What Is 31 / 5
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 5 min read
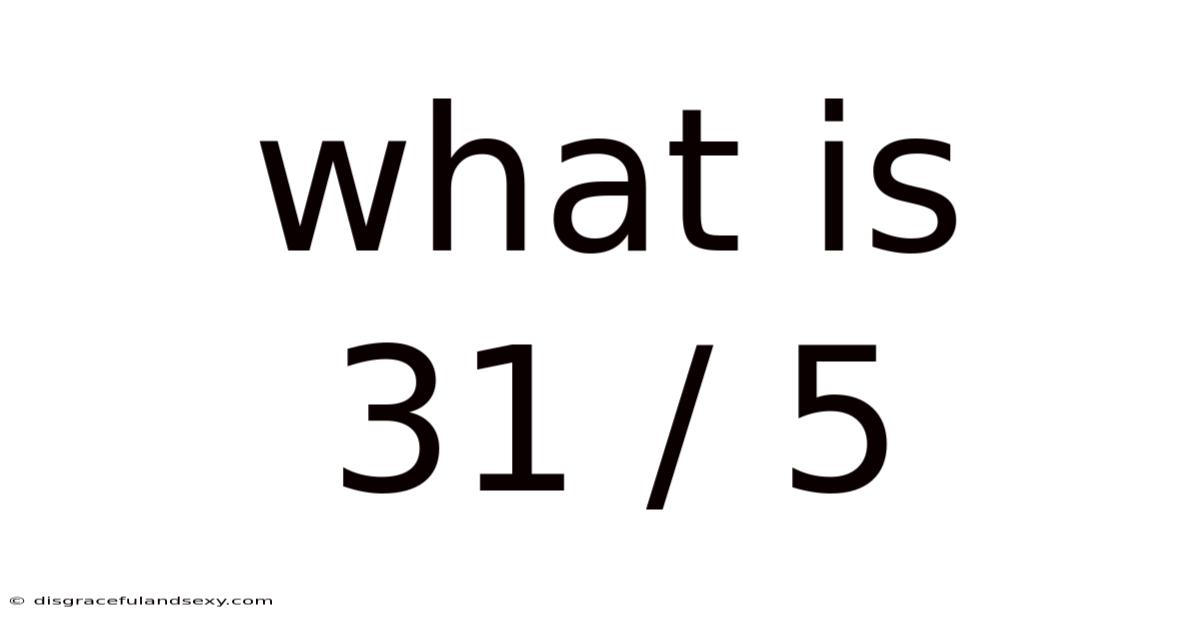
Table of Contents
Decoding 31/5: A Deep Dive into Division and Beyond
What is 31 divided by 5? This seemingly simple question opens the door to a fascinating exploration of division, fractions, decimals, and even the broader concepts of number systems and mathematical operations. This article will not only provide the answer but will delve into the "why" behind the calculation, exploring different methods and connecting the solution to more advanced mathematical ideas.
Introduction: Understanding Division
Division is one of the four fundamental arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It essentially involves splitting a quantity into equal parts. In the case of 31/5, we're asking how many times 5 fits into 31. The result will tell us the number of whole groups of 5 and any remaining amount that doesn't form a complete group. This remaining amount is known as the remainder.
Method 1: Long Division
The most traditional way to solve 31/5 is using long division. This method allows us to systematically break down the division process, revealing both the quotient (the result of the division) and the remainder.
-
Set up: Write 31 inside the long division symbol (÷) and 5 outside.
-
Divide: How many times does 5 go into 3? It doesn't, so we move to the next digit. How many times does 5 go into 31? It goes in 6 times (6 x 5 = 30).
-
Multiply: Multiply the quotient (6) by the divisor (5): 6 x 5 = 30.
-
Subtract: Subtract the result (30) from the dividend (31): 31 - 30 = 1.
-
Remainder: The remainder is 1.
Therefore, 31 divided by 5 is 6 with a remainder of 1. This can be written as 6 R1.
Method 2: Repeated Subtraction
Another approach is repeated subtraction. We repeatedly subtract the divisor (5) from the dividend (31) until we reach a number less than the divisor. The number of times we subtract represents the quotient, and the remaining number is the remainder.
31 - 5 = 26 26 - 5 = 21 21 - 5 = 16 16 - 5 = 11 11 - 5 = 6 6 - 5 = 1
We subtracted 5 six times before reaching a remainder of 1. Thus, the result is again 6 R1.
Method 3: Converting to a Mixed Number (Fraction)
The result of 6 R1 can be expressed more formally as a mixed number. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction. The whole number is the quotient (6), and the fraction represents the remainder (1) over the divisor (5).
Therefore, 31/5 = 6 ¹/₅
This representation shows that 31 contains six complete groups of 5, plus one-fifth of another group.
Method 4: Converting to a Decimal
We can also express the result as a decimal. To do this, we continue the division process beyond the remainder. We add a decimal point and a zero to the remainder (1), making it 10.
- Divide 10 by 5: 10 / 5 = 2
This gives us an additional 0.2. Therefore, 31/5 = 6.2
This decimal representation accurately represents the portion of the whole that the remainder represents.
The Scientific Explanation: Understanding Remainders and Fractions
Mathematically, the remainder arises because the dividend (31) is not perfectly divisible by the divisor (5). The remainder signifies the "leftover" portion that cannot be equally divided into groups of 5. This leftover part is crucial in understanding fractions.
A fraction (like ¹/₅) represents a part of a whole. The numerator (1) indicates the number of parts we have, and the denominator (5) represents the total number of parts that make up the whole. The fraction ¹/₅ indicates that we have one part out of five equal parts. In the context of 31/5, the fraction ¹/₅ represents the remainder as a proportion of the divisor.
The decimal representation (6.2) is essentially a more compact way of expressing the mixed number (6 ¹/₅). It signifies that we have 6 whole units and 2 tenths of another unit. This demonstrates the relationship between fractions and decimals: they are different ways to represent the same numerical value.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What if the remainder was zero? If the remainder was zero, it would mean that the dividend is perfectly divisible by the divisor. For instance, 30/5 = 6, with no remainder.
-
Why are there multiple ways to represent the answer? Different representations (mixed number, decimal, remainder) offer various perspectives on the result. The best representation depends on the specific context and the desired level of precision. Sometimes a remainder is sufficient, while other times a decimal or fraction is necessary for more accurate calculations.
-
Can I use a calculator? Yes, a calculator provides a quick and easy way to find the answer (6.2). However, understanding the underlying methods is essential for grasping the mathematical concepts involved.
-
How does this relate to other mathematical concepts? The principles of division and remainders are fundamental to many areas of mathematics, including modular arithmetic, number theory, and even more advanced topics like abstract algebra.
Conclusion: Beyond the Numbers
Solving 31/5 is more than just obtaining the answer 6.2. It's about understanding the process, exploring different methodologies, and appreciating the intricate relationships between division, fractions, decimals, and remainders. The journey to find the solution offers a glimpse into the elegance and power of mathematical concepts, building a strong foundation for further exploration in the world of numbers. The seemingly simple question, "What is 31/5?", unveils a rich tapestry of mathematical ideas that extend far beyond the immediate answer. This deeper understanding is what transforms a simple calculation into a meaningful learning experience.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 31 / 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.