What Is 2/3 Of 21
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
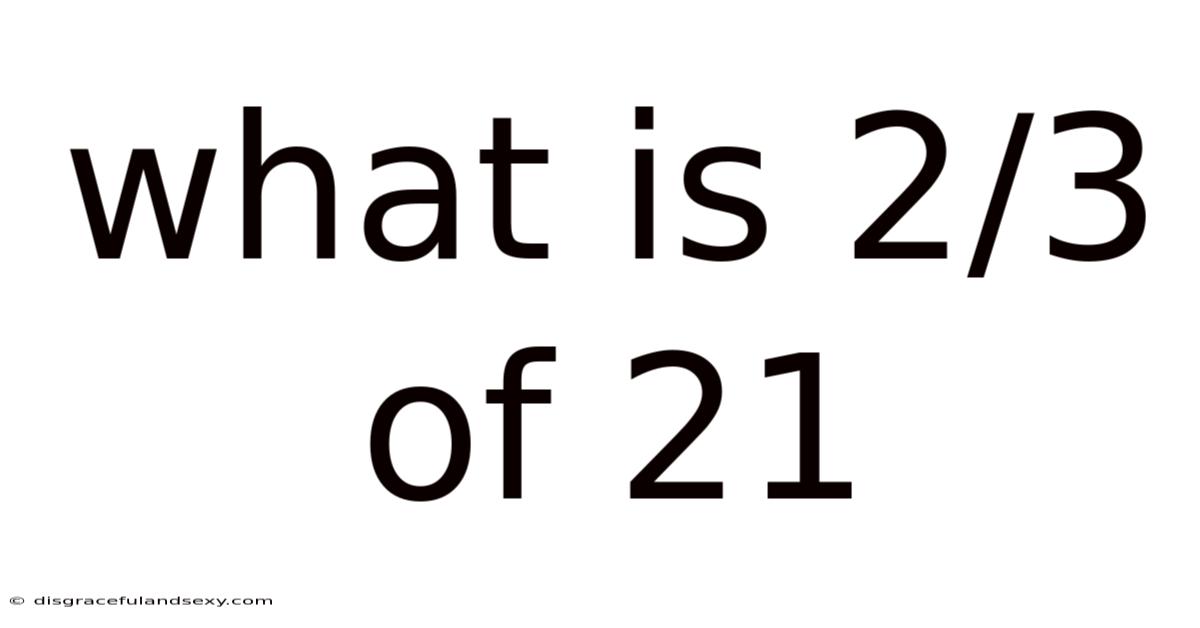
Table of Contents
What is 2/3 of 21? A Deep Dive into Fractions and Their Applications
Finding 2/3 of 21 might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, suitable only for elementary school students. However, understanding how to solve this seemingly basic question unlocks a deeper understanding of fractions, their practical applications, and their importance in various fields. This article will not only show you how to calculate 2/3 of 21 but will also explore the underlying concepts, provide different approaches to solving similar problems, and delve into the broader implications of fractional arithmetic.
Understanding Fractions: The Building Blocks of Calculation
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding 2/3 of 21, let's solidify our understanding of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts we have, while the denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into.
In our case, 2/3 represents two out of three equal parts. This means if we divide something into three equal pieces, 2/3 represents two of those pieces.
Method 1: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal
One straightforward way to find 2/3 of 21 is to convert the fraction 2/3 into its decimal equivalent. We do this by dividing the numerator (2) by the denominator (3):
2 ÷ 3 ≈ 0.6667 (we'll round to four decimal places for simplicity)
Now, we multiply this decimal by 21:
0.6667 x 21 ≈ 14
Therefore, 2/3 of 21 is approximately 14. Note that because we rounded the decimal, this is an approximation. The true answer, as we'll see later, is exactly 14.
Method 2: Using Multiplication Directly
Alternatively, we can solve this directly using multiplication. To find a fraction of a number, we multiply the fraction by the number. This can be expressed as:
(2/3) * 21
To perform this multiplication, we can rewrite 21 as a fraction with a denominator of 1:
(2/3) * (21/1)
Now, we multiply the numerators together and the denominators together:
(2 * 21) / (3 * 1) = 42/3
Finally, we simplify the resulting fraction by dividing the numerator by the denominator:
42 ÷ 3 = 14
So, 2/3 of 21 is exactly 14. This method avoids the approximation introduced by converting to a decimal.
Method 3: Understanding the Concept of "Of"
The word "of" in mathematical contexts often implies multiplication. So, "2/3 of 21" is equivalent to "(2/3) x 21". This understanding is crucial for solving various fraction problems. Consider the problem "What is 1/2 of 10?". This translates directly to (1/2) x 10 = 5. This emphasizes the importance of interpreting mathematical language correctly.
Real-World Applications of Fractional Calculations
The ability to calculate fractions isn't just an academic exercise. It's a fundamental skill used extensively in many aspects of daily life and various professions. Here are a few examples:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often involve fractional measurements. For example, a recipe might call for 2/3 cup of sugar or 1/4 teaspoon of salt. Understanding fractions is essential for accurate measurements and successful cooking.
-
Construction and Engineering: Fractions are vital in precise measurements and calculations in construction projects. Engineers rely on fractional calculations for designing structures and ensuring stability and safety.
-
Finance and Accounting: Fractions are used extensively in financial calculations, such as calculating interest rates, discounts, and profit margins. Understanding fractions is crucial for managing personal finances and business accounting.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Fractions are fundamental in statistical analysis. Representing proportions, probabilities, and sample sizes often involves fractions and their manipulation.
Further Exploring Fractions: Equivalent Fractions and Simplifying Fractions
Understanding equivalent fractions is crucial for efficient calculation. Equivalent fractions represent the same value but have different numerators and denominators. For example, 1/2, 2/4, and 3/6 are all equivalent fractions. They all represent one-half.
Simplifying fractions, also known as reducing fractions, involves finding an equivalent fraction with the smallest possible whole numbers for the numerator and denominator. This is achieved by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator and dividing both by it. For example, 42/3 can be simplified to 14/1, or simply 14. The GCD of 42 and 3 is 3, so we divide both by 3 to get 14.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if the fraction is an improper fraction (numerator larger than denominator)?
A: An improper fraction simply means you have more than one whole. You can convert it to a mixed number (a whole number and a fraction) or solve it directly using the multiplication method.
-
Q: How do I calculate a percentage of a number?
A: Percentages are simply fractions with a denominator of 100. For example, 50% is the same as 50/100, which simplifies to 1/2. To find a percentage of a number, convert the percentage to a decimal (by dividing by 100) and multiply by the number.
-
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with fractions?
A: Common mistakes include incorrectly multiplying or dividing numerators and denominators, forgetting to simplify fractions, and misunderstanding the concept of equivalent fractions.
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions – A Foundation for Mathematical Success
Calculating 2/3 of 21, while seemingly simple, provides a gateway to understanding the broader world of fractions. This article has demonstrated multiple approaches to solving this problem, highlighting the importance of both conceptual understanding and procedural fluency. Mastering fractional arithmetic isn't just about getting the right answer; it's about developing a deeper appreciation for the fundamental building blocks of mathematics and their widespread applications in various fields. By understanding fractions, you build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills. The ability to confidently work with fractions empowers you to tackle more complex challenges and opens doors to opportunities across numerous disciplines. From everyday tasks like cooking to complex engineering calculations, the versatility of fractional arithmetic makes it an essential skill for life-long learning and professional success.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 2/3 Of 21 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.