X 2 6x 16 Factor
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
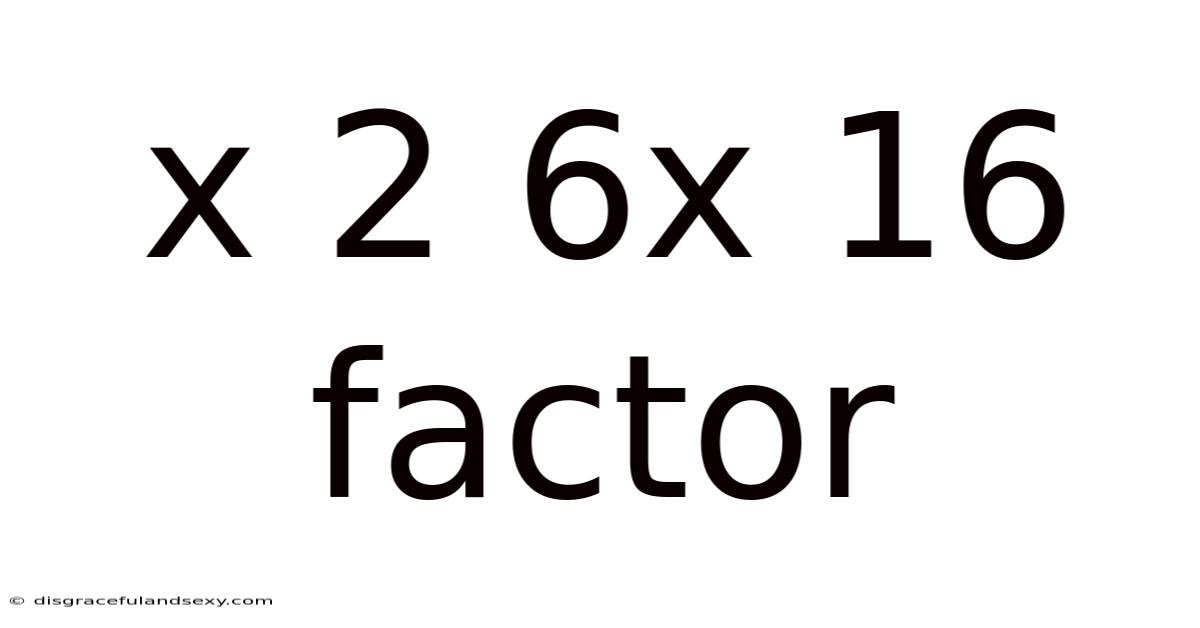
Table of Contents
Factoring Trinomials: A Deep Dive into x² + 6x + 16
This article provides a comprehensive guide to factoring the trinomial expression x² + 6x + 16. We'll explore various methods, discuss the concept of factoring in detail, and address common misconceptions. Understanding how to factor quadratic expressions is fundamental in algebra and has wide-ranging applications in higher-level mathematics and problem-solving. This guide aims to equip you with the skills and knowledge to confidently tackle similar problems.
Understanding Trinomials and Factoring
A trinomial is a polynomial expression with three terms. Our example, x² + 6x + 16, is a quadratic trinomial because the highest power of the variable x is 2. Factoring a trinomial involves expressing it as a product of two or more simpler expressions (usually binomials). This process reverses the expansion of binomials using the distributive property (often referred to as FOIL).
The goal is to find two binomials whose product equals the original trinomial. For a general quadratic trinomial of the form ax² + bx + c, we look for two numbers that add up to b and multiply to ac. This method is particularly effective when a = 1, as in our case.
Attempting to Factor x² + 6x + 16
Let's try to factor x² + 6x + 16 using the standard method. We are looking for two numbers that add up to 6 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 16 (the constant term). Let's consider the pairs of factors of 16:
- 1 and 16
- 2 and 8
- 4 and 4
None of these pairs add up to 6. This reveals a crucial point: not all quadratic trinomials are factorable using integers.
The Significance of the Discriminant
The discriminant of a quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0 is given by the expression b² - 4ac. The discriminant helps determine the nature of the roots (solutions) of the quadratic equation and indirectly indicates whether the quadratic expression is factorable using integers.
- If the discriminant is a perfect square, the quadratic expression is factorable using integers.
- If the discriminant is positive but not a perfect square, the quadratic expression is factorable using irrational numbers.
- If the discriminant is negative, the quadratic expression is not factorable using real numbers. It would require complex numbers.
Let's calculate the discriminant for x² + 6x + 16:
a = 1, b = 6, c = 16
Discriminant = b² - 4ac = 6² - 4(1)(16) = 36 - 64 = -28
Since the discriminant is -28 (a negative number), x² + 6x + 16 is not factorable using real numbers. This explains why we couldn't find integer factors that satisfy the conditions.
Exploring Other Methods and Concepts
While we've established that x² + 6x + 16 doesn't factor neatly with integers, let's explore some related concepts and alternative approaches:
-
Completing the Square: This method transforms the quadratic expression into a perfect square trinomial, plus a remaining constant. This is useful for solving quadratic equations and understanding the parabola's vertex. For our example:
x² + 6x + 16 = (x² + 6x + 9) + 7 = (x + 3)² + 7
-
Quadratic Formula: This formula directly solves for the roots of a quadratic equation, ax² + bx + c = 0:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
Applying this to x² + 6x + 16 = 0:
x = (-6 ± √(-28)) / 2 = (-6 ± 2i√7) / 2 = -3 ± i√7
The roots are complex numbers, further confirming the non-factorability over real numbers.
-
Graphing: Graphing the quadratic function y = x² + 6x + 16 reveals a parabola that doesn't intersect the x-axis. This visual representation shows that there are no real roots, reinforcing our earlier findings.
Prime Polynomials: A Special Case
A prime polynomial is a polynomial that cannot be factored into lower-degree polynomials using real numbers. x² + 6x + 16 is an example of a prime polynomial. It's important to recognize that the inability to factor using integers doesn't automatically mean the expression is meaningless; it simply means it's irreducible in this specific number system.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Many students struggle with factoring, often due to these common mistakes:
- Incorrectly applying the rules: Carefully review the signs and ensure proper distribution during the factoring process.
- Assuming all quadratics are factorable: Remember that not all trinomials factor using integers. The discriminant is a powerful tool to determine factorability.
- Ignoring the constant term: The constant term plays a vital role in finding the correct factors.
- Not checking your work: Always expand your factored expression to verify it matches the original trinomial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can x² + 6x + 16 be factored using complex numbers?
A: Yes, as shown using the quadratic formula, the roots are complex numbers (-3 + i√7) and (-3 - i√7). This means it can be factored as (x - (-3 + i√7))(x - (-3 - i√7)).
Q: Is it always necessary to find the discriminant before attempting to factor?
A: While not strictly necessary, calculating the discriminant is a helpful strategy, especially when dealing with larger coefficients or when you're unsure if factoring is even possible using real numbers.
Q: What if I encounter a more complex trinomial, like 2x² + 6x + 16?
A: For trinomials with a leading coefficient other than 1 (a ≠ 1), techniques like factoring by grouping or using the quadratic formula are more suitable.
Conclusion
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. While x² + 6x + 16 is not factorable using real numbers, understanding why it's not factorable is just as important as understanding how to factor those that are. This article has explored various methods, discussed the significance of the discriminant, and highlighted common pitfalls. Remember that not all quadratic trinomials are factorable using integers, and understanding this concept is crucial for mastery of algebraic manipulation and problem-solving. By understanding both successful and unsuccessful factoring attempts, you build a stronger foundation in algebra and develop a more nuanced approach to solving mathematical problems.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 6x 16 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.