X 2 6x 2 9
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 7 min read
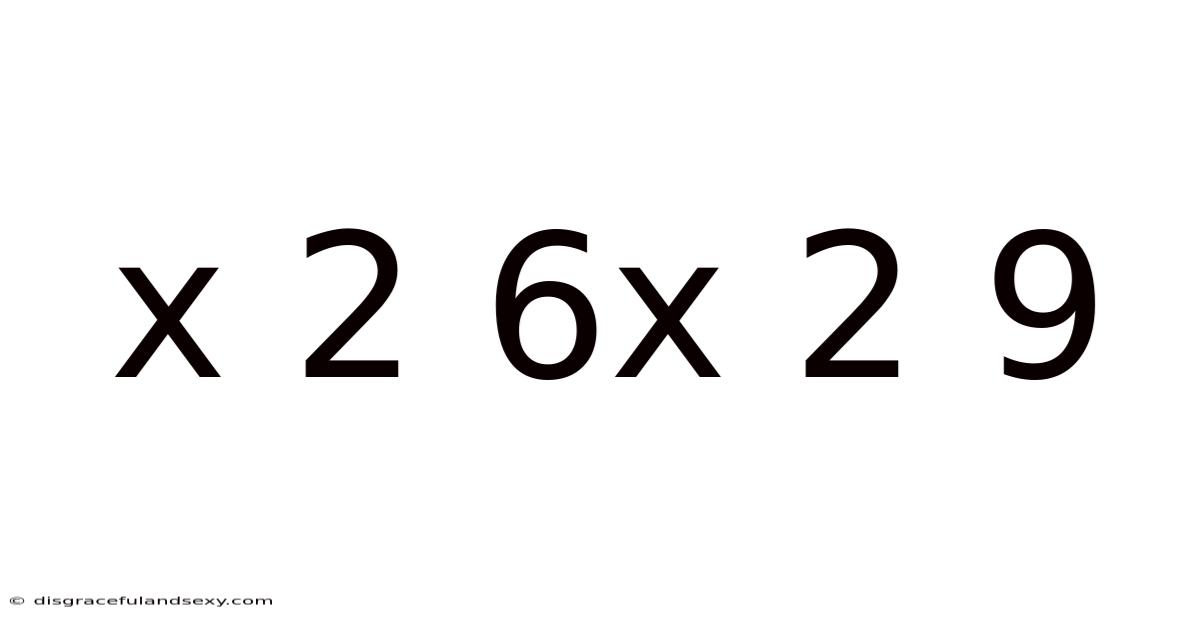
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Exploring the Mathematical Expression x² + 6x + 9
The expression x² + 6x + 9 is a fundamental concept in algebra, appearing frequently in various mathematical contexts. Understanding this seemingly simple expression unlocks doors to more complex algebraic manipulations and problem-solving strategies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of x² + 6x + 9, exploring its factorization, graphical representation, applications, and real-world relevance. We'll unravel the mystery behind this quadratic expression and equip you with the tools to confidently tackle similar challenges.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we dive into the specifics of x² + 6x + 9, let's establish a foundational understanding of quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a is not equal to zero. Our expression, x² + 6x + 9, fits this general form with a = 1, b = 6, and c = 9.
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: x² + 6x + 9
Factoring a quadratic expression means rewriting it as a product of simpler expressions. This is a crucial step in solving quadratic equations and simplifying more complex algebraic expressions. There are several methods to factor quadratics, but for x² + 6x + 9, the most straightforward approach is recognizing it as a perfect square trinomial.
A perfect square trinomial is a quadratic expression that can be factored into the square of a binomial. It follows the pattern: a² + 2ab + b² = (a + b)². In our case, we can see that:
- x² is the square of x (x² = x * x)
- 9 is the square of 3 (9 = 3 * 3)
- 6x is twice the product of x and 3 (6x = 2 * x * 3)
Therefore, x² + 6x + 9 perfectly matches the perfect square trinomial pattern, and we can factor it as:
x² + 6x + 9 = (x + 3)²
This factorization is incredibly useful because it simplifies the expression and allows us to easily solve related equations.
Graphical Representation: Parabolas and Vertex Form
Quadratic expressions are graphically represented as parabolas. A parabola is a U-shaped curve that opens upwards if a (the coefficient of x²) is positive and downwards if a is negative. The factored form of our expression, (x + 3)², allows us to easily identify key features of its graph.
-
Vertex: The vertex is the lowest (or highest) point on the parabola. For a parabola in the form (x - h)² + k, the vertex is at the point (h, k). In our case, (x + 3)² can be rewritten as (x - (-3))² + 0, so the vertex is at (-3, 0).
-
Axis of Symmetry: The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that passes through the vertex, dividing the parabola into two mirror-image halves. The equation of the axis of symmetry is x = h, which in our case is x = -3.
-
x-intercept: The x-intercepts are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis (where y = 0). Since (x + 3)² = 0, the only x-intercept is at x = -3. This confirms our vertex finding.
-
y-intercept: The y-intercept is the point where the parabola intersects the y-axis (where x = 0). Substituting x = 0 into the expression gives us (0 + 3)² = 9, so the y-intercept is at (0, 9).
By understanding these key features, we can accurately sketch the parabola representing x² + 6x + 9. It's a parabola that opens upwards, with its vertex at (-3, 0), passing through (0,9).
Solving Quadratic Equations: Applications of Factoring
The factorization of x² + 6x + 9 is instrumental in solving quadratic equations. A quadratic equation is an equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. If we have the equation x² + 6x + 9 = 0, we can use our factorization to solve it:
(x + 3)² = 0
Taking the square root of both sides:
x + 3 = 0
Solving for x:
x = -3
This means the equation x² + 6x + 9 = 0 has only one real solution, x = -3. This corresponds to the x-intercept of the parabola, indicating that the parabola touches the x-axis at only one point.
Expanding Beyond the Basics: Completing the Square
The expression x² + 6x + 9 illustrates a crucial technique in algebra known as completing the square. Completing the square is a method used to rewrite a quadratic expression in the form of a perfect square trinomial, which makes it easier to solve quadratic equations and perform other algebraic manipulations.
Let's consider a slightly different quadratic expression: x² + 6x. To complete the square, we need to add a constant term that makes it a perfect square trinomial. Observe that in x² + 6x + 9, the constant term 9 is (6/2)² = 3². So, to complete the square for x² + 6x, we add (6/2)² = 9:
x² + 6x + 9 = (x + 3)²
This demonstrates how completing the square can transform a quadratic expression into a perfect square, which simplifies various algebraic processes.
Real-World Applications: Geometry, Physics, and More
Quadratic expressions and equations have numerous real-world applications across various disciplines. Here are a few examples:
-
Projectile Motion: In physics, the trajectory of a projectile (e.g., a ball thrown in the air) is often modeled using a quadratic equation. The height of the projectile as a function of time can be represented by a quadratic expression similar to our example, helping predict its maximum height and the time it takes to reach the ground.
-
Area Calculations: Quadratic expressions can be used to calculate the area of geometric shapes. For instance, if we have a square with sides of length (x + 3), its area would be (x + 3)² = x² + 6x + 9.
-
Optimization Problems: Quadratic expressions are fundamental in optimization problems, where we aim to find the maximum or minimum value of a function. For example, maximizing the profit of a business or minimizing the cost of production might involve solving a quadratic equation.
-
Engineering and Design: Quadratic equations are used extensively in engineering and design to model curves, structures, and other physical phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between a quadratic expression and a quadratic equation?
A1: A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two (like x² + 6x + 9), while a quadratic equation is a statement that sets a quadratic expression equal to zero (like x² + 6x + 9 = 0).
Q2: Can all quadratic expressions be factored easily?
A2: No, not all quadratic expressions can be factored easily using simple methods like recognizing perfect square trinomials. Some require more advanced techniques like the quadratic formula or completing the square.
Q3: What is the significance of the discriminant in a quadratic equation?
A3: The discriminant (b² - 4ac) helps determine the nature of the roots (solutions) of a quadratic equation. If the discriminant is positive, there are two distinct real roots; if it's zero, there is one real root (as in our example); and if it's negative, there are no real roots (only complex roots).
Q4: How can I check if my factorization is correct?
A4: You can always check your factorization by expanding the factored form. If the expanded form matches the original expression, your factorization is correct. For example, expanding (x + 3)² gives x² + 6x + 9, confirming our factorization.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of x² + 6x + 9
Understanding the quadratic expression x² + 6x + 9 is more than just memorizing a formula; it's about grasping the fundamental concepts of algebra and their real-world applications. Through factorization, graphical representation, and problem-solving, this expression serves as a gateway to more advanced mathematical concepts. By mastering this seemingly simple expression, you build a strong foundation for tackling more complex algebraic challenges and appreciating the power of mathematics in solving real-world problems. Remember to practice regularly and explore different approaches to solidify your understanding. The journey to mastering algebra is a rewarding one, and x² + 6x + 9 is a crucial stepping stone on that path.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 6x 2 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.