X 2 6x 16 0
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
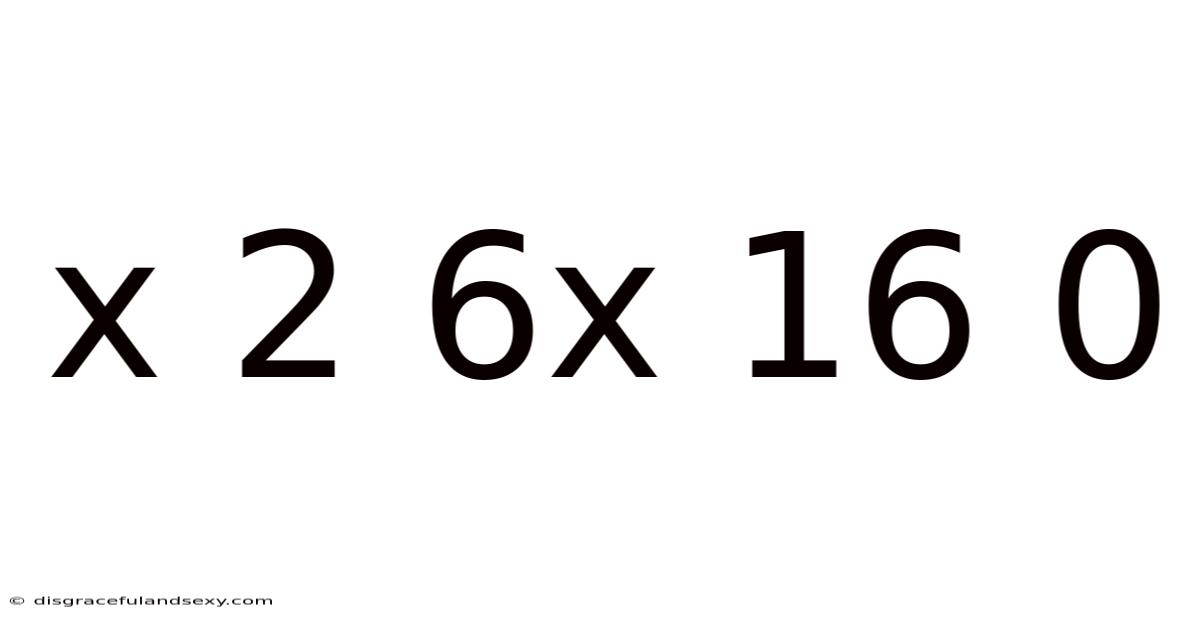
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: x² + 6x + 16 = 0 and the World of Quadratic Equations
This article delves into the seemingly simple, yet surprisingly rich, quadratic equation x² + 6x + 16 = 0. We'll explore various methods for solving it, understand its implications within the broader context of quadratic equations, and examine its properties, including its discriminant and the nature of its roots. This exploration will illuminate fundamental concepts in algebra and provide a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems.
Understanding Quadratic Equations
Before we tackle our specific equation, let's establish a firm understanding of quadratic equations in general. A quadratic equation is a second-degree polynomial equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. The solutions to this equation, also known as roots or zeros, represent the x-values where the corresponding parabola intersects the x-axis.
Methods for Solving Quadratic Equations
There are several methods available for solving quadratic equations, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
-
Factoring: This involves expressing the quadratic equation as a product of two linear factors. For example, x² + 5x + 6 = 0 can be factored as (x + 2)(x + 3) = 0, yielding solutions x = -2 and x = -3. However, not all quadratic equations are easily factorable.
-
Completing the Square: This method involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored. This is a particularly useful technique when factoring is difficult.
-
Quadratic Formula: This is a general formula that provides the solutions for any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it is factorable. The formula is:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
-
Graphing: Graphing the quadratic equation allows for a visual representation of the solutions. The x-intercepts of the parabola represent the roots of the equation.
Solving x² + 6x + 16 = 0
Now, let's apply these methods to our specific equation, x² + 6x + 16 = 0.
1. Attempting to Factor: We look for two numbers that add up to 6 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 16 (the constant term). However, no such integer pairs exist. Therefore, factoring is not a viable method for this equation.
2. Completing the Square:
- Start with the equation: x² + 6x + 16 = 0
- Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 6x = -16
- Take half of the coefficient of x (6/2 = 3), square it (3² = 9), and add it to both sides: x² + 6x + 9 = -16 + 9
- This creates a perfect square trinomial on the left side: (x + 3)² = -7
- Take the square root of both sides: x + 3 = ±√(-7)
- Solve for x: x = -3 ± √(-7)
3. Using the Quadratic Formula:
In our equation, a = 1, b = 6, and c = 16. Substituting these values into the quadratic formula:
x = (-6 ± √(6² - 4 * 1 * 16)) / (2 * 1) x = (-6 ± √(36 - 64)) / 2 x = (-6 ± √(-28)) / 2 x = (-6 ± 2i√7) / 2 x = -3 ± i√7
Understanding the Results: Complex Roots
The solutions we obtained, x = -3 ± i√7, are complex numbers. A complex number is a number that can be expressed in the form a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers, and 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1). The presence of complex roots indicates that the parabola represented by the equation x² + 6x + 16 = 0 does not intersect the x-axis.
The Discriminant: A Key Indicator
The expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula (b² - 4ac) is called the discriminant. It provides valuable information about the nature of the roots:
-
If the discriminant is positive (b² - 4ac > 0): The equation has two distinct real roots. The parabola intersects the x-axis at two points.
-
If the discriminant is zero (b² - 4ac = 0): The equation has one real root (a repeated root). The parabola touches the x-axis at one point.
-
If the discriminant is negative (b² - 4ac < 0): The equation has two complex conjugate roots. The parabola does not intersect the x-axis.
In our case, the discriminant is 36 - 64 = -28, which is negative. This confirms the presence of two complex conjugate roots, as we found using the quadratic formula.
Graphical Representation
Graphing the equation x² + 6x + 16 = 0 would reveal a parabola that opens upwards (since the coefficient of x² is positive) and lies entirely above the x-axis. This visual representation reinforces the fact that there are no real roots – the parabola never intersects the x-axis.
Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations have numerous applications in various fields:
-
Physics: Describing projectile motion, calculating the trajectory of objects under the influence of gravity.
-
Engineering: Designing bridges, arches, and other structures.
-
Economics: Modeling cost functions, revenue functions, and profit maximization.
-
Computer Graphics: Creating curves and shapes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are complex numbers important?
A: Complex numbers extend the number system beyond real numbers, allowing us to solve equations that have no real solutions. They are crucial in various areas of mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Q: Can I solve quadratic equations using only a calculator?
A: Yes, most scientific calculators have built-in functions to solve quadratic equations directly. You simply input the values of a, b, and c, and the calculator will output the solutions.
Q: What if the coefficient 'a' is zero?
A: If 'a' is zero, the equation is no longer quadratic; it becomes a linear equation. Linear equations have only one solution.
Q: Are there other methods to solve quadratic equations besides the ones mentioned?
A: While the methods discussed are the most common, there are other advanced techniques, such as using numerical methods for complex or difficult-to-factor equations.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple equation x² + 6x + 16 = 0 has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of quadratic equations. We've explored different solution methods, learned about the importance of the discriminant, understood the concept of complex numbers, and touched upon the broad applications of quadratic equations. This exploration highlights the depth and power of even fundamental mathematical concepts, showcasing how a single equation can reveal profound insights into the nature of numbers and their applications in various fields. Understanding quadratic equations is a cornerstone of further mathematical studies, empowering you to tackle more complex problems with confidence and a deeper appreciation for the elegance and utility of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 6x 16 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.