X 2 6x 25 0
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
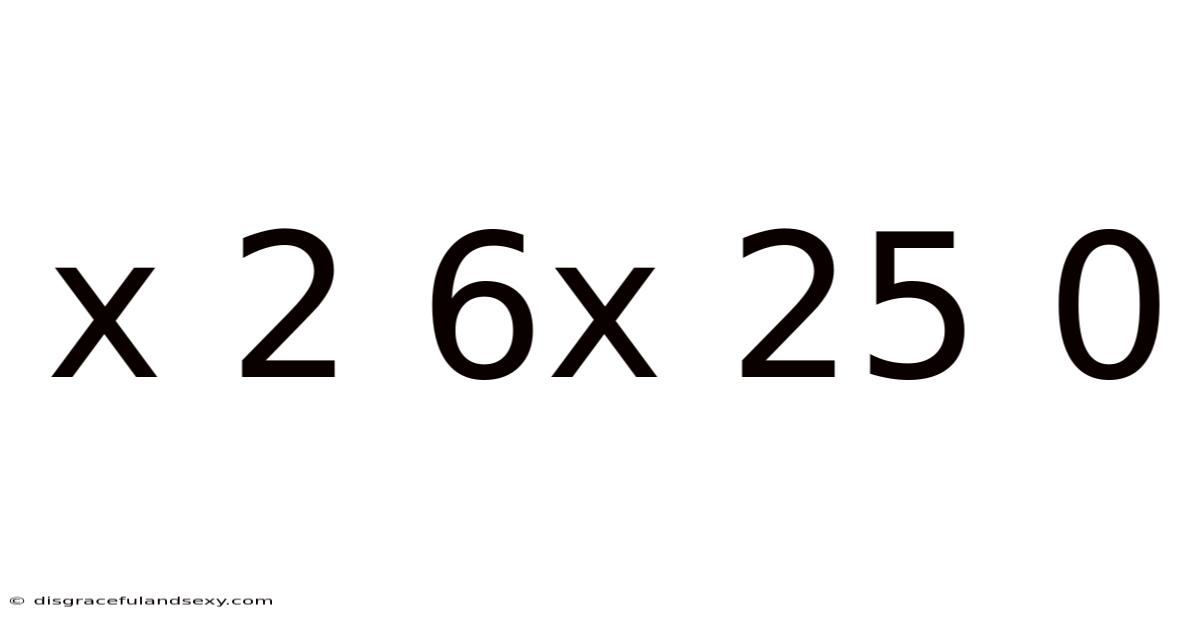
Table of Contents
Deciphering the Mystery: Exploring the Mathematical Expression "x² + 6x + 25 = 0"
This article delves into the mathematical expression x² + 6x + 25 = 0, exploring its nature, methods of solution, and the broader concepts it represents. We'll move beyond simply finding the solution and uncover the underlying mathematical principles involved. Understanding this seemingly simple quadratic equation opens doors to a deeper appreciation of algebra and its applications.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 2. The general form is ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. Our equation, x² + 6x + 25 = 0, fits this form with a = 1, b = 6, and c = 25. Solving quadratic equations is a fundamental skill in algebra with applications ranging from physics and engineering to economics and finance.
Methods for Solving Quadratic Equations: A Comparative Approach
Several methods exist for solving quadratic equations. Let's explore the most common ones and apply them to our specific equation:
-
1. Factoring: Factoring involves expressing the quadratic expression as a product of two linear expressions. This method is ideal when the quadratic expression can be easily factored. However, not all quadratic equations are easily factorable. In our case, x² + 6x + 25 = 0 cannot be factored using real numbers. This is because the discriminant (explained below) is negative.
-
2. Quadratic Formula: The quadratic formula is a powerful tool that provides solutions for any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it's factorable or not. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Applying this to our equation (a = 1, b = 6, c = 25):
x = [-6 ± √(6² - 4 * 1 * 25)] / 2 * 1 x = [-6 ± √(36 - 100)] / 2 x = [-6 ± √(-64)] / 2
Notice that we have the square root of a negative number (-64). This indicates that the solutions are complex numbers.
-
3. Completing the Square: Completing the square is a method that transforms the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve. Let's apply this method:
x² + 6x + 25 = 0 x² + 6x = -25 To complete the square, we take half of the coefficient of x (which is 6), square it (3² = 9), and add it to both sides: x² + 6x + 9 = -25 + 9 (x + 3)² = -16 Taking the square root of both sides: x + 3 = ±√(-16) x + 3 = ±4i (where 'i' is the imaginary unit, √-1) x = -3 ± 4i
Understanding Complex Numbers and the Imaginary Unit (i)
The solutions we obtained, x = -3 ± 4i, are complex numbers. Complex numbers have two parts: a real part and an imaginary part. The imaginary unit, denoted by 'i', is defined as the square root of -1 (i² = -1). Complex numbers are written in the form a + bi, where 'a' is the real part and 'b' is the imaginary part. In our case, the real part is -3, and the imaginary part is ±4.
Complex numbers extend the number system beyond real numbers, enabling us to solve equations that have no real solutions. They have numerous applications in various fields, including electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, and signal processing.
The Discriminant: Predicting the Nature of Roots
The expression b² - 4ac within the quadratic formula is called the discriminant. The discriminant helps predict the nature of the roots (solutions) of a quadratic equation:
- If b² - 4ac > 0: The equation has two distinct real roots.
- If b² - 4ac = 0: The equation has one real root (a repeated root).
- If b² - 4ac < 0: The equation has two complex conjugate roots (as in our case).
In our equation, x² + 6x + 25 = 0, the discriminant is 6² - 4 * 1 * 25 = -64, which is negative. This confirms that the equation has two complex conjugate roots.
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Solutions
The graph of a quadratic equation is a parabola. The x-intercepts of the parabola represent the real roots of the equation. Since our equation has no real roots, its parabola does not intersect the x-axis. Instead, the parabola lies entirely above the x-axis, indicating that all its y-values are positive.
Applications of Quadratic Equations: Real-World Examples
Quadratic equations are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have numerous real-world applications. For instance:
- Projectile Motion: The trajectory of a projectile (e.g., a ball thrown in the air) can be modeled using a quadratic equation. The equation helps determine the maximum height reached and the time it takes to land.
- Area Calculations: Finding the dimensions of a rectangular area given its area and other constraints often involves solving a quadratic equation.
- Engineering and Physics: Many engineering and physics problems involve solving quadratic equations to determine various parameters, such as the resistance in an electrical circuit or the displacement of an object under acceleration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why are complex numbers important?
A: Complex numbers are essential for extending mathematical operations to cases where real numbers are insufficient. They have widespread applications in fields like electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, and signal processing.
-
Q: Can all quadratic equations be solved using the quadratic formula?
A: Yes, the quadratic formula is a universal method for solving any quadratic equation, regardless of whether it has real or complex solutions.
-
Q: What does it mean when a quadratic equation has no real roots?
A: It means that the parabola representing the equation does not intersect the x-axis. The solutions are complex numbers.
-
Q: Is there a graphical way to find the solutions of a quadratic equation?
A: Yes. The x-intercepts of the parabola representing the quadratic equation correspond to its real roots. If there are no x-intercepts, the roots are complex.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Quadratic Equations
The seemingly simple equation x² + 6x + 25 = 0 opens a door to a deeper understanding of quadratic equations, complex numbers, and their various applications. Through different solution methods and analyzing the discriminant, we've seen how to approach and interpret the results, even when dealing with complex numbers. This knowledge extends beyond simple equation solving, providing a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and real-world problem-solving. The exploration of this equation provides a valuable learning experience, highlighting the power and elegance of mathematics in its ability to describe and solve problems across diverse fields.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 6x 25 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.