The Importance of Signs: A Deeper Look
The sign of the result in division involving negative numbers is determined by the signs of the dividend (the number being divided) and the divisor (the number you are dividing by). We can summarize the rules as follows:
- Negative ÷ Positive = Negative
- Positive ÷ Negative = Negative
- Negative ÷ Negative = Positive
- Positive ÷ Positive = Positive
Understanding these rules is crucial for accurate calculations and problem-solving.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can arise when dealing with negative numbers in division:
- Ignoring the signs: Forgetting to consider the signs of the numbers can lead to incorrect results. Always pay close attention to whether the numbers are positive or negative.
- Confusing division with subtraction: Division and subtraction are distinct operations. Remember that division asks "how many times does one number go into another," while subtraction involves finding the difference between two numbers.
- Incorrect application of the rules: Misapplying the rules of multiplication involving negative numbers can lead to incorrect results in division. Carefully review these rules to avoid errors.
Real-World Applications
Division with negative numbers isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it has numerous real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
- Finance: Calculating losses or debts. A company losing $3 million over three years would show a loss of -$1 million per year (-$3,000,000 ÷ 3 years = -$1,000,000/year).
- Physics: Calculating changes in velocity or acceleration. A car decelerating at a rate of -3 m/s² over 3 seconds would have a deceleration of -1 m/s² per second.
- Temperature: Determining average temperature changes. If the temperature drops -3 degrees Celsius over 3 hours, the average drop is -1 degree Celsius per hour.
These examples illustrate the practical significance of understanding division with negative numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What happens if I divide zero by a negative number?
A: Dividing zero by any non-zero number, whether positive or negative, always results in zero. 0 ÷ -3 = 0.
Q: What happens if I divide a negative number by zero?
A: Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. It's not possible to divide any number by zero.
Q: Can I use a calculator to check my work?
A: Yes, calculators are valuable tools for verifying calculations. However, it's crucial to understand the underlying principles. A calculator can provide the answer, but it won't necessarily enhance your understanding of why that's the correct answer.
Conclusion: Mastering Negative Division
Understanding how to divide negative numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. By grasping the relationship between division and multiplication, applying the rules of signs consistently, and practicing with various examples, you can confidently tackle problems involving negative division. Remember, mastering this concept is not just about getting the right answer; it's about developing a deeper understanding of the mathematical principles that govern operations with negative numbers. This foundation will serve you well in future mathematical endeavors and across various disciplines that utilize mathematical principles. So, the next time you encounter a problem like -3 ÷ 3, you'll not only know the answer (-1) but also understand the "why" behind it, making you a more confident and capable mathematician.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Negative 3 Divided By 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.