What Is 15 Times 4
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
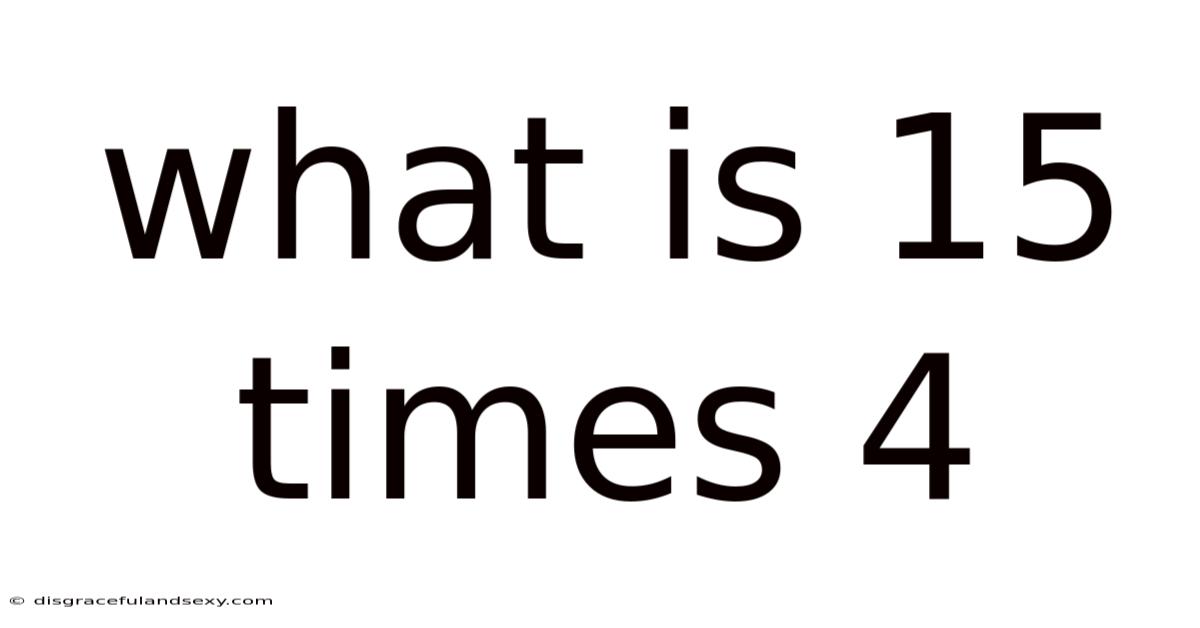
Table of Contents
What is 15 Times 4? A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This seemingly simple question, "What is 15 times 4?", opens the door to a fascinating exploration of multiplication, its underlying principles, and its widespread applications in various fields. While the answer itself is straightforward (60), the journey to understanding how we arrive at that answer reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts and practical uses. This article will not only provide the solution but also delve into the various methods of solving this multiplication problem, explore the theoretical foundations of multiplication, and demonstrate its relevance in everyday life and advanced studies.
Understanding Multiplication: The Basics
Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation representing repeated addition. When we say "15 times 4," we mean adding 15 to itself four times: 15 + 15 + 15 + 15. This simple concept forms the bedrock of more complex mathematical operations. Understanding this foundational concept is crucial before progressing to more advanced topics. Think of it like building a house; you need a solid foundation before you can construct the walls and roof. Similarly, a solid understanding of basic multiplication is essential for mastering more advanced mathematical concepts.
Methods for Solving 15 x 4
There are several ways to solve 15 x 4, each offering a different perspective and highlighting different mathematical principles:
1. Repeated Addition: As mentioned earlier, the most basic approach is repeated addition: 15 + 15 + 15 + 15 = 60. This method is intuitive and easily understood, particularly for younger learners. It directly connects multiplication to its underlying principle of repeated addition.
2. Distributive Property: This method breaks down the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. We can rewrite 15 as (10 + 5). Then, we apply the distributive property:
4 x (10 + 5) = (4 x 10) + (4 x 5) = 40 + 20 = 60
This method demonstrates the distributive property of multiplication over addition, a crucial concept in algebra and beyond. It showcases the flexibility and power of manipulating mathematical expressions to simplify calculations.
3. Array Method: This visual approach represents the multiplication problem using an array or grid. Imagine a rectangle with 15 rows and 4 columns. Counting the total number of squares in this rectangle gives us the answer, 60. This method is particularly helpful for visual learners and provides a concrete representation of the abstract concept of multiplication.
4. Multiplication Table: The multiplication table provides a pre-calculated set of multiplication facts. By looking up the intersection of 15 and 4 in the table, we directly find the answer: 60. While convenient for simple calculations, understanding the underlying principles is still essential for solving more complex problems.
5. Long Multiplication: This method, suitable for larger numbers, involves multiplying each digit of one number by each digit of the other number and then adding the partial products. For 15 x 4:
15
x 4
----
60
In this case, 4 multiplied by 5 equals 20, and 4 multiplied by 1 (representing 10) equals 40. Adding these together (20 + 40) results in 60.
The Theoretical Foundations of Multiplication
Beyond the practical methods of solving 15 x 4, understanding the underlying theoretical framework enhances our comprehension of the operation. Key concepts include:
-
Commutative Property: This property states that the order of the numbers in a multiplication problem does not affect the outcome. That is, 15 x 4 = 4 x 15 = 60. This seemingly simple property has far-reaching consequences in mathematical proofs and calculations.
-
Associative Property: This property deals with the grouping of numbers in a multiplication problem with more than two factors. For example, (2 x 3) x 4 = 2 x (3 x 4) = 24. This property allows for flexibility in the order of operations when dealing with multiple factors.
-
Identity Property: The number 1 is the multiplicative identity because any number multiplied by 1 equals itself (15 x 1 = 15). This simple yet fundamental property provides a basis for various mathematical manipulations.
-
Zero Property: Any number multiplied by 0 equals 0 (15 x 0 = 0). This property is crucial for understanding and solving equations and simplifying expressions.
These properties are not merely abstract mathematical concepts; they are fundamental tools that underpin more advanced mathematical operations and problem-solving techniques. Understanding them provides a deeper insight into the nature of multiplication and its place within the broader mathematical landscape.
Applications of Multiplication in Real Life
The seemingly simple operation of multiplying 15 by 4 has far-reaching applications in various aspects of our daily lives:
-
Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple items. If you buy 4 items costing $15 each, the total cost is 15 x 4 = $60.
-
Cooking: Scaling recipes. If a recipe calls for 15 grams of an ingredient and you want to quadruple the recipe, you need 15 x 4 = 60 grams.
-
Construction: Calculating materials needed. If you need 15 bricks per row and you need 4 rows, you need 15 x 4 = 60 bricks.
-
Travel: Calculating distances. If you travel at a speed of 15 km/hour for 4 hours, you travel 15 x 4 = 60 km.
-
Finance: Calculating interest. While interest calculations are more complex, they are fundamentally based on multiplication.
These are only a few examples; multiplication is integral to various professions and everyday tasks. From simple daily calculations to complex scientific modeling, multiplication is an essential tool for navigating the quantitative aspects of our world.
Multiplication in Advanced Studies
The understanding of multiplication extends far beyond basic arithmetic. It forms the foundation for:
-
Algebra: Solving equations, manipulating expressions, and understanding functions all rely heavily on the principles of multiplication.
-
Calculus: Derivatives and integrals involve repeated multiplication and division, making multiplication a fundamental building block of calculus.
-
Linear Algebra: Matrix multiplication, a key aspect of linear algebra, expands the concept of multiplication to operate on arrays of numbers. This is crucial in computer graphics, physics simulations and many other applications.
-
Geometry: Calculating areas and volumes involves multiplication. For example, the area of a rectangle is length times width, a direct application of multiplication.
-
Statistics and Probability: Calculating probabilities and statistical measures often involves multiplying probabilities or frequencies.
These are just a few examples demonstrating the broad applicability of multiplication in advanced studies. A firm grasp of this fundamental operation is crucial for success in many academic disciplines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What if I forget the multiplication table? Don't worry! You can always use repeated addition, the distributive property, or long multiplication to find the answer.
-
Are there any shortcuts for multiplication? Yes, various shortcuts and tricks exist, depending on the numbers involved. Learning these can improve your calculation speed and efficiency.
-
Why is multiplication important? Multiplication is a fundamental operation that underlies numerous mathematical concepts and real-world applications. Mastering multiplication opens doors to more advanced mathematical understanding and problem-solving.
-
How can I improve my multiplication skills? Practice regularly using different methods and focusing on understanding the underlying concepts. Use flashcards, online games, and real-life applications to reinforce your learning.
Conclusion
The question "What is 15 times 4?" may seem trivial at first glance. However, exploring this seemingly simple problem reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and real-world applications. From the foundational principles of repeated addition to the sophisticated applications in advanced mathematics and various professions, multiplication stands as a cornerstone of quantitative understanding and problem-solving. Understanding not only that 15 times 4 equals 60, but why and how it does, is crucial for developing a solid foundation in mathematics and its diverse applications in life. This journey beyond the answer itself is what truly enriches our understanding of this fundamental operation and empowers us to tackle more complex mathematical challenges with confidence.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 15 Times 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.