X 2 13x 36 0
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
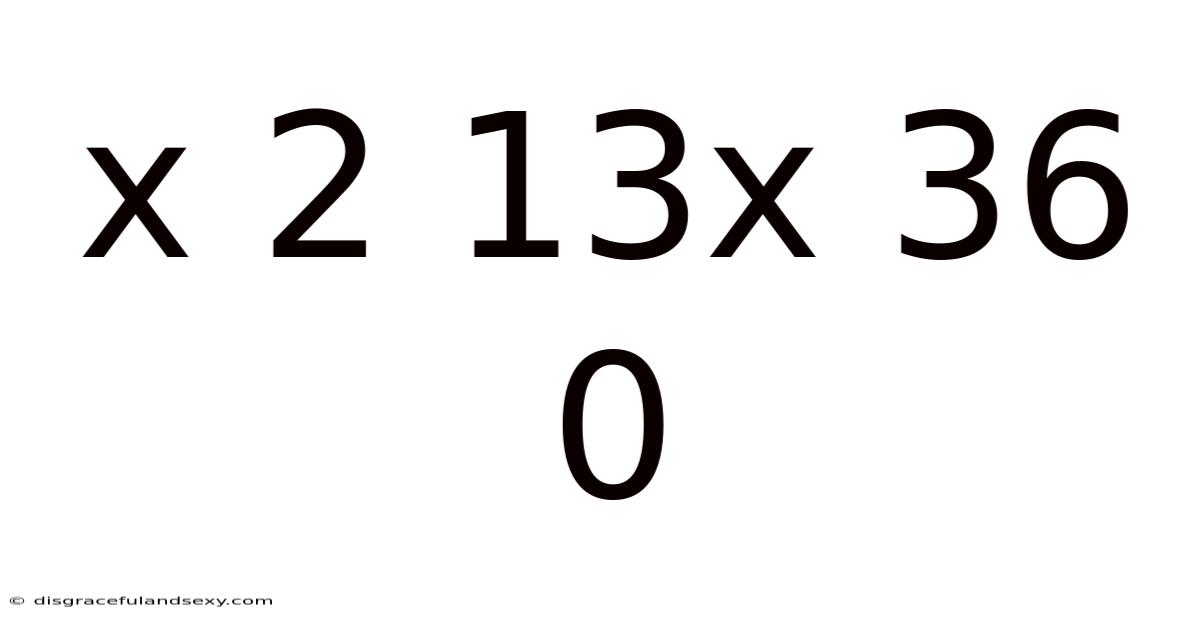
Table of Contents
Deciphering the Sequence: x 2 13x 36 0 – A Journey into Pattern Recognition and Mathematical Problem Solving
This article delves into the intriguing sequence "x 2 13x 36 0," exploring potential patterns, mathematical operations, and problem-solving strategies. We will move beyond a simple answer and explore the underlying principles of pattern recognition, critical for various fields, from mathematics and programming to data science and cryptography. Understanding this sequence requires a blend of logical deduction, algebraic manipulation, and a healthy dose of creative thinking. We will unpack various possibilities, demonstrating the importance of considering multiple perspectives when tackling mathematical puzzles.
Understanding the Challenge
The sequence "x 2 13x 36 0" presents a unique challenge because the 'x' acts as a wildcard, obscuring the underlying pattern. The presence of both a variable and seemingly unrelated numbers (2, 13, 36, 0) hints at a more complex relationship than a simple arithmetic progression. Our objective is to find a consistent mathematical rule or operation that connects these elements and determines the value of 'x'.
Possible Approaches and Solutions
Several approaches can be used to tackle this problem. Let's explore some possibilities:
1. Treating 'x' as a Single Variable:
We could attempt to find a single value for 'x' that makes the sequence follow a logical pattern. This could involve considering various arithmetic operations (+, -, *, /) or even more complex mathematical functions.
-
Linear Relationships: Could the sequence represent a linear function of the form y = mx + c, where 'x' represents the position in the sequence (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and 'y' represents the corresponding value (x, 2, 13x, 36, 0)? If so, finding the appropriate values for 'm' and 'c' would provide a solution for 'x'.
-
Polynomial Relationships: A more complex polynomial function could be considered. This involves finding a polynomial equation that fits the sequence's values. The degree of the polynomial would depend on the number of terms in the sequence. Finding a suitable polynomial requires more complex algebraic manipulation and potentially the use of matrix methods or numerical techniques.
-
Trial and Error: A brute-force approach involves trying different values of 'x' to see if a consistent pattern emerges. This is less elegant but potentially effective, particularly with the aid of computational tools.
2. Treating 'x' as a Placeholder for an Operation:
Instead of seeking a single value for 'x', we might consider it as a placeholder for a specific mathematical operation or a sequence of operations.
-
Hidden Operations: The sequence could be interpreted as a series of operations where 'x' represents an operation rather than a numerical value. For example: x could represent "multiply by 3," "add 10," "subtract 5," or other operations that might produce a pattern when applied sequentially to the sequence.
-
Recursive Relationships: The sequence may be defined recursively, meaning that each term is calculated based on the preceding term(s). This would require identifying a recursive formula that produces the given values when iterated.
3. Considering Multiple Solutions and Context:
The sequence may not have a unique solution. Depending on how the sequence is framed, several different solutions might be valid. The lack of context makes it challenging to definitively identify the correct approach. Additional information regarding the origin or purpose of the sequence would significantly aid in finding a meaningful interpretation.
4. Exploring Number Properties:
Analysing the number properties of 2, 13, 36, and 0 might uncover hidden relationships. Looking for prime factorizations, common divisors, or patterns in their digital roots could offer clues.
-
Prime Factorization: The prime factorizations of these numbers are: 2 = 2, 13 = 13, 36 = 2² * 3², and 0 = 0. There's no immediate apparent pattern here.
-
Digital Roots: The digital roots are 2, 4, 9, 0 respectively. Again, this doesn't reveal a significant underlying pattern.
Mathematical Techniques and Tools:
Solving this type of problem could involve several sophisticated mathematical techniques, depending on the chosen approach:
-
Linear Algebra: If a linear relationship is suspected, techniques from linear algebra, such as matrix operations and least squares fitting, could be employed to find the best fit line.
-
Polynomial Interpolation: If a polynomial relationship is suspected, techniques from numerical analysis, such as Lagrange interpolation or Newton's divided difference method, could be used to determine the coefficients of the polynomial.
-
Calculus: If the sequence suggests a continuous function, calculus could help analyze its rate of change or find extremal points.
-
Computational Tools: Software packages such as MATLAB, Python (with libraries like NumPy and SciPy), or Wolfram Mathematica could significantly speed up computations, especially for more complex approaches involving numerical analysis or symbolic manipulation.
Illustrative Examples (with Limitations)
Let's illustrate some potential approaches, keeping in mind that without further context, these are just possibilities.
Example 1 (Linear Approach):
Let's assume a simple linear relationship. We could try to fit a line to three points: (1, x), (2, 2), (3, 13x). However, this approach is limited as it will most likely produce conflicting values for 'x'. The inclusion of 36 and 0 would further complicate and likely invalidate a linear relationship.
Example 2 (Recursive Approach):
Perhaps each term is generated based on the previous one. However, creating a recursive function that produces this sequence is highly challenging without more information about how 'x' relates to subsequent terms. A potential recursive formula might be highly complex and potentially non-unique.
Example 3 (Operation-based Approach):
Let's say 'x' represents the operation "add 1". Then we have 1+1=2. Following a different pattern, perhaps we say that 13x means 13 multiplied by the previous term (2) and so on. This might yield a pattern, but it would be completely arbitrary without further contextual information.
Conclusion: The Importance of Context and Further Investigation
The sequence "x 2 13x 36 0" highlights the critical role of context in mathematical problem-solving. Without further information about the sequence's origin or intended meaning, it's impossible to definitively determine the value of 'x' or the underlying pattern. The exploration of various mathematical approaches, however, demonstrates the power of systematic problem-solving and the importance of considering multiple perspectives. To obtain a conclusive answer, we need more information. This problem serves as a valuable exercise in pattern recognition, highlighting the need for careful consideration of various approaches and demonstrating that sometimes, the most important element isn't the solution itself but the problem-solving process it evokes. This sequence can serve as an excellent foundation for discussing more advanced mathematical concepts and tools.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 13x 36 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.