Solve X 2 X 7
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
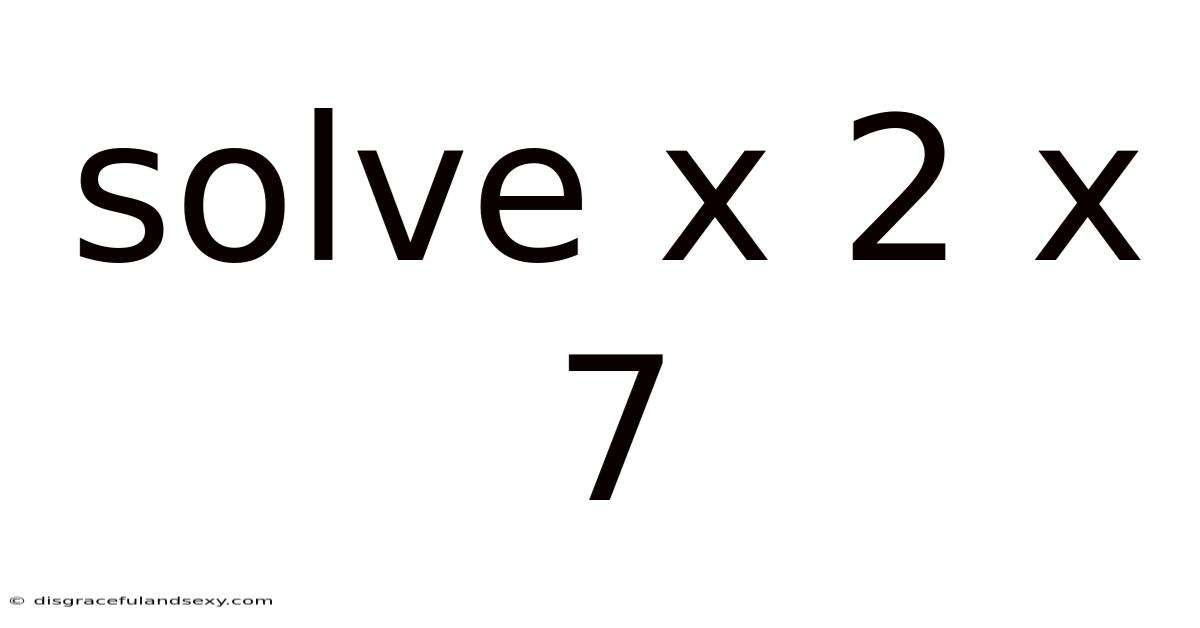
Table of Contents
Decoding "Solve x² + 7": A Comprehensive Guide to Quadratic Equations
This article explores the solution to the equation x² + 7 = 0, delving into the fundamental concepts of quadratic equations, their various solving methods, and the interpretation of complex numbers. Understanding this seemingly simple equation unlocks a deeper understanding of algebra and its applications in various fields. We'll cover everything from basic algebraic manipulation to the intricacies of complex numbers, ensuring a thorough grasp of the subject matter for readers of all levels.
Introduction to Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and a is not equal to zero. Our equation, x² + 7 = 0, is a specific case of this general form, where a = 1, b = 0, and c = 7.
The solutions to a quadratic equation are called its roots or zeros. These roots represent the values of x that make the equation true. Finding these roots is the core objective of solving a quadratic equation. While some quadratic equations have real number solutions, others, like the one we're examining, yield complex numbers.
Solving x² + 7 = 0: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's systematically solve the equation x² + 7 = 0:
-
Isolate the x² term: Subtract 7 from both sides of the equation: x² = -7
-
Take the square root: To solve for x, we take the square root of both sides. Remember that the square root of a number has two solutions – a positive and a negative value. Therefore: x = ±√(-7)
-
Introducing Complex Numbers: The square root of a negative number is not a real number. This is where complex numbers come into play. A complex number is a number that can be expressed in the form a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers, and 'i' is the imaginary unit, defined as the square root of -1 (i.e., i² = -1).
-
Simplifying the Solution: We can rewrite √(-7) using the imaginary unit: √(-7) = √(7 * -1) = √7 * √(-1) = √7i
Therefore, the solutions to the equation x² + 7 = 0 are:
x = √7i and x = -√7i
These are two distinct complex numbers, each representing a root of the quadratic equation.
Understanding Complex Numbers: A Deeper Dive
Complex numbers might seem abstract at first, but they are essential in many areas of mathematics, physics, and engineering. Let's explore their key aspects:
-
Real Part and Imaginary Part: In a complex number a + bi, 'a' is the real part and 'b' is the imaginary part. In our solution, the real part is 0, and the imaginary part is ±√7.
-
Complex Conjugates: Complex numbers that have the same real part but opposite imaginary parts are called complex conjugates. In our case, √7i and -√7i are complex conjugates. Complex conjugates often appear in pairs as solutions to quadratic equations with real coefficients.
-
Representing Complex Numbers Geometrically: Complex numbers can be visualized on a complex plane, also known as an Argand diagram. The horizontal axis represents the real part, and the vertical axis represents the imaginary part. Each complex number can be plotted as a point on this plane.
-
Polar Form of Complex Numbers: Besides the rectangular form (a + bi), complex numbers can also be expressed in polar form, using magnitude (or modulus) and argument (or phase). This form is particularly useful for certain operations involving complex numbers.
Alternative Methods for Solving Quadratic Equations
While the method above directly solves x² + 7 = 0, let's explore other general methods applicable to various quadratic equations:
-
Factoring: Factoring involves expressing the quadratic expression as a product of two linear expressions. This method is straightforward for certain quadratic equations but isn't always applicable. Our equation, x² + 7 = 0, cannot be factored easily using real numbers.
-
Quadratic Formula: The quadratic formula is a powerful tool for solving any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it can be factored easily. The formula is:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
For our equation (a = 1, b = 0, c = 7), applying the quadratic formula yields the same complex solutions we obtained earlier.
-
Completing the Square: Completing the square is a technique that transforms the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve. While applicable to our equation, it leads to the same complex solutions.
Applications of Quadratic Equations and Complex Numbers
The seemingly abstract concept of complex numbers finds practical applications in numerous fields:
-
Electrical Engineering: Complex numbers are used extensively in analyzing alternating current (AC) circuits, where impedance and phase shifts are crucial concepts.
-
Quantum Mechanics: Complex numbers are fundamental to the mathematical framework of quantum mechanics, describing the wave function of particles.
-
Signal Processing: Complex numbers are used in the Fourier transform, a powerful tool for analyzing signals and extracting information.
-
Fluid Dynamics: Complex numbers are applied in solving certain fluid flow problems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are complex numbers necessary to solve x² + 7 = 0?
A: Because the equation requires taking the square root of a negative number (-7), which is not possible within the realm of real numbers. Complex numbers extend the number system to include the imaginary unit 'i', allowing us to find solutions.
Q: Are there always two solutions to a quadratic equation?
A: Yes, every quadratic equation has two solutions, although they might be the same (repeated roots). These solutions can be real numbers, complex numbers, or a combination of both.
Q: What is the significance of the complex conjugate solutions?
A: For quadratic equations with real coefficients, complex solutions always appear in conjugate pairs. This is a fundamental property of complex numbers and their relationship to polynomial equations.
Q: Can I use a calculator to find the approximate values of the solutions?
A: Yes, you can use a scientific calculator with complex number capabilities to approximate the values of √7i and -√7i. Remember that these are approximate values, as √7 is an irrational number.
Conclusion
Solving the equation x² + 7 = 0 provides a gateway to a deeper understanding of quadratic equations and the fascinating world of complex numbers. While seemingly a simple algebraic problem, its solution reveals the limitations of real numbers and the necessity of extending the number system to encompass complex numbers. These complex numbers, despite their abstract nature, play a crucial role in various scientific and engineering disciplines, highlighting the interconnectedness and practical relevance of mathematical concepts. The journey from a simple equation to the realm of complex numbers demonstrates the power and beauty of mathematics in unlocking the secrets of our world. Through a step-by-step approach and a detailed explanation of complex numbers and alternative solving methods, this article aimed to provide a comprehensive and engaging exploration of this fundamental mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Solve X 2 X 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.