Square Root Of 55 Simplified
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 5 min read
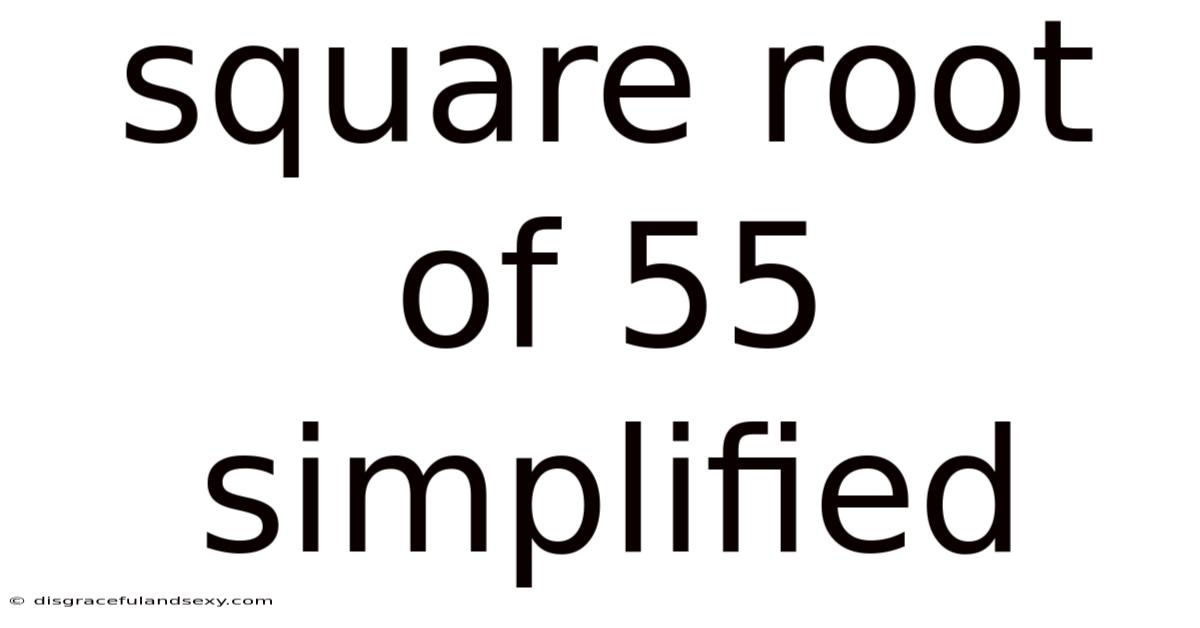
Table of Contents
Understanding and Simplifying the Square Root of 55
The square root of 55, denoted as √55, is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. While we can't find a perfect whole number answer, we can simplify √55 to its most concise form and explore its properties. This article will delve into the process of simplifying square roots, explain why √55 is irrational, explore its approximate value, and demonstrate practical applications.
What is a Square Root?
Before diving into the specifics of √55, let's refresh our understanding of square roots. The square root of a number 'x' is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 'x'. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 * 3 = 9. Similarly, the square root of 16 (√16) is 4 because 4 * 4 = 16.
However, not all numbers have perfect square roots that are whole numbers. Numbers like 2, 3, 5, 7, and many others have square roots that are irrational numbers – meaning they continue infinitely without repeating decimal patterns. This is the case with √55.
Simplifying √55: Finding Perfect Square Factors
Simplifying a square root involves finding perfect square factors within the number. A perfect square is a number that results from squaring a whole number (e.g., 4, 9, 16, 25, etc.). To simplify √55, we need to determine if it has any perfect square factors.
Let's examine the factors of 55: 1, 5, 11, and 55. None of these are perfect squares. This means that √55 cannot be simplified further using whole numbers. It remains in its simplest radical form as √55. This is crucial to understanding that we can't find a neat, whole number answer.
Why is √55 Irrational?
The fact that √55 cannot be simplified to a fraction of whole numbers is directly related to its irrationality. An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a fraction (a ratio) of two integers. The proof of irrationality often involves proof by contradiction, a common method in mathematical proofs.
Let's assume, for the sake of contradiction, that √55 is rational. This means we can express it as a fraction a/b, where 'a' and 'b' are integers and b ≠ 0, and the fraction is in its simplest form (meaning 'a' and 'b' share no common factors other than 1).
If √55 = a/b, then squaring both sides gives us 55 = a²/b². This implies that 55b² = a². Since the left side is divisible by 55, the right side (a²) must also be divisible by 55. Because 55 = 5 * 11, 'a' must be divisible by both 5 and 11. Therefore, we can write a = 5 * 11 * k, where 'k' is another integer.
Substituting this back into the equation, we get 55b² = (5 * 11 * k)² = 275 * k². This simplifies to b² = 5k². This means 'b' is also divisible by 5.
However, we initially assumed that 'a' and 'b' share no common factors. The fact that both 'a' and 'b' are divisible by 5 contradicts this assumption. This contradiction proves our initial assumption that √55 is rational must be false. Therefore, √55 is irrational.
Approximating the Value of √55
Although we cannot express √55 as a simple fraction or a terminating decimal, we can approximate its value using various methods:
-
Calculator: The most straightforward method is to use a calculator. Most calculators will provide an approximate decimal value, usually around 7.416.
-
Linear Approximation: We can find nearby perfect squares. We know that √49 = 7 and √64 = 8. Since 55 is closer to 49 than to 64, the square root of 55 will be closer to 7 than to 8. This gives us a rough estimate.
-
Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): This iterative method refines an initial guess to obtain a more accurate approximation. Starting with an initial guess (e.g., 7), we repeatedly apply the formula: x_(n+1) = (x_n + 55/x_n) / 2. Each iteration brings us closer to the actual value.
-
Taylor Series Expansion: For those familiar with calculus, the Taylor series expansion of the square root function can be used to approximate √55 around a known point.
Practical Applications of √55
While it might seem that an irrational number like √55 has limited real-world applications, it appears in various contexts within mathematics and other disciplines:
-
Geometry: Calculations involving triangles and other geometric figures might involve √55. For instance, the diagonal of a rectangle with sides of length 5 and 10 units involves calculating √125 which can be simplified to 5√5. Problems involving similar triangles or the Pythagorean theorem might also result in expressions including √55 or its simplified equivalents.
-
Physics: Physical phenomena often involve irrational numbers. Formulas in mechanics, electromagnetism, or quantum physics might contain square roots of non-perfect squares, potentially involving a value like √55 as part of a broader calculation.
-
Engineering: Design and construction projects often incorporate mathematical calculations. The dimensions and angles of structural elements might involve irrational numbers like √55 within the calculations.
-
Computer Science: √55 might appear in algorithms and simulations involving geometrical calculations or numerical analysis. Computer programs often handle irrational numbers using approximate decimal values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can √55 be simplified any further?
A: No, √55 is already in its simplest radical form. It does not contain any perfect square factors other than 1.
Q: What is the exact value of √55?
A: The exact value of √55 is an irrational number. It cannot be represented as a finite decimal or a simple fraction.
Q: How can I calculate √55 without a calculator?
A: You can approximate it using methods like linear approximation or the Babylonian method. These methods provide progressively more accurate estimates.
Q: Is √55 a rational or irrational number?
A: √55 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
Conclusion
While the square root of 55 cannot be expressed as a neat whole number or a simple fraction, understanding its properties as an irrational number is crucial. This article has explored the process of simplifying square roots, demonstrated why √55 is irrational, discussed methods for approximating its value, and highlighted its relevance in various fields. Remember, even seemingly abstract mathematical concepts like irrational numbers find practical applications in the real world. By understanding the fundamentals of number theory and square roots, we can better appreciate the intricate beauty and practical utility of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Square Root Of 55 Simplified . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.