What Is 2 X 1
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
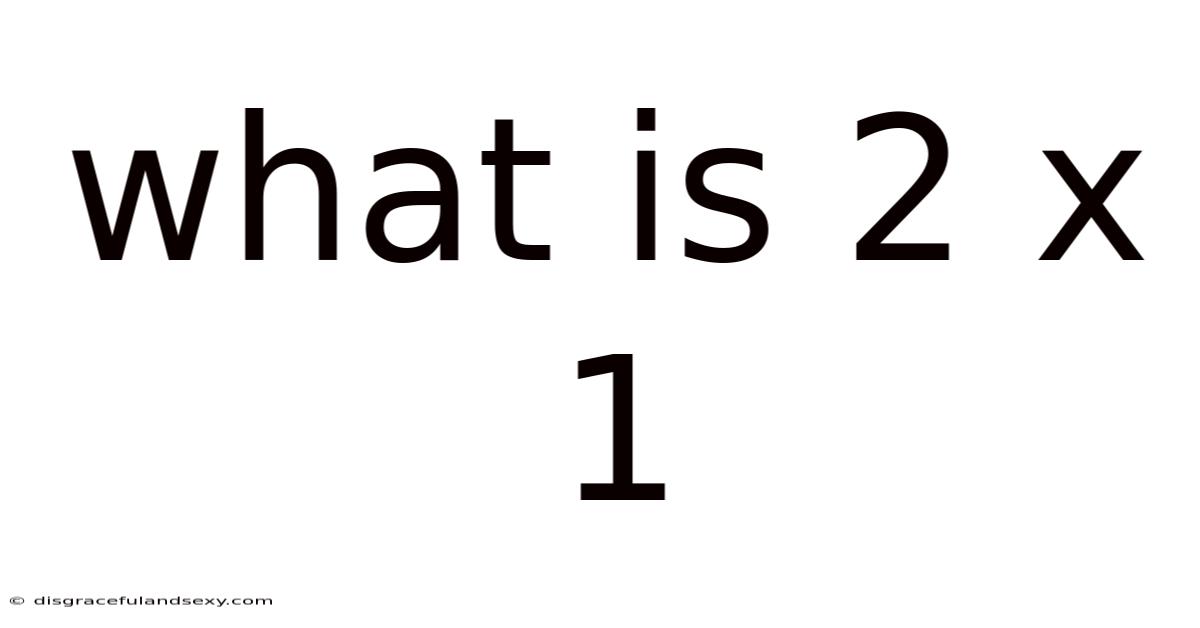
Table of Contents
What is 2 x 1? A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Fundamentals
The seemingly simple question, "What is 2 x 1?", opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts. While the answer – 2 – is readily apparent to most, exploring this fundamental equation allows us to delve into the core principles of multiplication, its applications, and its significance in various fields. This article will not only answer the question directly but also provide a comprehensive understanding of multiplication, its history, and its relevance in our daily lives.
Introduction: Understanding the Basics of Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, is a form of repeated addition. When we say 2 x 1, we are essentially asking: "What is the result of adding 1 to itself 2 times?" This can be visually represented as: 1 + 1 = 2. Therefore, 2 x 1 = 2. This simple equation lays the groundwork for understanding more complex multiplications. It introduces the concepts of multiplicand (the number being multiplied – in this case, 1), the multiplier (the number indicating how many times to add – 2), and the product (the result of the multiplication – 2).
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of 2 x 1
Let's break down the calculation of 2 x 1 in a methodical way, emphasizing the underlying principles:
-
Identify the Multiplier and Multiplicand: We have a multiplier of 2 and a multiplicand of 1.
-
Visual Representation: Imagine two groups, each containing one item. This visual representation immediately shows us a total of two items.
-
Repeated Addition: Add the multiplicand (1) to itself the number of times indicated by the multiplier (2): 1 + 1 = 2.
-
The Product: The result of this repeated addition, 2, is the product of the multiplication.
The Commutative Property and its Implications
A crucial aspect of multiplication is the commutative property. This property states that the order of the numbers in a multiplication equation does not affect the product. Therefore, 2 x 1 is equal to 1 x 2. Both equations result in a product of 2. Understanding the commutative property is vital for solving more complex multiplication problems and grasping algebraic concepts later on.
Expanding the Concept: Multiplication Beyond 2 x 1
While 2 x 1 provides a basic understanding, let's expand upon the concept by exploring related multiplications:
-
2 x 2: This is equivalent to 2 + 2 = 4. It shows the pattern of multiplication where increasing the multiplier increases the product.
-
2 x 3: This is 2 + 2 + 2 = 6. Continuing this pattern, we can see how multiplication efficiently represents repeated addition.
-
1 x 1: This represents a single group containing one item, resulting in a product of 1. This highlights the multiplicative identity property, where any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged.
-
0 x 1: This introduces the concept of multiplication with zero. Any number multiplied by zero equals zero. This is because we have zero groups of one item.
-
2 x 0: This further demonstrates the zero property of multiplication. Two groups of zero items still results in zero.
Multiplication in Different Contexts: Real-world Applications
Multiplication isn't confined to abstract mathematical exercises; it's a fundamental tool used in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple identical items. For instance, buying two apples at $1 each requires a simple 2 x 1 calculation.
-
Cooking: Doubling or tripling recipes. If a recipe calls for 1 cup of flour and you want to double it, you would need 2 x 1 cups.
-
Construction: Calculating the total amount of materials needed for a project.
-
Finance: Computing interest, calculating the total cost of goods with tax, and determining profits.
-
Science: Multiplying quantities in scientific experiments and calculations.
The History of Multiplication: A Journey Through Time
The concept of multiplication has ancient roots, evolving alongside the development of human civilization. Early civilizations, even without a formal system of mathematics as we know it, intuitively understood the principle of repeated addition in the context of counting objects or resources. The evolution of multiplication notation and algorithms took centuries, with various civilizations contributing to its development, including the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, and Indians. The development of symbolic notation, like the "x" symbol, significantly simplified and standardized the representation of multiplication, leading to more advanced mathematical breakthroughs.
Beyond the Basics: Connecting Multiplication to Other Mathematical Concepts
Understanding 2 x 1 opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts:
-
Division: Division is the inverse operation of multiplication. If 2 x 1 = 2, then 2 ÷ 1 = 2 and 2 ÷ 2 = 1.
-
Algebra: Multiplication is foundational to algebraic equations and manipulations. Understanding multiplication helps solve for unknowns in algebraic expressions.
-
Geometry: Calculating areas and volumes involves multiplication. The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length and width.
-
Calculus: Multiplication is used extensively in calculus, forming the basis of concepts such as derivatives and integrals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is 2 x 1 important?
A: While seemingly simple, 2 x 1 is a foundational concept that underpins more complex mathematical operations. It demonstrates the basic principles of multiplication and sets the stage for learning advanced concepts.
Q: What happens if I multiply 2 x 1 by another number?
A: Multiplying the product (2) by another number simply extends the multiplication process. For example, (2 x 1) x 3 = 6.
Q: Are there different ways to represent 2 x 1?
A: Yes, 2 x 1 can be represented in various ways: using dots, lines, or other visual aids to show repeated addition. It can also be expressed as 2(1), where parentheses imply multiplication.
Q: Is multiplication always about repeated addition?
A: While repeated addition is a useful way to understand multiplication at its most basic level, particularly with whole numbers, the concept expands into other mathematical contexts involving fractions, decimals, and even complex numbers, where the notion of repeated addition may become less intuitive.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Equation
The seemingly simple equation, 2 x 1 = 2, holds a profound significance in the realm of mathematics and beyond. It’s a gateway to understanding multiplication, its applications, and its interconnectedness with other mathematical concepts. From basic arithmetic to complex calculations, the principles demonstrated by this simple equation serve as a cornerstone of mathematical literacy and problem-solving. Mastering this fundamental concept empowers us to approach more challenging mathematical problems with confidence and proficiency. The journey from a simple calculation to a deeper understanding of its implications highlights the power of mathematical exploration and the beauty of numerical relationships.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 2 X 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.