Square Root Of 33 Simplified
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 5 min read
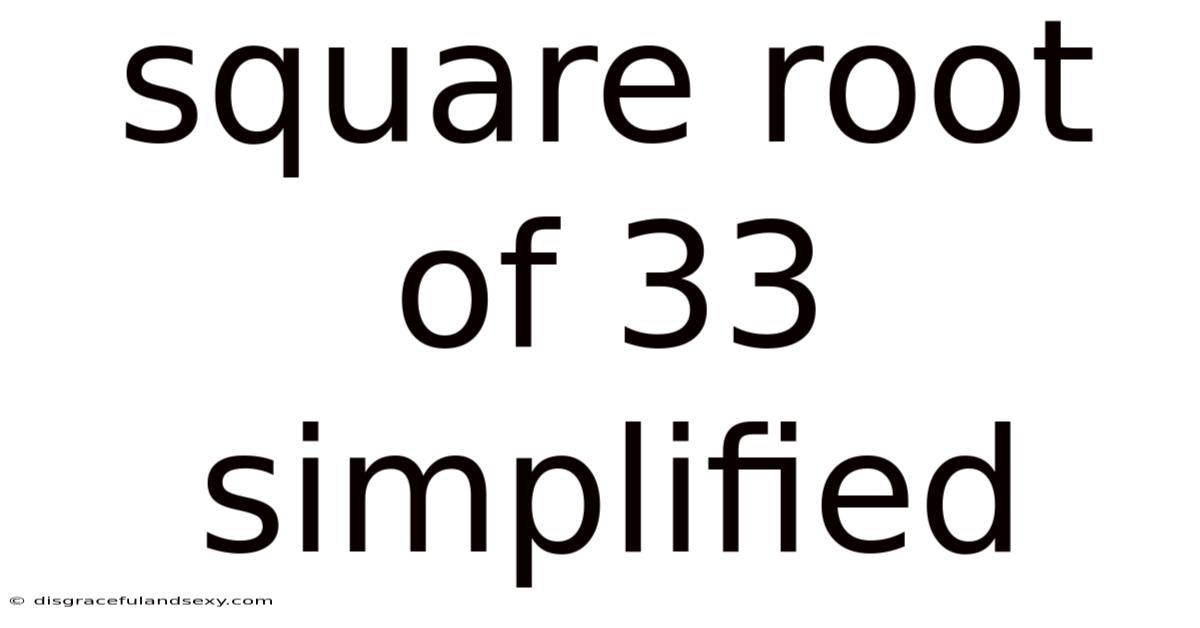
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of √33: A Deep Dive into Simplification and Approximation
Finding the square root of 33 might seem like a simple task at first glance. However, delving deeper reveals fascinating mathematical concepts and techniques. This comprehensive guide will explore the simplification of √33, discussing why it's an irrational number, examining different methods for approximating its value, and touching upon the broader implications of working with square roots. We'll uncover the beauty and elegance hidden within this seemingly straightforward mathematical problem.
Understanding Square Roots and Irrational Numbers
Before tackling the simplification of √33, let's establish a foundational understanding. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. For instance, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. However, not all square roots yield such neat whole numbers.
Numbers like √33 fall into the category of irrational numbers. An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating; it goes on forever without establishing a predictable pattern. This is in contrast to rational numbers, which can be expressed as fractions (e.g., 1/2, 3/4, -5/7).
The fact that √33 is irrational means we can't simplify it to a neat fraction or a terminating decimal. This doesn't mean we can't work with it; it simply means our answer will always involve an approximation or the use of the radical symbol (√).
Why √33 Cannot Be Simplified Further
The process of simplifying a square root involves finding perfect square factors within the number under the radical sign. A perfect square is a number that results from squaring an integer (e.g., 4, 9, 16, 25). If the number under the radical has a perfect square factor, we can simplify it. For example:
√12 = √(4 x 3) = √4 x √3 = 2√3
Here, we factored 12 into 4 (a perfect square) and 3. We then took the square root of 4, leaving 3 under the radical.
However, 33 has no perfect square factors other than 1. The prime factorization of 33 is 3 x 11. Neither 3 nor 11 are perfect squares. Therefore, √33 is already in its simplest form. We cannot simplify it further using this method.
Methods for Approximating √33
Since we can't find an exact value for √33, we resort to approximation techniques. Here are a few methods:
1. Using a Calculator: The simplest method is using a calculator. Most calculators have a square root function (√). Inputting √33 will give you an approximate decimal value, typically around 5.74456.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): This iterative method refines an initial guess to get closer and closer to the actual square root.
- Step 1: Make an initial guess. Let's guess 6, as 6 x 6 = 36, which is close to 33.
- Step 2: Improve the guess. Divide 33 by your initial guess: 33 / 6 = 5.5
- Step 3: Average the guess and the result. (6 + 5.5) / 2 = 5.75
- Step 4: Repeat steps 2 and 3. Using 5.75 as the new guess, we get:
- 33 / 5.75 ≈ 5.739
- (5.75 + 5.739) / 2 ≈ 5.7445
- Continue this process until you reach the desired level of accuracy. Each iteration gets you closer to the true value.
3. Linear Approximation: This method uses the tangent line to the graph of y = √x at a nearby point to estimate the value. It's less accurate than the Babylonian method but simpler to perform without a calculator.
Let's use the point x = 36 (√36 = 6). The derivative of √x is 1/(2√x). At x = 36, the slope is 1/(2√36) = 1/12.
The equation of the tangent line is: y - 6 = (1/12)(x - 36)
Substituting x = 33: y - 6 = (1/12)(-3) => y ≈ 5.75
This approximation is relatively close, though less precise than the Babylonian method.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The existence of irrational numbers like √33 highlights the richness and complexity of the number system. While we can't express them as simple fractions, they are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and science. Understanding how to work with these numbers – through approximation techniques or symbolic representation – is crucial for progress in fields like:
-
Geometry: Irrational numbers frequently appear in geometric calculations, particularly those involving circles and triangles. The Pythagorean theorem, for instance, often leads to irrational square roots.
-
Physics: Many physical constants and calculations involve irrational numbers, reflecting the inherent complexity of the natural world.
-
Calculus: Irrational numbers are central to calculus, which deals with continuous change and limits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can √33 be expressed as a decimal?
A: Yes, but only approximately. A calculator will provide a decimal approximation, but the decimal representation will be non-terminating and non-repeating.
Q: Is there any other way to simplify √33 besides looking for perfect square factors?
A: No, there isn't. Since 33 has no perfect square factors greater than 1, it's already in its simplest radical form.
Q: Why is it important to learn about irrational numbers?
A: Irrational numbers are fundamental to mathematics and science. Understanding them is essential for solving problems in various fields and developing a deeper appreciation for the number system.
Q: Are all square roots of non-perfect squares irrational?
A: Yes, this is a general rule. The square root of any positive integer that is not a perfect square will be an irrational number.
Conclusion
While √33 cannot be simplified in the traditional sense of finding a whole number or fractional representation, its exploration unveils the beauty and significance of irrational numbers. Understanding its properties, employing approximation methods, and grasping the broader context of irrational numbers in mathematics and science expands our mathematical understanding and strengthens our problem-solving skills. The journey towards comprehending √33 is not just about finding a numerical answer; it's about appreciating the elegance and complexity of the mathematical world. Remember, even seemingly simple mathematical concepts can lead to rich and rewarding explorations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Square Root Of 33 Simplified . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.