X 2 3x 40 Factor
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
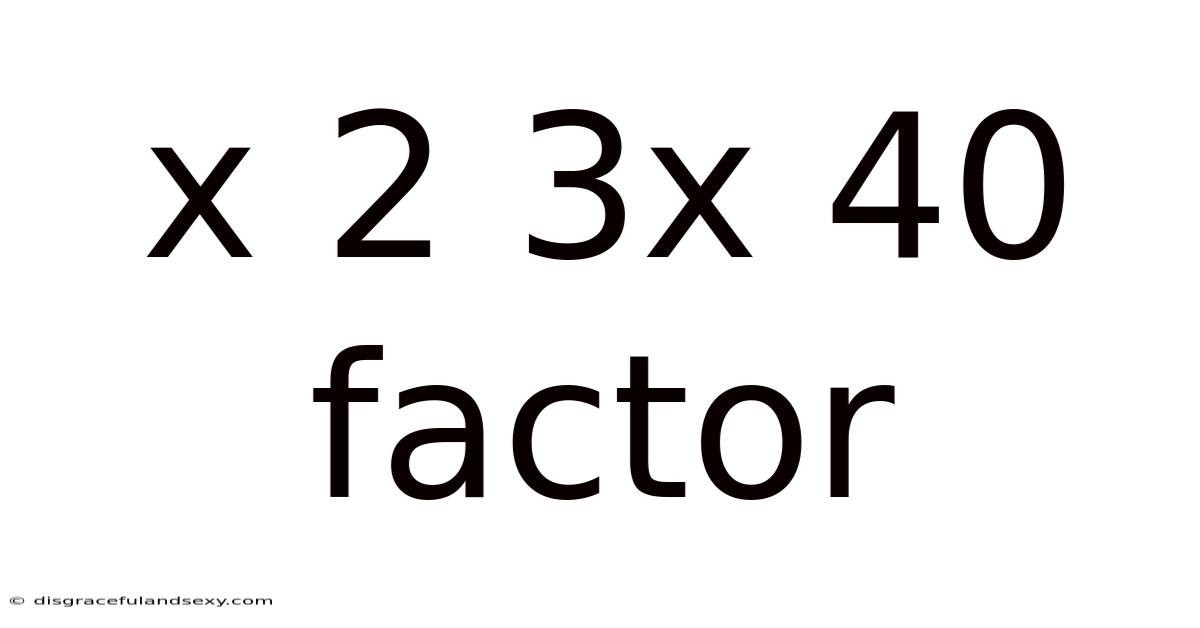
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mystery: Exploring the Factors of x² + 3x + 40
Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions like x² + 3x + 40 is a cornerstone of algebra. This seemingly simple expression holds within it the key to solving equations, graphing parabolas, and understanding more complex mathematical concepts. This article will delve deep into the process of factoring this particular quadratic, exploring various methods, and explaining the underlying mathematical principles. We'll also address common misconceptions and provide you with the tools to tackle similar problems with confidence.
Introduction: What Does Factoring Mean?
Factoring, in the context of algebra, involves breaking down a mathematical expression into smaller, simpler components that, when multiplied together, reproduce the original expression. Think of it like reverse multiplication. For example, factoring the number 12 might give you 2 x 2 x 3. Similarly, factoring the quadratic x² + 3x + 40 involves finding two binomial expressions (expressions with two terms) whose product equals the original quadratic.
This process is crucial for solving quadratic equations (equations where the highest power of the variable is 2), finding the roots (or zeros) of a quadratic function, and simplifying more complex algebraic expressions. While some quadratics factor easily, others require more sophisticated techniques.
Attempting to Factor x² + 3x + 40: The Standard Approach
The most common method for factoring quadratic expressions of the form ax² + bx + c is to look for two numbers that add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 'c' (the constant term). In our case, we're looking for two numbers that add up to 3 and multiply to 40.
Let's try some possibilities:
- 1 and 40: 1 + 40 = 41 (doesn't work)
- 2 and 20: 2 + 20 = 22 (doesn't work)
- 4 and 10: 4 + 10 = 14 (doesn't work)
- 5 and 8: 5 + 8 = 13 (doesn't work)
- -1 and -40: -1 + (-40) = -41 (doesn't work)
- -2 and -20: -2 + (-20) = -22 (doesn't work)
- -4 and -10: -4 + (-10) = -14 (doesn't work)
- -5 and -8: -5 + (-8) = -13 (doesn't work)
Notice that none of these pairs of factors add up to 3. This leads us to a crucial conclusion: x² + 3x + 40 cannot be factored using integers.
Why Doesn't it Factor? Understanding the Discriminant
The reason x² + 3x + 40 doesn't factor neatly using integers is related to a concept called the discriminant. The discriminant (represented by Δ or D) is a part of the quadratic formula and is calculated as:
Δ = b² - 4ac
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are the coefficients of the quadratic equation ax² + bx + c.
In our case, a = 1, b = 3, and c = 40. Let's calculate the discriminant:
Δ = 3² - 4 * 1 * 40 = 9 - 160 = -151
The discriminant is negative. A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation x² + 3x + 40 = 0 has no real roots. This means there are no real numbers that, when substituted for 'x', will make the equation true. Consequently, the quadratic expression cannot be factored into real binomial factors.
Exploring Complex Numbers: A Deeper Dive
While the quadratic doesn't factor using real numbers, it does factor using complex numbers. Complex numbers involve the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1. The quadratic formula provides the solution:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting our values:
x = [-3 ± √(-151)] / 2
This simplifies to:
x = [-3 ± i√151] / 2
Therefore, the factors of x² + 3x + 40, when considering complex numbers, are:
(x - [-3 + i√151] / 2) and (x - [-3 - i√151] / 2)
These are the binomial factors that, when multiplied, will result in x² + 3x + 40. However, it's important to note that these factors involve complex numbers, and they are not typically encountered in basic algebra problems.
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Parabola
The inability to factor x² + 3x + 40 with real numbers has a clear visual representation when we graph the corresponding quadratic function y = x² + 3x + 40. The parabola will not intersect the x-axis (where y = 0). This confirms that there are no real roots, hence no real factors. The parabola will open upwards (since the coefficient of x² is positive) and its vertex will lie above the x-axis.
Practical Applications and Context
While this specific quadratic may not have immediate real-world applications in simple scenarios, the principles involved in attempting to factor it and understanding the meaning of a negative discriminant are incredibly important. These concepts are fundamental to understanding:
- Solving quadratic equations: Many real-world problems, from projectile motion to optimizing business models, involve solving quadratic equations. Understanding factoring (or using the quadratic formula) is essential.
- Analyzing quadratic functions: Understanding the graph of a quadratic function, its roots, and its vertex is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
- Advanced mathematical concepts: The concepts introduced here form the foundation for more advanced topics in algebra, calculus, and other areas of mathematics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why is factoring important?
A: Factoring is a crucial algebraic skill used to simplify expressions, solve equations, and understand the behavior of functions. It's a fundamental building block for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Q: What if I encounter a similar problem that doesn't factor easily?
A: If a quadratic expression doesn't factor readily using integers, you can use the quadratic formula to find its roots (solutions) and express it in factored form using complex numbers if necessary. Alternatively, you might need to use techniques like completing the square.
Q: Are there other methods for factoring quadratics?
A: Yes, besides the method of finding two numbers that add up to 'b' and multiply to 'c', there are other techniques such as completing the square and using the quadratic formula. These are useful when the standard method fails.
Q: What does a negative discriminant actually tell us?
A: A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has no real roots. Graphically, it means the parabola representing the quadratic function does not intersect the x-axis. This also implies that the quadratic expression cannot be factored using real numbers.
Conclusion: The Importance of Persistence and Understanding
While x² + 3x + 40 cannot be factored using real numbers, exploring its properties has allowed us to delve into fundamental concepts of algebra. The inability to factor this specific expression highlights the importance of understanding the discriminant and the existence of complex numbers. Remember, not every quadratic will factor neatly, and encountering such cases is an opportunity to learn more about the richness and complexity of mathematical concepts. Keep practicing, keep exploring, and you will develop the skills and understanding needed to tackle any algebraic challenge you may encounter. The key is persistence and a genuine desire to understand the underlying principles.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 3x 40 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.