Sin X Cos X 2
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
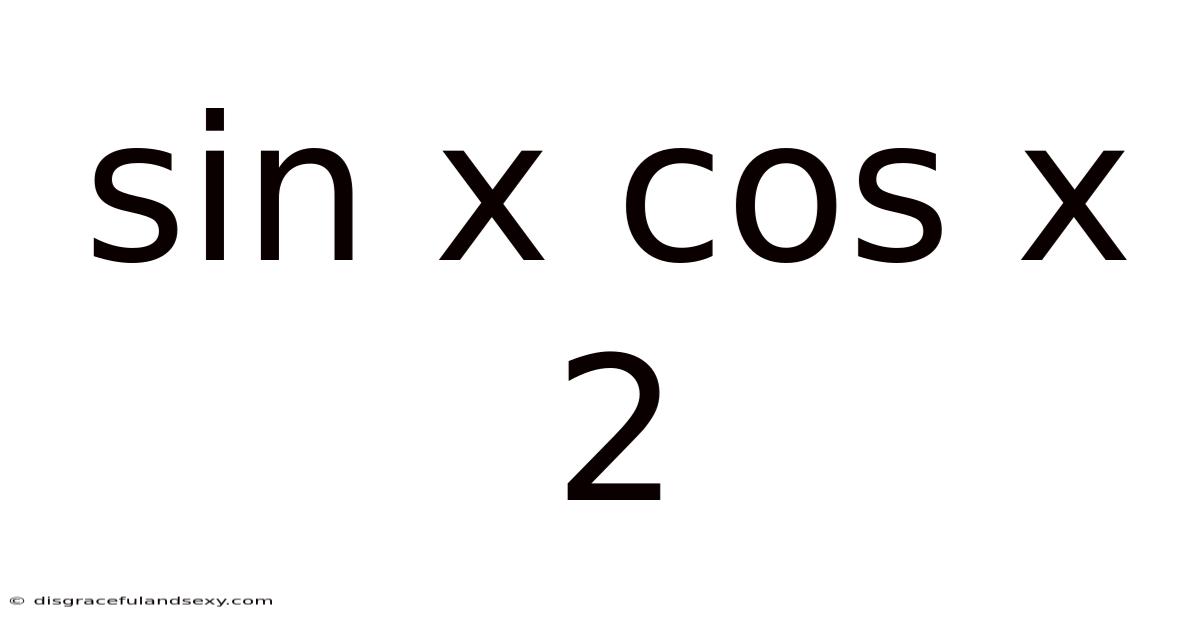
Table of Contents
Decoding the Trigonometric Identity: sin x cos x 2
Understanding trigonometric identities is fundamental to mastering advanced mathematics, especially calculus and physics. This article delves deep into the trigonometric expression sin x cos x 2, exploring its various forms, derivations, applications, and common misconceptions. We will unravel its complexities, providing a comprehensive guide suitable for students of all levels, from high school to undergraduate studies. This exploration will equip you with a solid understanding of how to manipulate and apply this specific identity, enriching your knowledge of trigonometry.
Introduction: Unpacking sin x cos x 2
The expression sin x cos x 2 is a seemingly simple trigonometric expression, yet it holds significant importance due to its connections to other fundamental identities and its applications in solving complex equations and problems. At first glance, it might seem like a standalone expression, but through strategic manipulation, we can transform it into more manageable and interpretable forms. This transformation hinges on our understanding of double-angle identities and other trigonometric relationships. This article will guide you through these manipulations, revealing the hidden power within this seemingly simple expression. We'll explore how it relates to concepts such as amplitude, phase shift, and frequency, demonstrating its practical significance beyond mere theoretical understanding.
Deriving Alternative Forms: Unveiling the Double Angle Identity
The key to unlocking the potential of sin x cos x 2 lies in the application of the double angle identity for sine. Recall that the double angle identity for sine is given by:
sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x
Notice the striking similarity between this identity and our target expression. By manipulating this identity, we can express sin x cos x in terms of sin(2x):
sin x cos x = sin(2x) / 2
Therefore, sin x cos x 2 can be rewritten as:
sin x cos x 2 = (sin(2x) / 2) 2 = sin(2x) / 4
This simplified form is significantly easier to work with in various contexts. This transformation drastically simplifies calculations and allows for a deeper understanding of the expression's behavior.
Graphical Representation and Interpretation
Visualizing the expression is crucial to grasp its behavior. Plotting the graph of y = sin x cos x 2 (or equivalently, y = sin(2x) / 4) reveals a sinusoidal wave with an amplitude of 1/4 and a period of π. This contrasts sharply with the graphs of sin x and cos x, which have amplitudes of 1 and periods of 2π. The amplitude scaling by a factor of 1/4 is a direct consequence of the division by 4. The period reduction to π is a consequence of the argument being 2x inside the sine function. The graph clearly shows the oscillatory nature of the function, highlighting its cyclical behavior. Understanding the graphical representation helps in comprehending its applications in modeling periodic phenomena.
Applications in Solving Trigonometric Equations
The simplified form, sin(2x) / 4, proves invaluable in solving trigonometric equations. For example, consider the equation:
sin x cos x = 1/8
Using our derived identity, we can rewrite this equation as:
sin(2x) / 2 = 1/8
This simplifies to:
sin(2x) = 1/4
Solving this equation for 2x using inverse trigonometric functions, and then dividing by 2, provides the solutions for x. This demonstrates how the identity simplifies the process of solving equations which might otherwise seem complex.
Calculus Applications: Differentiation and Integration
The simplified form of sin x cos x 2 also lends itself well to calculus operations.
Differentiation:
To differentiate sin x cos x 2 with respect to x, we can use the simplified form:
d/dx [sin(2x)/4] = (1/4) * d/dx [sin(2x)] = (1/4) * 2cos(2x) = cos(2x)/2
This straightforward differentiation highlights the ease of working with the simplified expression compared to directly differentiating the original form.
Integration:
Similarly, integration becomes significantly easier. The integral of sin x cos x 2 with respect to x is:
∫ sin x cos x 2 dx = ∫ sin(2x)/4 dx = (-cos(2x))/8 + C
where C is the constant of integration. This demonstrates the elegance and efficiency of applying the double angle identity before performing integration. The integration process is simplified considerably, avoiding the complexities associated with integration by parts or other advanced techniques.
Connection to Other Trigonometric Identities: Expanding the Knowledge Base
The expression sin x cos x 2 isn't isolated; it's interconnected with a broader web of trigonometric identities. Understanding these connections enriches our understanding of trigonometric relationships and strengthens our problem-solving capabilities. For example:
-
Product-to-Sum Identities: This identity can be expressed using product-to-sum identities, providing an alternative derivation and further highlighting its connections within the broader trigonometric framework.
-
Power Reduction Formulas: The expression can also be manipulated using power reduction formulas to express it in terms of powers of cosine or sine. While less efficient in this specific case, this reveals another avenue for manipulation and problem-solving.
-
Complex Numbers: The expression can be linked to complex exponential representations of sine and cosine, providing a bridge between trigonometry and complex analysis. This connection underscores the unifying power of mathematics and the deeper connections between seemingly disparate areas.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
Several common misconceptions surrounding this expression need clarification:
-
Incorrect Simplification: A frequent mistake is attempting to simplify sin x cos x 2 directly without utilizing the double angle identity, leading to incorrect results. Remember the power of rewriting the expression using known identities.
-
Neglecting the Constant of Integration: When integrating, remember to include the constant of integration, C, as it's crucial for obtaining a complete solution.
-
Confusing Amplitude and Period: Students may confuse the amplitude and period of the resulting function, particularly when comparing it to the standard sine and cosine functions. Carefully analyze the effects of the scaling factor and the argument modification on the wave characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can sin x cos x 2 be simplified further than sin(2x)/4?
A: While sin(2x)/4 is a simplified form, further simplification depends on the context. It can be expressed in other forms depending on the required application, as discussed in the section on connections to other identities.
Q: What are the practical applications of this identity beyond mathematical theory?
A: This identity has applications in various fields, including physics (modeling oscillations, waves), engineering (signal processing), and computer graphics (representing periodic phenomena).
Q: How can I verify my solutions when working with this identity?
A: You can verify your solutions by substituting them back into the original equation or by using graphing calculators or software to visualize the function and its solutions.
Q: Is there a way to solve for x directly without using the inverse trigonometric functions?
A: Directly solving for x without using inverse trigonometric functions usually isn't possible. The inverse functions are necessary to isolate x from the trigonometric equation. Numerical methods might be necessary in some complex scenarios.
Conclusion: Mastering sin x cos x 2 and Beyond
This in-depth exploration of sin x cos x 2 demonstrates that even seemingly simple trigonometric expressions can reveal hidden complexities and powerful applications. By mastering the manipulation of this expression and understanding its relationships to other identities, you've taken a significant step toward a deeper comprehension of trigonometry. Remember, the key is understanding the underlying principles, recognizing the opportunities to apply fundamental identities, and carefully analyzing the results. This knowledge empowers you to tackle more complex trigonometric problems and enhances your appreciation for the beauty and elegance of mathematical relationships. The journey of understanding trigonometric identities is a continuous process of learning and application, and each new identity mastered builds a stronger foundation for more advanced concepts. This comprehensive guide should provide you with a solid base to continue exploring the fascinating world of trigonometry.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sin X Cos X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.