X 1 Times X 1
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
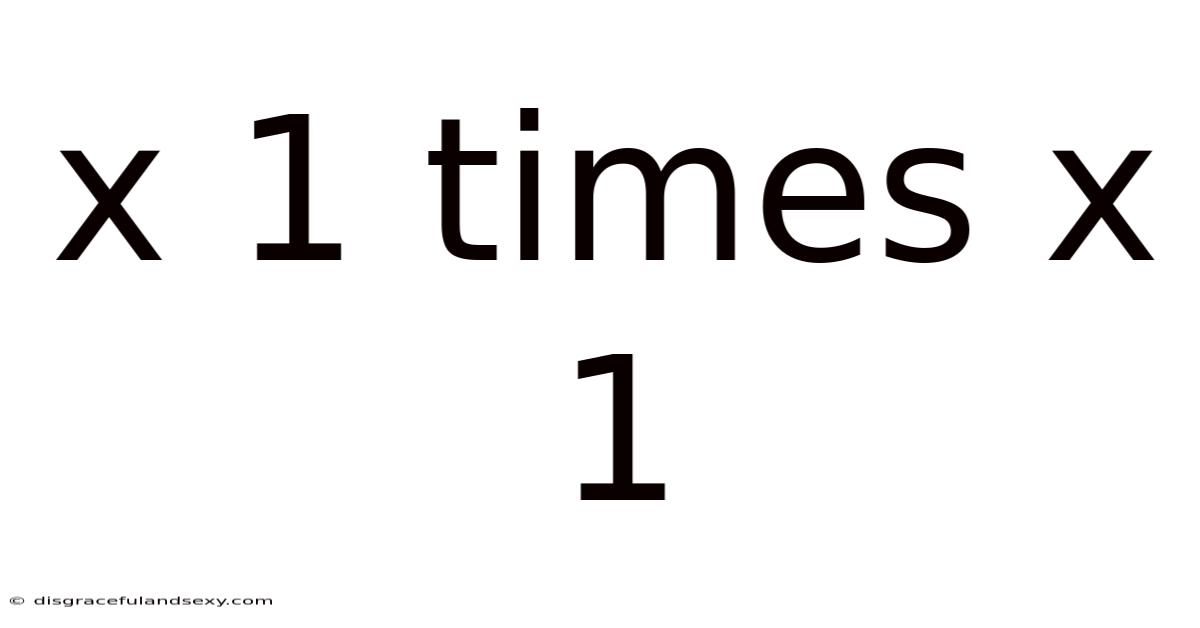
Table of Contents
Understanding the Fundamental Concept: x 1 Times x 1
This article delves into the seemingly simple yet profoundly important mathematical concept of "x 1 times x 1," exploring its various interpretations, applications, and implications across different mathematical fields. While the statement might appear trivial at first glance, its underlying principles form the bedrock of more complex algebraic manipulations, geometric constructions, and even advanced concepts in calculus and beyond. Understanding this fundamental operation is crucial for building a solid foundation in mathematics.
Introduction: Beyond the Obvious
At its most basic level, "x 1 times x 1" signifies the multiplication of a variable, x, by itself once. This translates to x² (x squared) or x to the power of 2. The simplicity of this equation, however, belies its significance. This operation isn't just about finding a numerical answer; it represents a powerful concept with far-reaching consequences in numerous areas of mathematics and beyond.
This article aims to unpack this seemingly simple mathematical expression, exploring its different facets, practical applications, and its role in the broader mathematical landscape. We will delve into the following aspects:
- The Fundamental Operation of Multiplication: Revisiting the core principles of multiplication and its application to algebraic expressions.
- Understanding Exponents and Powers: Exploring the concept of exponents and how they relate to repeated multiplication.
- Geometric Interpretation of x²: Visualizing x² through the lens of geometry and area calculation.
- Algebraic Applications of x²: Utilizing x² in solving equations, simplifying expressions, and performing algebraic manipulations.
- Applications in Calculus and Beyond: Briefly touching upon the role of x² in calculus and other advanced mathematical concepts.
- Real-World Applications: Exploring how this simple concept finds its way into real-world problems and scenarios.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Addressing common queries and misconceptions related to x² and its implications.
The Fundamental Operation of Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, is repeated addition. When we say 3 times 4, we mean 4 added to itself three times (4 + 4 + 4 = 12). Similarly, when we multiply a variable x by 1, we're essentially saying "add x to itself one time," which results in x. However, when we say x 1 times x 1, we're performing the multiplication x * x, which is expressed as x².
This seemingly simple shift from adding x once to multiplying x by itself has profound consequences in the complexity and application of the resulting expression.
Understanding Exponents and Powers
The expression x² introduces the concept of exponents or powers. The small '2' written above and to the right of the x is called the exponent, indicating how many times the base (x) is multiplied by itself. In this case, the exponent is 2, signifying that x is multiplied by itself twice. This concept extends beyond 2; we can have x³, x⁴, and so on, representing x multiplied by itself three times, four times, and so on, respectively. This powerful notation allows us to express repeated multiplication concisely and elegantly.
Geometric Interpretation of x²
The expression x² can be visually interpreted geometrically. Imagine a square with sides of length x. The area of this square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the length of the other side, which is x * x = x². Thus, x² represents the area of a square with sides of length x. This geometric interpretation provides a valuable visual understanding of the concept and its applications. For instance, if x represents 5 units, then x² represents the area of a square with sides of 5 units, resulting in an area of 25 square units.
Algebraic Applications of x²
The expression x² plays a crucial role in various algebraic manipulations and equation-solving techniques. It appears frequently in:
- Quadratic Equations: These equations involve x², and solving them often involves techniques like factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula.
- Polynomial Expressions: x² is a fundamental component of polynomial expressions, which are sums of terms involving variables raised to non-negative integer powers.
- Expanding and Simplifying Expressions: Understanding how to expand and simplify expressions involving x² is essential for manipulating algebraic expressions efficiently. For instance, (x+2)² expands to x² + 4x + 4.
- Graphing Parabolas: The equation y = x² represents a parabola, a U-shaped curve. Understanding the properties of x² is crucial for sketching and analyzing parabolas.
Applications in Calculus and Beyond
The concept of x² extends far beyond basic algebra. In calculus, it plays a crucial role in:
- Derivatives and Integrals: Finding the derivative of x² is a fundamental calculation in differential calculus, resulting in 2x. Similarly, integrating x² is also a common operation in integral calculus.
- Optimization Problems: x² often appears in optimization problems where we need to find the maximum or minimum value of a function.
Real-World Applications
The seemingly abstract concept of x² has numerous practical applications in the real world:
- Area Calculations: As mentioned before, x² directly represents the area of a square. This applies to various real-world scenarios involving area calculations, such as determining the area of a square room, a square plot of land, or a square-shaped object.
- Physics: x² appears in numerous physics equations, often representing distance, area, or other physical quantities. For instance, in projectile motion, the horizontal distance traveled by an object is often related to time squared.
- Engineering: Engineers utilize x² in various calculations, including structural design, fluid dynamics, and other engineering disciplines.
- Computer Science: The concept of x² is fundamental to many algorithms and data structures in computer science.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between x and x²?
A: x represents a single instance of the variable, while x² represents x multiplied by itself. Think of it as the difference between having one apple (x) and having the area of a square with sides of length x (x²).
Q: Can x² ever be negative?
A: If x is a real number, x² will always be non-negative (greater than or equal to zero). This is because the product of two identical numbers (positive or negative) is always positive. However, if x is a complex number, x² can be negative.
Q: What is the significance of x² in quadratic equations?
A: The presence of x² defines a quadratic equation. It determines the parabolic shape of the graph and influences the solution methods used to find the roots (values of x that make the equation equal to zero).
Q: How does x² relate to other powers like x³ or x⁴?
A: All these are examples of exponents or powers. They represent repeated multiplication of the base (x). x³ means x * x * x, x⁴ means x * x * x * x, and so on. They form a progression of powers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of a Simple Concept
While seemingly simple, "x 1 times x 1" (or x²) represents a fundamental concept that underpins a vast expanse of mathematical understanding and application. From basic algebra to advanced calculus and real-world problem-solving, its significance cannot be overstated. Understanding this core principle lays a crucial foundation for mastering more complex mathematical concepts and unlocking the power of mathematical reasoning. Its seemingly simple nature belies its profound impact on our ability to model and understand the world around us. Grasping this concept thoroughly empowers us to tackle more intricate mathematical challenges with confidence and clarity. The journey from understanding x² to mastering more advanced mathematical principles begins with a solid understanding of this fundamental building block.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 1 Times X 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.