Square Root Of 4 9
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
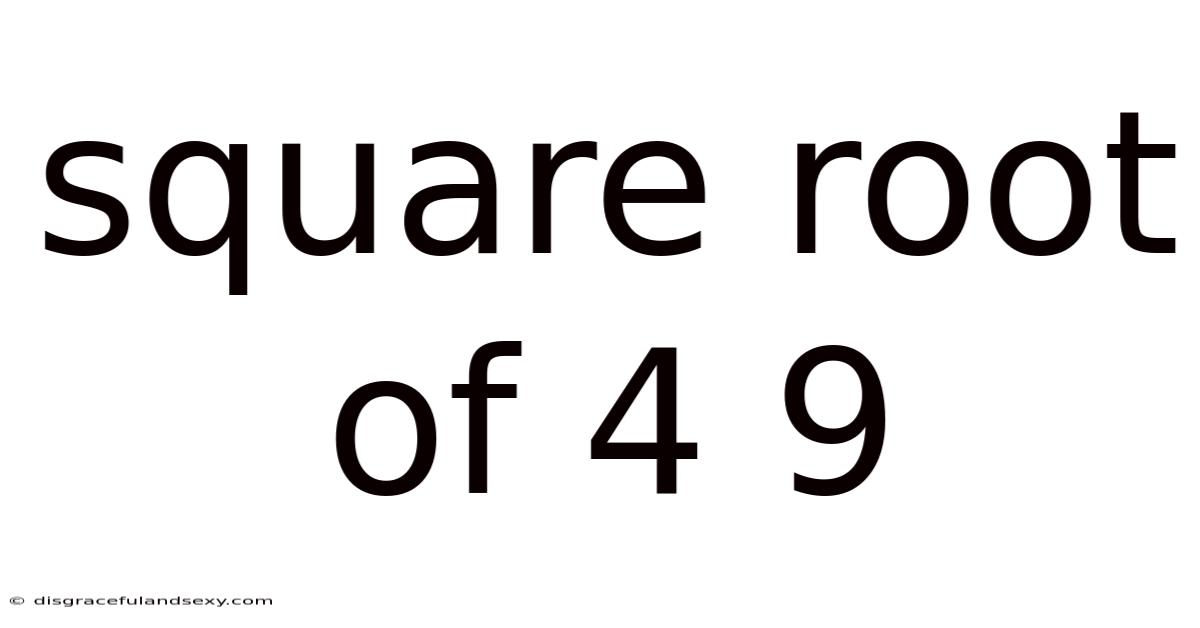
Table of Contents
Understanding the Square Root of 49: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the square root of 49 might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, suitable only for elementary school students. However, a deeper dive into this seemingly basic concept reveals a wealth of mathematical principles and applications relevant to various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the square root of 49, examining its calculation, its significance in mathematics, and its real-world applications. We'll also address common misconceptions and frequently asked questions.
What is a Square Root?
Before we delve into the square root of 49 specifically, let's establish a clear understanding of what a square root is. In simple terms, the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 multiplied by 3 (3 x 3 = 3²) equals 9. This process is the inverse operation of squaring a number.
Mathematically, we represent the square root using the radical symbol (√). So, the square root of 49 is written as √49. This notation signifies the question: "What number, when multiplied by itself, equals 49?"
Calculating the Square Root of 49
The simplest way to find the square root of 49 is to recall the multiplication tables. We're looking for a number that, when multiplied by itself, yields 49. If you remember your times tables, you'll quickly realize that 7 x 7 = 49. Therefore, the square root of 49 is 7.
We can also express this mathematically as:
√49 = 7
It's important to note that every positive number has two square roots: a positive and a negative root. While 7 x 7 = 49, (-7) x (-7) also equals 49. Therefore, the complete solution to the square root of 49 is ±7 (plus or minus 7). However, unless specifically indicated otherwise, the principal square root (the positive root) is usually assumed. In this guide, unless stated differently, we'll focus on the principal square root.
Beyond Simple Calculation: Understanding the Concept
While calculating the square root of 49 is straightforward, the underlying concept holds significant importance in various mathematical areas and real-world applications. Let's explore some of these:
-
Pythagorean Theorem: The Pythagorean theorem, a cornerstone of geometry, states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Finding the length of a side often involves calculating a square root. For instance, if you know the lengths of two sides, and you need to find the hypotenuse, you'll likely encounter a square root calculation.
-
Algebra: Square roots are frequently encountered in solving algebraic equations. Quadratic equations, for example, often require the use of square roots to find their solutions. Understanding square roots is crucial for manipulating and solving these equations.
-
Coordinate Geometry: The distance formula in coordinate geometry involves calculating the square root of a sum of squares to determine the distance between two points on a coordinate plane.
-
Calculus: Square roots play a role in various calculus concepts, including differentiation and integration. Understanding square roots is fundamental for mastering these advanced mathematical techniques.
-
Physics and Engineering: Square roots appear extensively in physics and engineering calculations. For example, calculations involving velocity, acceleration, and energy often necessitate the use of square roots.
-
Computer Science: Square root calculations are integral to various algorithms and computations in computer science, especially in areas like graphics processing and numerical analysis.
Methods for Calculating Square Roots: Beyond Simple Memorization
While memorizing some common perfect squares (like 49) is helpful, we often need to calculate square roots of numbers that aren't perfect squares. Several methods exist for this:
-
Estimation and Approximation: For numbers close to perfect squares, you can estimate the square root. For example, if you needed the square root of 50, you know it's slightly more than 7 (√49 = 7).
-
Long Division Method: This is a traditional method for manually calculating square roots, although it can be tedious for large numbers.
-
Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): This iterative method provides increasingly accurate approximations of the square root. It involves repeatedly refining an initial guess until the desired accuracy is achieved.
-
Calculators and Computers: Modern calculators and computers efficiently compute square roots to a high degree of accuracy. This is the most practical method for most applications.
Common Misconceptions about Square Roots
Several common misconceptions surround square roots:
-
The square root of a negative number is always undefined: This is incorrect for real numbers. However, the concept of imaginary numbers (denoted by 'i', where i² = -1) is introduced to handle the square roots of negative numbers. For example, √-49 = 7i.
-
The square root is always a whole number: This is false. Most numbers do not have whole number square roots. The square root of a number can be a rational number (a fraction) or an irrational number (a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal).
-
√a + √b = √(a + b): This is a common mistake. The square root operation does not distribute over addition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the cube root of 49?
A: The cube root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, equals the original number. The cube root of 49 is approximately 3.659. This is not a whole number and requires a calculator or other method to approximate.
Q: How is the square root related to exponents?
A: Square roots and exponents are inverse operations. The square root of a number is equivalent to raising that number to the power of ½ (or 0.5). Therefore, √49 = 49^(1/2) = 7.
Q: Are there square roots of fractions?
A: Yes, fractions also have square roots. For example, √(1/4) = 1/2 because (1/2) x (1/2) = 1/4.
Q: What is the significance of the ± symbol when discussing square roots?
A: The ± (plus-minus) symbol indicates that there are two possible solutions for the square root: a positive and a negative value. This is because multiplying two negative numbers results in a positive number.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple calculation of the square root of 49 opens a door to a broader understanding of mathematical concepts and their applications. From the Pythagorean theorem to advanced calculus, square roots play a fundamental role in numerous fields. While a quick calculation might reveal that √49 = 7, the journey of understanding this seemingly simple concept enriches our mathematical knowledge and equips us to tackle more complex problems in various disciplines. This article aims to be a stepping stone to exploring the depths and breadth of square root calculations and their significance in our world. Further exploration into the mathematical concepts surrounding square roots will only enhance your appreciation for this important mathematical function.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Square Root Of 4 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.