X 2 2x 17 0
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
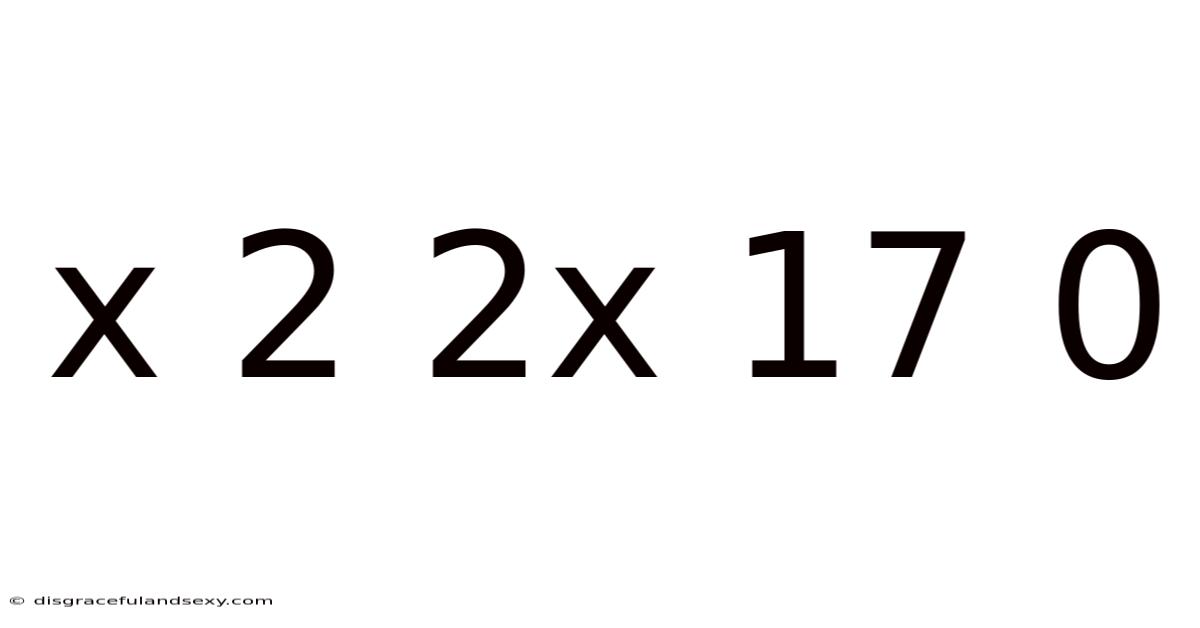
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mathematical Puzzle: x² + 2x + 17 = 0
This article delves into the seemingly simple yet surprisingly rich mathematical puzzle presented by the quadratic equation x² + 2x + 17 = 0. We will explore various methods for solving this equation, examine its properties, and discuss its implications within the broader context of algebra and number theory. Understanding this seemingly basic equation unlocks deeper insights into the behavior of quadratic functions and their solutions.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. Our specific equation, x² + 2x + 17 = 0, fits this general form with a = 1, b = 2, and c = 17. Solving this equation means finding the values of 'x' that make the equation true.
Method 1: Using the Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula provides a direct method for solving any quadratic equation. It's a powerful tool derived from completing the square, a technique we'll explore later. The formula is:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
Plugging in the values from our equation (a = 1, b = 2, c = 17), we get:
x = (-2 ± √(2² - 4 * 1 * 17)) / (2 * 1) x = (-2 ± √(4 - 68)) / 2 x = (-2 ± √(-64)) / 2
Notice that we have the square root of a negative number (-64). This indicates that the solutions to this equation are complex numbers. Complex numbers involve the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1. We can rewrite √(-64) as √(64 * -1) = 8i.
Therefore, the solutions are:
x = (-2 + 8i) / 2 = -1 + 4i x = (-2 - 8i) / 2 = -1 - 4i
These are the two complex roots of the equation. They are conjugates of each other, meaning they have the same real part (-1) but opposite imaginary parts (+4i and -4i).
Method 2: Completing the Square
Completing the square is an algebraic technique that transforms a quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve. The process involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square on one side.
Starting with x² + 2x + 17 = 0:
-
Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 2x = -17
-
Take half of the coefficient of 'x' (which is 2), square it (1), and add it to both sides: x² + 2x + 1 = -17 + 1 x² + 2x + 1 = -16
-
Factor the left side as a perfect square: (x + 1)² = -16
-
Take the square root of both sides: x + 1 = ±√(-16) = ±4i
-
Solve for x: x = -1 ± 4i
This method confirms the same complex roots we found using the quadratic formula: -1 + 4i and -1 - 4i.
Method 3: Graphical Representation
While the previous methods provide the exact solutions, visualizing the equation graphically offers valuable insights. The equation x² + 2x + 17 = 0 represents a parabola. Since the coefficient of x² is positive, the parabola opens upwards. The solutions to the equation are the x-intercepts (where the parabola intersects the x-axis). However, because the solutions are complex numbers, the parabola does not intersect the x-axis. This is a key characteristic of quadratic equations with complex roots – they have no real solutions, and their graphs do not cross the x-axis.
The Discriminant and Nature of Roots
The expression b² - 4ac within the quadratic formula is called the discriminant. It determines the nature of the roots of the quadratic equation:
- b² - 4ac > 0: Two distinct real roots. The parabola intersects the x-axis at two points.
- b² - 4ac = 0: One real root (a repeated root). The parabola touches the x-axis at one point (its vertex).
- b² - 4ac < 0: Two complex conjugate roots. The parabola does not intersect the x-axis.
In our case, the discriminant is 2² - 4(1)(17) = -64, which is less than 0. This confirms that the equation has two complex conjugate roots, as we've already calculated.
Exploring Complex Numbers
The solutions to our equation highlight the importance of complex numbers in mathematics. Complex numbers are numbers of the form a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers, and 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1). They extend the real number system and are essential for solving many mathematical problems that cannot be solved using only real numbers. Complex numbers have wide applications in various fields, including electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, and signal processing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why are the roots complex in this equation?
- A: Because the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is negative. A negative discriminant always indicates complex roots. This means the parabola represented by the equation does not intersect the x-axis.
-
Q: Can complex numbers be represented graphically?
- A: Yes, they are represented on a complex plane, where the horizontal axis represents the real part and the vertical axis represents the imaginary part.
-
Q: What is the significance of conjugate complex roots?
- A: Conjugate complex roots often arise from quadratic equations with real coefficients. They always appear in pairs, and their product is always a real number.
-
Q: Are there other methods to solve quadratic equations?
- A: Yes, other methods include factorization (when possible) and numerical methods for approximating roots when exact solutions are difficult to obtain.
-
Q: What are some real-world applications of quadratic equations?
- A: Quadratic equations are used to model various phenomena, including projectile motion, the path of a ball thrown in the air, and the shape of certain curves and structures in architecture and engineering.
Conclusion: Beyond the Equation
The seemingly simple equation x² + 2x + 17 = 0 serves as a gateway to a deeper understanding of quadratic equations, the power of the quadratic formula, the nature of complex numbers, and the importance of the discriminant. While the equation itself might appear straightforward at first glance, its solution unveils a richer mathematical landscape, demonstrating the elegance and interconnectedness of various mathematical concepts. The exploration of this equation underscores the fact that even seemingly basic problems can lead to profound insights and a deeper appreciation for the beauty and utility of mathematics. The journey from the equation to the understanding of complex numbers illustrates the progressive nature of mathematical learning – one concept building upon another, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the mathematical world. This journey of understanding not only solves the specific equation but also enhances our ability to tackle more complex problems in the future.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 2x 17 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.