What Is Half Of 130
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
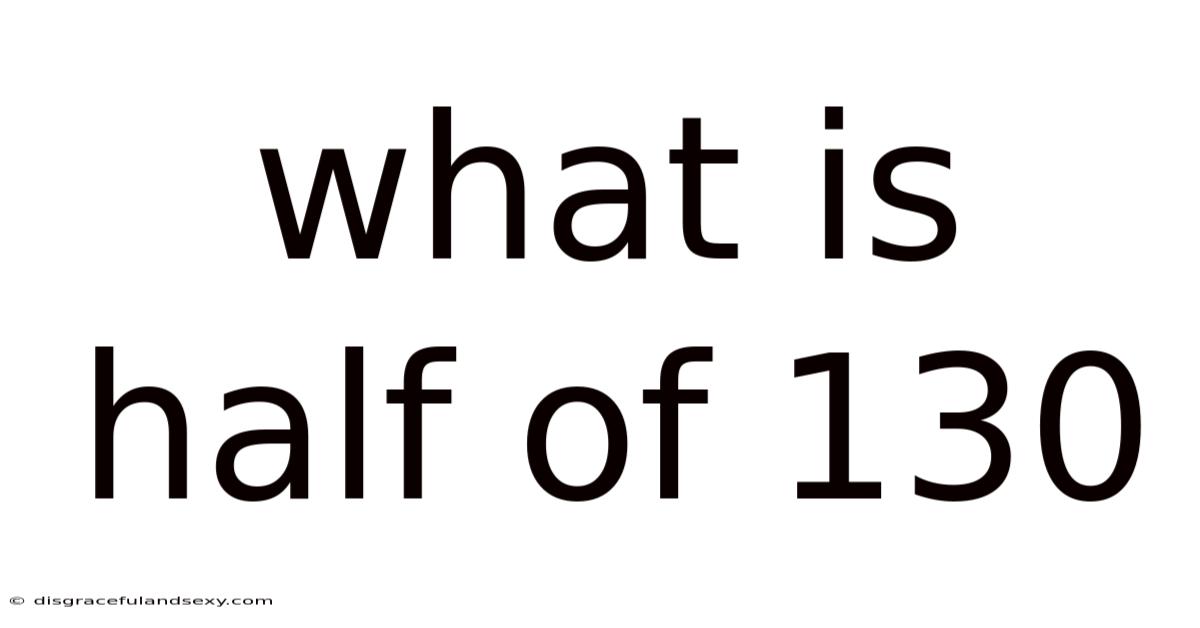
Table of Contents
What is Half of 130? A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
Finding half of a number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications in everyday life and advanced studies. This seemingly simple question, "What is half of 130?", opens the door to exploring the broader world of division, fractions, and their practical uses. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the underlying mathematical principles, explore different methods of calculation, and highlight real-world examples where understanding halves is essential.
Understanding the Concept of Halves
Before we jump into calculating half of 130, let's clarify the concept of "half." A half represents one of two equal parts of a whole. If you divide something into two identical pieces, each piece is one-half (or 1/2) of the original whole. This concept is directly related to the mathematical operation of division. Finding half of a number is the same as dividing that number by 2.
Calculating Half of 130: The Simple Approach
The most straightforward method to find half of 130 is to perform the division: 130 ÷ 2. Using long division or a calculator, we find that:
130 ÷ 2 = 65
Therefore, half of 130 is 65.
Alternative Methods: Fractions and Decimal Representation
While division is the most direct method, we can also approach this problem using fractions and decimal representations.
- Fractions: Finding half of a number is equivalent to multiplying the number by the fraction 1/2. So, half of 130 can be calculated as:
(1/2) * 130 = 130/2 = 65
- Decimals: The fraction 1/2 is also equal to the decimal 0.5. Therefore, we can calculate half of 130 by multiplying it by 0.5:
0.5 * 130 = 65
All three methods – division, fractions, and decimal multiplication – yield the same result: 65. This consistency underscores the interconnectedness of these mathematical concepts.
Beyond the Basics: Expanding the Understanding of Division
The seemingly simple act of finding half of 130 provides a stepping stone to understanding more complex division problems. Let's explore some related concepts:
-
Dividing larger numbers: The same principle applies to larger numbers. To find half of any even number, simply divide it by 2. For odd numbers, the result will be a decimal or a fraction representing the half-value.
-
Dividing by fractions: Dividing by a fraction is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. For example, finding one-third of 130 would involve dividing 130 by 1/3, which is the same as multiplying 130 by 3 (the reciprocal of 1/3). This results in 390.
-
Percentage calculations: Understanding halves is crucial for working with percentages. Half is equivalent to 50%. Therefore, finding 50% of a number is the same as finding its half.
Real-World Applications: Where Halves Matter
The concept of finding half appears frequently in various real-world scenarios:
-
Sharing equally: If you have 130 candies and want to share them equally between two friends, each friend receives half, or 65 candies.
-
Measurement and Conversion: Many measurement systems rely on halves. For instance, converting yards to feet involves understanding that one yard is equal to three feet, and half a yard is 1.5 feet.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often call for half of an ingredient's quantity. Understanding halves is essential for accurate measurements in cooking and baking.
-
Finance and Budgeting: Halving budgets or splitting expenses evenly among individuals requires understanding this fundamental mathematical concept.
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning: Finding the midpoint of a line segment or dividing shapes into equal halves necessitates the application of division by 2.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Calculating the median (middle value) of a dataset often involves finding the half-way point.
-
Computer Science and Programming: Many programming algorithms involve dividing data sets or performing calculations that rely on the concept of halving.
Understanding Fractions: A Deeper Dive
The concept of "half" is intrinsically linked to fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. The fraction 1/2 signifies one part out of two equal parts. Understanding fractions is crucial for advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Equivalent Fractions: Multiple fractions can represent the same value. For example, 1/2, 2/4, 3/6, and 4/8 are all equivalent fractions, representing the same half.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Fractions can be simplified by dividing both the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number) by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For instance, the fraction 10/20 can be simplified to 1/2 by dividing both numbers by 10.
-
Adding and Subtracting Fractions: Adding and subtracting fractions require a common denominator. For example, to add 1/2 and 1/4, we would first find a common denominator (4) and then add the equivalent fractions: 2/4 + 1/4 = 3/4.
-
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions: Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators together and the denominators together. Dividing fractions involves multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
Exploring Decimal Representation
Decimal representation provides another way to understand halves and fractions. The decimal 0.5 is equivalent to the fraction 1/2. Understanding decimals is important for:
-
Decimal to Fraction Conversion: Converting a decimal to a fraction involves writing the decimal as a fraction with a power of 10 as the denominator and then simplifying the fraction. For example, 0.75 can be written as 75/100, which simplifies to 3/4.
-
Fraction to Decimal Conversion: Converting a fraction to a decimal involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. For example, 1/4 is equal to 0.25.
-
Decimal Arithmetic: Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing decimals follows the same rules as whole numbers, but with careful attention to decimal points.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is half of an odd number?
A: Half of an odd number will always result in a decimal or a fraction. For example, half of 13 is 6.5 or 13/2.
Q: How do I calculate half of a number quickly without a calculator?
A: For even numbers, divide the number by 2. For odd numbers, you can divide the closest even number by 2 and then adjust accordingly (add 0.5 to the result).
Q: Are there any real-world examples where understanding halves is critical?
A: Yes, numerous situations rely on the understanding of halves, such as sharing resources equally, recipe scaling in cooking, and financial budgeting. Even in advanced fields like computer science, algorithms often utilize the concept of halving (e.g., binary search).
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Halves
The seemingly simple question, "What is half of 130?" serves as a gateway to exploring fundamental mathematical concepts. Understanding halves involves not only performing a basic division but also grasping the interconnectedness of division, fractions, decimals, and their numerous applications in daily life and advanced fields. By mastering these concepts, you equip yourself with crucial problem-solving skills applicable across various disciplines. The ability to accurately and efficiently calculate halves forms a cornerstone of mathematical literacy and practical problem-solving abilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Half Of 130 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.