Simplify X 3 Y 3
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
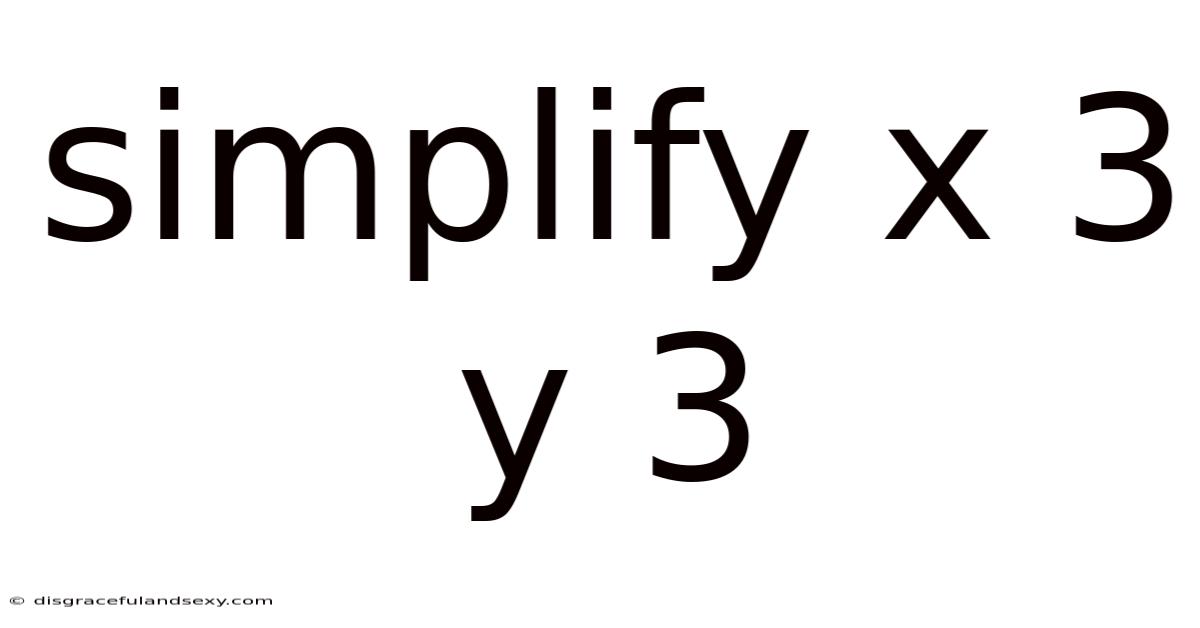
Table of Contents
Simplifying x³y³: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to simplify algebraic expressions is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide delves into the simplification of the expression x³y³, explaining the underlying principles and providing various approaches to tackle similar problems. We'll cover the basics, explore advanced concepts, and address frequently asked questions, ensuring a thorough understanding for learners of all levels.
Introduction: Understanding the Basics
The expression x³y³ represents a product of variables raised to powers. Let's break it down:
- x³: This means x multiplied by itself three times (x * x * x). The '3' is called the exponent or power.
- y³: Similarly, this means y multiplied by itself three times (y * y * y).
- x³y³: The entire expression represents the product of x³ and y³, meaning (x * x * x) * (y * y * y).
Our goal is to simplify this expression, which in this case means expressing it in its most concise and efficient form. While this particular expression may seem simple at first glance, mastering the techniques used to simplify it forms the basis for tackling more complex algebraic expressions later on.
Method 1: Direct Simplification using the Laws of Exponents
The most straightforward approach to simplifying x³y³ involves applying the fundamental laws of exponents. There isn't any inherent simplification possible for this specific expression unless we are provided with specific values for x and y. However, understanding the laws of exponents is crucial for simplifying more complex expressions.
- Rule 1: Product of Powers: When multiplying variables with the same base, you add the exponents. For example, x² * x³ = x^(2+3) = x⁵.
- Rule 2: Power of a Product: When raising a product to a power, you raise each factor to that power. For example, (xy)² = x²y².
- Rule 3: Power of a Power: When raising a power to another power, you multiply the exponents. For example, (x²)³ = x^(2*3) = x⁶.
In the case of x³y³, we can see that the bases (x and y) are different. Therefore, we cannot combine the exponents directly. The simplified form of x³y³ is simply x³y³. There are no like terms to combine, and no further simplification is possible without additional information.
Method 2: Expanding the Expression (For Understanding)
To solidify our understanding, let's expand the expression fully:
x³y³ = (x * x * x) * (y * y * y) = xxyyxy
While this expanded form is equivalent to x³y³, it's not considered a simplification. The original form, x³y³, is far more concise and efficient. This exercise helps illustrate what the expression actually represents, reinforcing the meaning of exponents and the product of variables.
Method 3: Considering Factorization (Advanced Concept)
While not strictly a simplification in the conventional sense, we can consider factorization. Factorization involves expressing an expression as a product of its factors. For x³y³, the factors are already explicitly shown. However, this approach becomes significant when dealing with more complex polynomial expressions. For instance, if we had x³y³ - x²y², we could factor out x²y² resulting in x²y²(xy - 1). This technique demonstrates a different type of simplification which involves expressing a larger expression as a product of smaller expressions.
Working with Numerical Coefficients
Let's explore scenarios where numerical coefficients are involved. Suppose we had the expression 2x³y³. In this case, the '2' is a coefficient multiplying the variable terms. The simplified form remains 2x³y³. We cannot combine the coefficient with the exponents because they represent different mathematical operations (multiplication vs. exponentiation).
Now let's consider a more complex example: 3x³y³ + 5x³y³. Here, the terms 3x³y³ and 5x³y³ are like terms, meaning they have the same variables raised to the same powers. In such cases, we can combine the coefficients:
3x³y³ + 5x³y³ = (3 + 5)x³y³ = 8x³y³
This demonstrates how the simplification process can involve combining like terms when dealing with sums or differences of similar expressions.
Addressing More Complex Scenarios
The principles demonstrated with x³y³ are fundamental to simplifying far more complex algebraic expressions. Consider these examples:
- (2x³y³)²: Applying the power of a product rule, this simplifies to 4x⁶y⁶.
- (x³y³)(2xy): Applying the product of powers rule, this simplifies to 2x⁴y⁴.
- x³y³ / xy: Applying the rule for dividing powers (subtract the exponents), this simplifies to x²y².
- x³y³ + 2x²y² - 5xy: This expression cannot be simplified further because there are no like terms.
These examples highlight how the basic principles of exponent manipulation extend to more complicated situations. The key is to identify like terms, apply the appropriate rules of exponents, and perform the necessary arithmetic operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I simplify x³y³ further if I know the values of x and y?
A1: Yes, absolutely! If you're given numerical values for x and y, you can substitute those values into the expression and evaluate it to get a numerical result. For example, if x = 2 and y = 3, then x³y³ = 2³ * 3³ = 8 * 27 = 216. This is a numerical simplification, distinct from the algebraic simplification discussed previously.
Q2: What if I have an expression like x³y³ + z³?
A2: This expression cannot be simplified further because x³y³, and z³ are unlike terms. They contain different variables. Simplification only applies when we can combine like terms or apply exponent rules.
Q3: Is there a specific order of operations when simplifying expressions?
A3: Yes, the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) applies here. Parentheses/Brackets first, followed by Exponents/Orders, then Multiplication and Division (from left to right), and finally Addition and Subtraction (from left to right). This ensures consistent and accurate simplification.
Q4: How do I know when an expression is fully simplified?
A4: An expression is considered fully simplified when it cannot be further reduced by combining like terms, applying exponent rules, or factoring. It's expressed in its most concise and efficient form.
Q5: What resources are available to practice simplifying algebraic expressions?
A5: Many online resources offer practice problems and tutorials on simplifying algebraic expressions. Textbooks and educational websites provide numerous examples and exercises to help you develop your skills.
Conclusion: Mastering Algebraic Simplification
Simplifying expressions like x³y³ is a crucial skill in algebra and mathematics overall. While x³y³ itself doesn't allow for much simplification algebraically, understanding the fundamental principles involved – such as the laws of exponents, combining like terms, and the concept of factorization – is essential for tackling more challenging algebraic manipulations. By practicing and mastering these techniques, you'll build a strong foundation for success in higher-level mathematics. Remember to always follow the order of operations and look for opportunities to combine like terms or apply the laws of exponents to achieve the most concise and efficient representation of an algebraic expression. Continue practicing, and you'll soon be able to simplify complex expressions with ease and confidence.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Simplify X 3 Y 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.