X 2 12x 36 Factor
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 6 min read
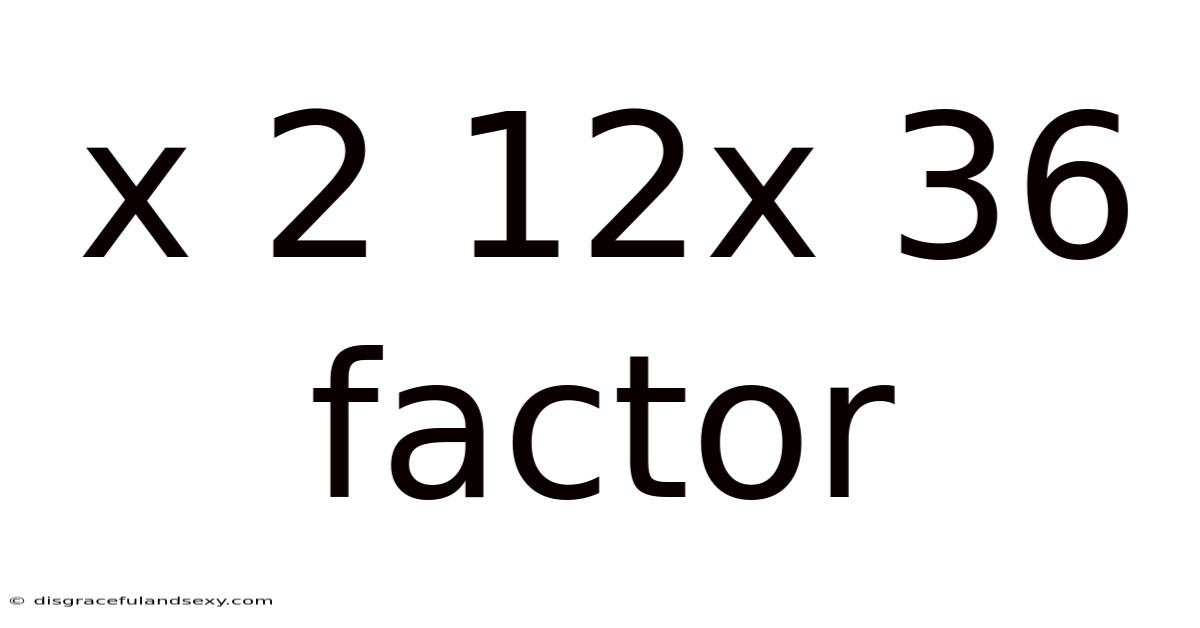
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: Factoring x² + 12x + 36
Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions is a cornerstone of algebra. This seemingly simple skill unlocks doors to solving complex equations, graphing parabolas, and even understanding more advanced mathematical concepts. This article delves deep into factoring the specific quadratic expression x² + 12x + 36, explaining the process step-by-step, providing the underlying mathematical reasoning, and addressing frequently asked questions. By the end, you'll not only know how to factor this expression but also why the method works.
Introduction: What is Factoring?
Factoring, in the context of algebra, is the process of breaking down a mathematical expression into simpler components that, when multiplied together, produce the original expression. Think of it like reverse multiplication. Just as we can multiply (x + 2)(x + 3) to get x² + 5x + 6, factoring involves starting with x² + 5x + 6 and finding the original (x + 2)(x + 3). This seemingly simple process is fundamental to solving many algebraic problems. Our focus here is on factoring the trinomial x² + 12x + 36.
Step-by-Step Factoring of x² + 12x + 36
Factoring this quadratic expression involves finding two binomials that, when multiplied, result in x² + 12x + 36. We'll use the method often called the "AC method" or "splitting the middle term." While other methods exist, this is a widely applicable and straightforward approach.
1. Identify a, b, and c:
First, identify the coefficients of each term in the quadratic expression, which is in the standard form ax² + bx + c. In our case:
- a = 1 (the coefficient of x²)
- b = 12 (the coefficient of x)
- c = 36 (the constant term)
2. Find two numbers that add up to 'b' and multiply to 'ac':
This is the core of the factoring process. We need to find two numbers that meet these two criteria simultaneously:
- Sum: The two numbers must add up to 'b' (which is 12).
- Product: The two numbers must multiply to 'ac' (which is 1 * 36 = 36).
Let's brainstorm pairs of numbers that multiply to 36:
- 1 and 36
- 2 and 18
- 3 and 12
- 4 and 9
- 6 and 6
Now, let's check which pair also adds up to 12: Only 6 and 6 satisfy both conditions (6 + 6 = 12 and 6 * 6 = 36).
3. Rewrite the expression using the two numbers:
Now, we rewrite the original expression, splitting the middle term (12x) using the two numbers we found (6 and 6):
x² + 6x + 6x + 36
4. Factor by grouping:
Next, we factor by grouping. This involves grouping the first two terms and the last two terms and factoring out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each group:
x(x + 6) + 6(x + 6)
Notice that both terms now share a common factor of (x + 6).
5. Final factored form:
Finally, we factor out the common binomial (x + 6):
(x + 6)(x + 6) or (x + 6)²
Therefore, the factored form of x² + 12x + 36 is (x + 6)².
Mathematical Explanation: Why This Method Works
The success of this method hinges on the distributive property of multiplication. When we expand (x + 6)(x + 6), we use the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last):
- First: x * x = x²
- Outer: x * 6 = 6x
- Inner: 6 * x = 6x
- Last: 6 * 6 = 36
Combining these terms gives us x² + 6x + 6x + 36 = x² + 12x + 36 – our original expression. The method we used is essentially reversing this process.
Understanding Perfect Square Trinomials
x² + 12x + 36 is a special type of quadratic expression known as a perfect square trinomial. This means it's the result of squaring a binomial. Recognizing this pattern can simplify the factoring process. A perfect square trinomial follows this general form:
a² + 2ab + b² = (a + b)²
or
a² - 2ab + b² = (a - b)²
In our case, a = x and b = 6. Notice how 12x (our 'b' term) is twice the product of x and 6 (2 * x * 6 = 12x), and 36 (our 'c' term) is the square of 6 (6² = 36). This confirms that x² + 12x + 36 is indeed a perfect square trinomial.
Applications of Factoring
The ability to factor quadratic expressions has numerous applications across mathematics and other fields:
- Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring allows us to solve equations like x² + 12x + 36 = 0 by setting each factor to zero and solving for x. In this case, (x + 6)² = 0, leading to x = -6.
- Graphing Parabolas: The factored form of a quadratic equation reveals the x-intercepts (roots) of the parabola, which are crucial for sketching its graph.
- Calculus: Factoring is essential for simplifying expressions and solving problems in calculus, particularly those involving derivatives and integrals.
- Physics and Engineering: Quadratic equations frequently appear in physics and engineering problems involving projectile motion, oscillations, and other phenomena. Factoring helps in solving these equations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the quadratic expression cannot be factored easily?
A1: Not all quadratic expressions can be factored using simple integer coefficients. In such cases, you can use the quadratic formula: x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a. This formula will always provide the solutions, even if factoring isn't straightforward.
Q2: Are there other methods for factoring quadratic expressions?
A2: Yes, besides the AC method, other techniques include trial and error, the box method, and using the difference of squares (for expressions like a² - b²). The best method often depends on the specific quadratic expression and your personal preference.
Q3: What if the coefficient of x² is not 1?
A3: If 'a' is not 1, the process is slightly more involved. You still need to find two numbers that add up to 'b' and multiply to 'ac,' but then you'll need to use a slightly modified grouping method or other techniques to factor the expression completely.
Q4: Why is factoring important in higher-level mathematics?
A4: Factoring is a fundamental skill that underlies many more advanced concepts. It's crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding the behavior of functions in calculus, linear algebra, and other mathematical disciplines.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Factoring
Factoring quadratic expressions like x² + 12x + 36 might seem like a small step in your mathematical journey, but its importance cannot be overstated. This seemingly simple skill unlocks doors to more complex problem-solving and is a foundation for further mathematical exploration. By understanding the step-by-step process, the underlying mathematical principles, and the various applications of factoring, you'll not only be able to factor this specific expression but also confidently tackle a wide range of other quadratic equations and beyond. Remember to practice regularly, explore different methods, and don't be afraid to ask questions – mastering algebra takes time and effort, but the rewards are significant.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 12x 36 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.