What Is 3/2 Times 2
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
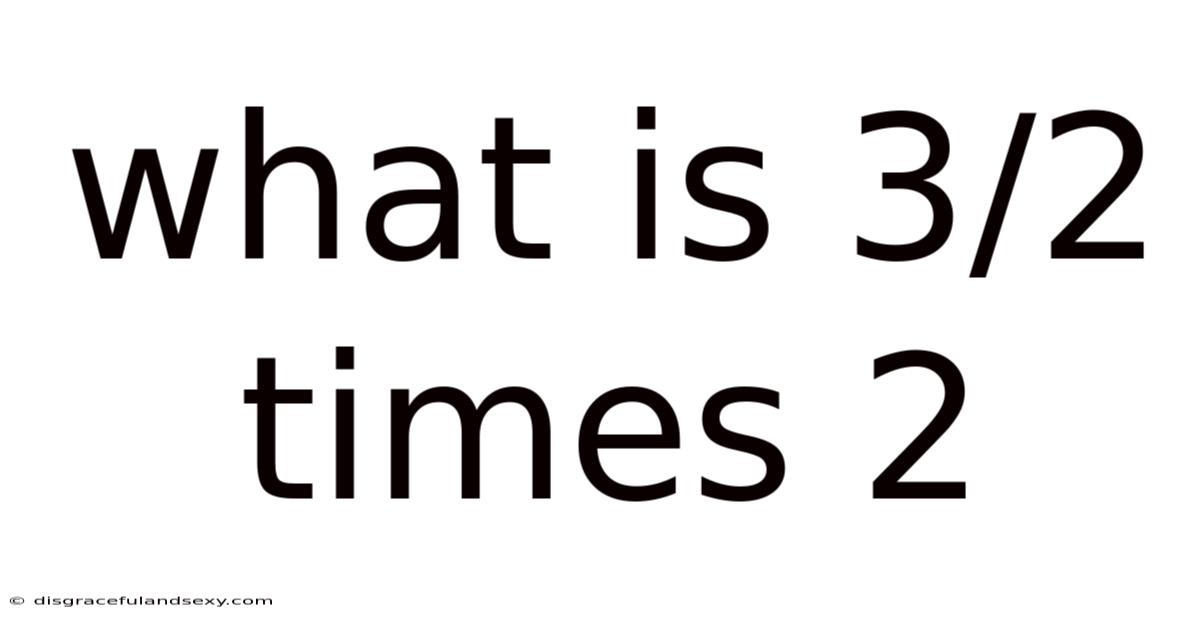
Table of Contents
What is 3/2 Times 2? A Deep Dive into Fraction Multiplication
This seemingly simple question, "What is 3/2 times 2?", offers a wonderful opportunity to explore fundamental concepts in mathematics, specifically fraction multiplication and its practical applications. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the why behind the calculation is crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation. This article will delve into the process of multiplying fractions, explore different approaches to solving this problem, and delve into the broader context of fraction arithmetic.
Introduction: Understanding Fractions and Multiplication
A fraction, like 3/2, represents a part of a whole. The top number (3) is the numerator, indicating the number of parts we have, and the bottom number (2) is the denominator, indicating the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into. In this case, 3/2 represents one and a half.
Multiplication, in its simplest form, represents repeated addition. When we say 2 x 3, we mean 2 added to itself three times (2 + 2 + 2 = 6). However, multiplying fractions introduces a slightly different perspective. Instead of repeated addition, we're essentially finding a fraction of a fraction or a part of a part.
Methods for Solving 3/2 x 2
There are several ways to solve 3/2 x 2, each offering a slightly different insight into the underlying mathematical principles.
Method 1: Direct Multiplication of Numerator and Denominator
The most straightforward method involves multiplying the numerators together and then multiplying the denominators together. In this case:
(3/2) x 2 = (3 x 2) / (2 x 1) = 6/2
This simplifies to 3. Therefore, 3/2 times 2 equals 3.
Method 2: Canceling Common Factors (Simplification Before Multiplication)
Before multiplying, we can simplify the expression by canceling out common factors between the numerator and the denominator. Notice that there's a '2' in both the numerator (implicitly as 2/1) and the denominator. We can cancel these out:
(3/2) x (2/1) = 3/1 = 3
This method highlights the principle of simplification, which makes calculations easier and prevents dealing with larger numbers. It’s a crucial skill in more complex fraction problems.
Method 3: Visual Representation using Area Models
A visual approach can significantly enhance understanding, particularly for beginners. Imagine a rectangle representing the whole. Divide this rectangle into two equal parts (the denominator of 3/2). Shade three of these parts (the numerator of 3/2). This represents 3/2.
Now, we multiply by 2. This means we take two of the sets we just created. Visually, you would have two rectangles, each with three-halves shaded. Combining these two, you’ll see you have a total of six halves, which simplifies to three whole rectangles. This reinforces that (3/2) x 2 = 3.
Method 4: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal
Another approach involves converting the fraction to its decimal equivalent before multiplying. 3/2 is equal to 1.5. Therefore:
1.5 x 2 = 3
This method is useful when dealing with fractions that are easily converted to decimals, and it connects fraction arithmetic with decimal arithmetic. However, this method sometimes leads to rounding errors with more complex fractions that have repeating decimals.
The Importance of Understanding the "Why"
It's not enough to simply know that 3/2 x 2 = 3. It's crucial to understand why this is the case. This understanding is essential for solving more complex problems involving fractions, decimals, and other mathematical concepts. By mastering the fundamentals of fraction multiplication, you build a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Expanding the Concept: More Complex Fraction Multiplication
The principles discussed above extend to more complex scenarios. Let's look at an example:
What is (5/3) x (6/7)?
Using the direct multiplication method:
(5/3) x (6/7) = (5 x 6) / (3 x 7) = 30/21
Now, we simplify by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 30 and 21, which is 3:
30/21 = (30 ÷ 3) / (21 ÷ 3) = 10/7
This result, 10/7, can be expressed as a mixed number (1 and 3/7) or a decimal (approximately 1.43). The process remains the same: multiply the numerators, multiply the denominators, and then simplify.
Real-World Applications of Fraction Multiplication
Fraction multiplication isn't confined to the classroom; it appears frequently in everyday life:
- Cooking: Scaling recipes up or down requires fraction multiplication. If a recipe calls for 1/2 cup of flour, and you want to double it, you multiply 1/2 by 2.
- Construction: Calculating materials needed for a project often involves fractions. Determining the amount of wood needed for a project, considering fractional measurements, requires accurate fraction multiplication.
- Finance: Calculating percentages, interest rates, and discounts frequently involves fraction multiplication (percentages are simply fractions expressed as a hundredth).
- Science: Numerous scientific calculations, particularly in chemistry and physics, utilize fractions and require multiplying them accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What if one of the numbers isn't a fraction? Treat the whole number as a fraction with a denominator of 1. For example, 2 can be written as 2/1. Then apply the standard fraction multiplication rules.
-
What if the result is an improper fraction (numerator is larger than denominator)? Convert the improper fraction to a mixed number (a whole number and a fraction) for easier interpretation. For example, 10/7 is equal to 1 and 3/7.
-
Why is canceling common factors important? Canceling common factors simplifies the calculations, reduces the risk of errors, and leads to a simplified answer. It’s a core principle of simplifying algebraic expressions as well.
-
Can I use a calculator for fraction multiplication? Yes, most calculators can handle fraction multiplication directly, but understanding the underlying principles remains crucial for problem-solving.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Multiplication
Understanding fraction multiplication is a cornerstone of mathematical literacy. This article has explored various methods to solve 3/2 times 2, emphasizing the importance of grasping the fundamental concepts behind the calculations. By mastering these principles, you not only solve problems efficiently but also develop a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts. Remember to practice regularly and explore different methods to solidify your understanding. The more comfortable you become with fraction multiplication, the more confident you'll be when tackling more complex mathematical problems. It's a skill that will serve you well throughout your educational journey and in many aspects of your life.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 3/2 Times 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.