What Is Cos Pi 2
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
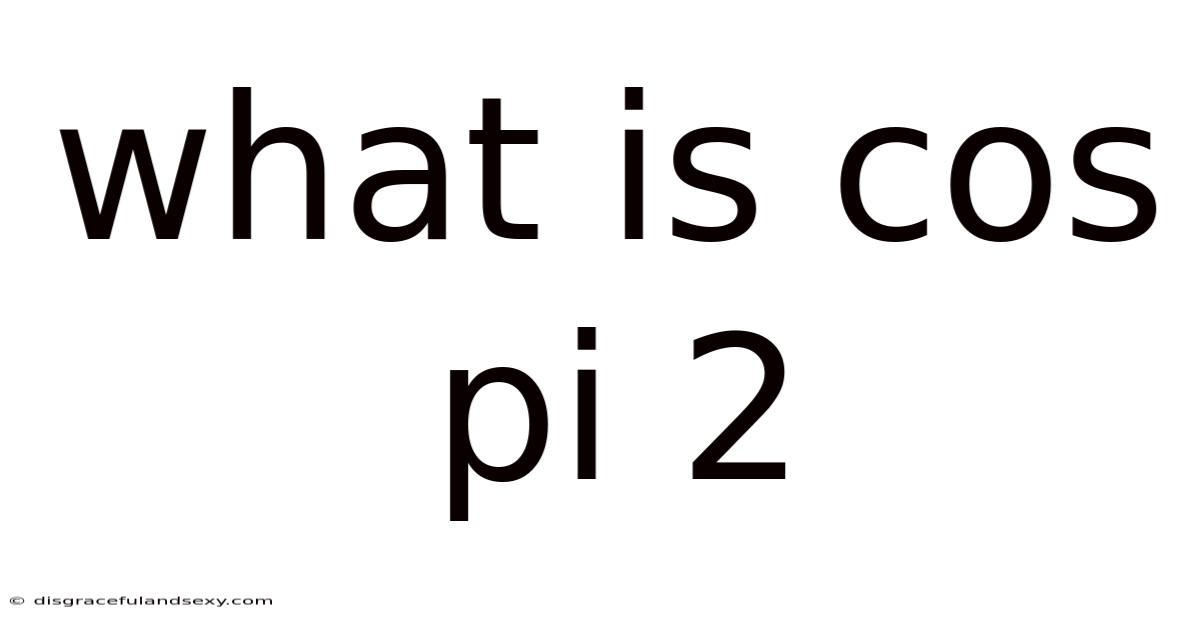
Table of Contents
What is cos π/2? Unraveling the Mystery of Trigonometric Functions
Understanding the value of cos π/2 is fundamental to grasping trigonometry. This seemingly simple question opens the door to a deeper understanding of trigonometric functions, their relationships, and their applications in various fields like physics, engineering, and computer science. This comprehensive guide will not only answer "What is cos π/2?" but also delve into the underlying principles, provide visual representations, and explore related concepts.
Introduction: A Journey into the World of Trigonometry
Trigonometry, at its core, studies the relationships between angles and sides of triangles. It expands beyond triangles, however, to describe cyclical patterns and oscillations found in numerous natural phenomena. The trigonometric functions – sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan) – are the fundamental building blocks of this field. These functions, when applied to an angle, provide ratios related to the lengths of sides in a right-angled triangle. Understanding their behavior, especially at specific angles like π/2 (which is 90 degrees in degrees), is crucial. This article will focus on the cosine function and its value at π/2 radians.
Understanding Angles in Radians and Degrees
Before diving into the calculation, it's essential to understand the two common units for measuring angles: degrees and radians. Degrees are a familiar unit, dividing a circle into 360 equal parts. Radians, on the other hand, are based on the radius of a circle. One radian is defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius. The conversion between radians and degrees is:
- 180 degrees = π radians
Therefore, π/2 radians is equivalent to (π/2) * (180/π) = 90 degrees.
Defining the Cosine Function
The cosine function, denoted as cos(θ), where θ represents the angle, is defined in the context of a right-angled triangle as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
- cos(θ) = Adjacent side / Hypotenuse
However, the cosine function's definition extends beyond right-angled triangles. It can be represented using the unit circle, a circle with a radius of 1. In this context, for any angle θ, the x-coordinate of the point where the terminal side of the angle intersects the unit circle is equal to cos(θ).
Visualizing cos π/2 using the Unit Circle
Imagine the unit circle centered at the origin (0,0) of a Cartesian coordinate system. An angle of π/2 radians (90 degrees) starts from the positive x-axis and rotates counter-clockwise by 90 degrees. The point where the terminal side of this angle intersects the unit circle lies on the positive y-axis. The x-coordinate of this point is 0. Since the x-coordinate represents cos(θ), we can conclude that:
- cos(π/2) = 0
Mathematical Proof: Deriving cos π/2
While the unit circle provides a visual understanding, a rigorous mathematical proof can be derived using the trigonometric identities and limits. One approach involves using the Taylor series expansion of the cosine function:
cos(x) = 1 - x²/2! + x⁴/4! - x⁶/6! + ...
Substituting x = π/2, we get an infinite series:
cos(π/2) = 1 - (π/2)²/2! + (π/2)⁴/4! - (π/2)⁶/6! + ...
Although this series converges to 0, it's computationally intensive to achieve high accuracy. A simpler approach leverages the relationship between cosine and sine functions:
- sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1
At θ = π/2, we know that sin(π/2) = 1. Substituting this into the identity:
1² + cos²(π/2) = 1
Solving for cos(π/2), we get:
cos²(π/2) = 0
Therefore,
- cos(π/2) = 0
Applications of cos π/2 in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly simple value of cos π/2 has significant implications in various fields:
-
Physics: In oscillatory motion (like a pendulum or a spring), the cosine function describes the displacement from equilibrium. At π/2 radians (90 degrees) in the cycle, the displacement is zero, representing the point where the object changes its direction of motion.
-
Engineering: Cosine functions are fundamental in signal processing and AC circuit analysis. Understanding cos(π/2) helps in calculating instantaneous values of voltage and current.
-
Computer Graphics and Animation: Cosine functions are employed extensively in creating smooth curves and animations. The value at π/2 often signifies a transition point or a change in direction within the animation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between cos(π/2) and cos(90°)?
A: There is no difference. π/2 radians and 90 degrees represent the same angle.
-
Q: Is cos(π/2) always 0, regardless of the units used (degrees or radians)?
A: Yes, as long as the angle is equivalent to 90 degrees.
-
Q: How can I calculate cos(π/2) using a calculator?
A: Most scientific calculators will directly compute cos(π/2) by entering the value in radians mode. Ensure your calculator is set to radians, not degrees, before calculating.
-
Q: Are there any other angles where the cosine function is 0?
A: Yes, the cosine function is 0 at odd multiples of π/2. For example, cos(3π/2), cos(5π/2), etc., all equal 0.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of Trigonometry
Understanding the value of cos π/2 is a cornerstone of trigonometric knowledge. This article not only provided the answer (0) but also explored the underlying concepts, used visual aids, and presented mathematical proofs. Moreover, we highlighted the practical applications of this fundamental trigonometric value in various fields. By grasping these principles, you lay a strong foundation for further exploration of more complex trigonometric concepts and their applications in diverse areas of science, engineering, and technology. The journey into the world of trigonometry begins with understanding seemingly simple yet crucial concepts like this one, paving the way for a deeper comprehension of the broader mathematical landscape.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Cos Pi 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.