X 2 6x 7 Factor
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
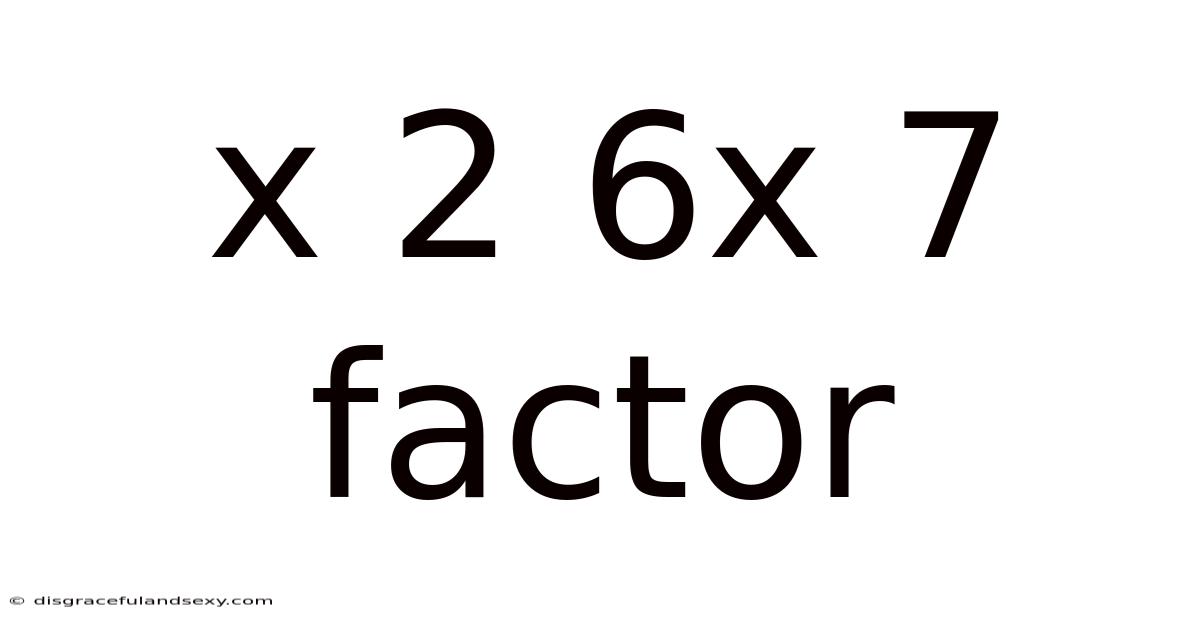
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: Factoring x² + 6x + 7
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding many mathematical concepts. This article delves into the process of factoring the specific quadratic expression x² + 6x + 7, explaining the methods involved, providing step-by-step solutions, and exploring the underlying mathematical principles. We'll cover various techniques, address common misconceptions, and even look at how this seemingly simple problem relates to more advanced algebraic concepts. This comprehensive guide aims to leave you with a thorough understanding of factoring this particular quadratic and the broader skill of factoring itself.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we dive into factoring x² + 6x + 7, let's briefly review what a quadratic expression is. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. In our case, a = 1, b = 6, and c = 7.
The goal of factoring a quadratic expression is to rewrite it as a product of two simpler expressions, usually linear binomials. This process is the reverse of expanding binomials using the FOIL (First, Outer, Inner, Last) method.
Method 1: Factoring by Finding Two Numbers
This method is the most common and straightforward approach for factoring simple quadratics like x² + 6x + 7. We look for two numbers that satisfy two specific conditions:
- Their sum is equal to the coefficient of the x term (b). In our case, this is 6.
- Their product is equal to the constant term (c). In our case, this is 7.
Let's find these numbers:
The factors of 7 are 1 and 7 (and -1 and -7). Since the sum of these factors must be 6, we choose 1 and 7.
Therefore, we can rewrite x² + 6x + 7 as (x + 1)(x + 7).
Verification: Expanding (x + 1)(x + 7) using the FOIL method gives us:
x² + 7x + x + 7 = x² + 6x + 7
This confirms that our factoring is correct.
Method 2: Completing the Square (Less Efficient for this Case)
While the previous method is the most efficient for this specific quadratic, completing the square is a more general technique applicable to any quadratic expression. It involves manipulating the expression to create a perfect square trinomial. Let's illustrate the process:
-
Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 6x = -7
-
Take half of the coefficient of the x term (6/2 = 3), square it (3² = 9), and add it to both sides: x² + 6x + 9 = -7 + 9
-
Rewrite the left side as a perfect square trinomial: (x + 3)² = 2
-
Take the square root of both sides: x + 3 = ±√2
-
Solve for x: x = -3 ± √2
This method gives us the roots of the quadratic equation x² + 6x + 7 = 0. While it doesn't directly give the factored form, it demonstrates an alternative approach and is crucial for solving quadratic equations that cannot be easily factored. Note that this approach is less direct for obtaining the factored form compared to Method 1.
Method 3: Quadratic Formula (Indirect Factoring)
The quadratic formula provides a direct way to find the roots of a quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The formula is:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
For our expression, a = 1, b = 6, and c = 7. Substituting these values, we get:
x = (-6 ± √(6² - 4 * 1 * 7)) / 2 * 1 = (-6 ± √8) / 2 = -3 ± √2
The roots are -3 + √2 and -3 - √2. While this doesn't directly give the factored form (x + 1)(x + 7), it shows that the quadratic can be expressed as (x - (-3 + √2))(x - (-3 - √2)). This form is less convenient than the simpler (x + 1)(x + 7), highlighting the importance of choosing the most appropriate factoring method depending on the specific quadratic.
Why Factoring is Important
The ability to factor quadratic expressions is vital for various reasons:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Setting the factored quadratic equal to zero allows you to easily find the roots (solutions) of the equation. For example, (x + 1)(x + 7) = 0 implies x = -1 or x = -7.
-
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions: Factoring allows you to simplify complex expressions and make them easier to manipulate.
-
Graphing Quadratic Functions: The factored form provides information about the x-intercepts (where the graph crosses the x-axis) of the parabola represented by the quadratic function.
-
Foundation for Advanced Concepts: Factoring is a foundational skill used in more advanced algebraic topics such as partial fraction decomposition, solving higher-degree polynomial equations, and working with rational functions.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
-
Assuming all quadratics are factorable: Not all quadratic expressions can be factored using integers. Some require irrational or complex numbers.
-
Incorrect application of the factoring methods: Carefully following the steps of the chosen method is essential to avoid errors.
-
Forgetting to check your work: Always expand your factored form to verify that it matches the original quadratic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can I use a calculator to factor this quadratic? A: While some calculators have built-in factoring functions, understanding the underlying methods is more valuable than relying solely on a calculator. The methods explained here will help you factor various quadratic expressions.
-
Q: What if the leading coefficient (a) is not 1? A: When a ≠ 1, you might need to use techniques such as factoring by grouping or the AC method. These methods are more complex than those used here, and are suitable for more complicated quadratic equations.
-
Q: What happens if the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is negative? A: A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has no real roots. The roots are complex numbers involving the imaginary unit i (√-1).
Conclusion
Factoring x² + 6x + 7, while seemingly simple, illustrates the fundamental principles of factoring quadratic expressions. Mastering this skill provides a strong foundation for more advanced algebraic concepts. Remember to choose the most efficient method for the given quadratic and always verify your work. The methods discussed here – finding two numbers, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula – offer different approaches to understanding and solving this type of problem, enriching your algebraic toolbox. Practice is key to developing proficiency in factoring, and understanding the "why" behind each step will further solidify your mathematical understanding.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 6x 7 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.