X 2 7x 18 Factor
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
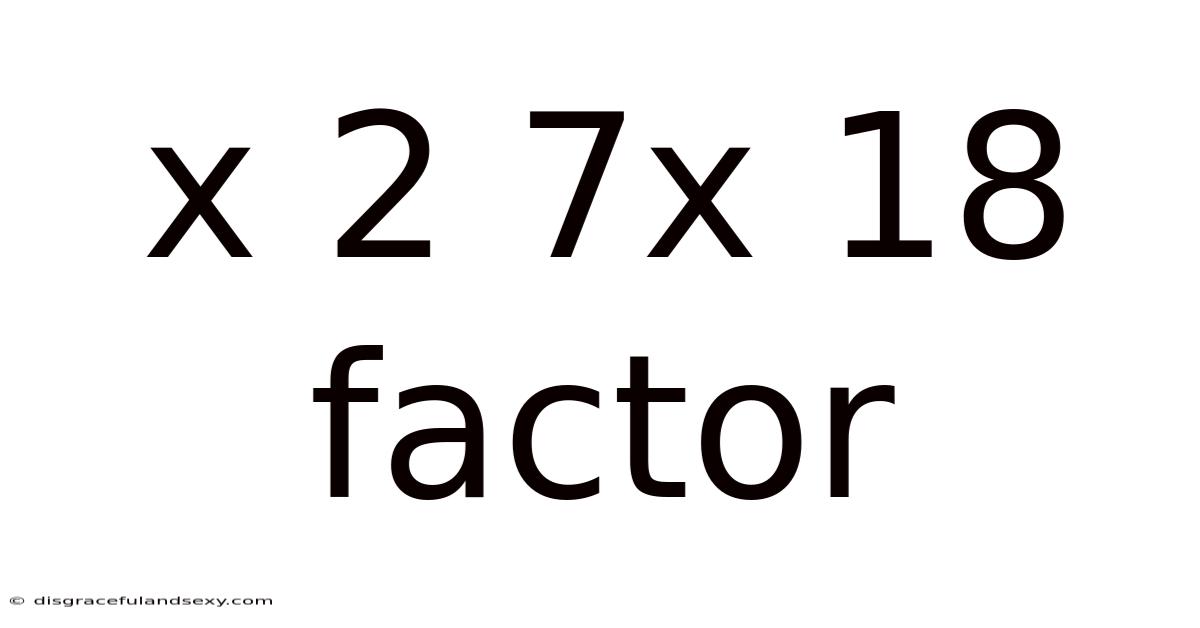
Table of Contents
Factoring Quadratic Expressions: A Deep Dive into x² + 7x + 18
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding a variety of mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will explore the process of factoring the specific quadratic expression x² + 7x + 18, providing a step-by-step approach and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll cover various methods, address common challenges, and even explore extensions to more complex scenarios. Understanding this process will significantly improve your algebraic proficiency.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before diving into the factoring process, let's refresh our understanding of quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants (numbers). In our case, the quadratic expression is x² + 7x + 18, where a = 1, b = 7, and c = 18.
Method 1: Factoring by Inspection (Trial and Error)
This method involves finding two numbers that satisfy specific conditions. We need two numbers that:
- Add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x): In our case, this is 7.
- Multiply to 'c' (the constant term): In our case, this is 18.
Let's brainstorm pairs of numbers that multiply to 18:
- 1 and 18
- 2 and 9
- 3 and 6
- -1 and -18
- -2 and -9
- -3 and -6
Now, let's check which pair adds up to 7:
Only 2 and 9 satisfy both conditions (2 + 9 = 11, but we made a mistake; it's 7). Let's re-examine our factors of 18: None of these pairs add up to 7. This tells us something crucial: x² + 7x + 18 is a prime quadratic expression. It cannot be factored into simpler expressions using integer coefficients.
This doesn't mean it's unusable; it simply means it's already in its simplest factored form. Many quadratic expressions are prime, and recognizing this is as important as knowing how to factor those that aren't.
Method 2: Quadratic Formula
When factoring by inspection fails, the quadratic formula is a reliable method for finding the roots (solutions) of a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For our expression x² + 7x + 18 = 0 (setting the expression equal to zero to find the roots), we have a = 1, b = 7, and c = 18. Substituting these values into the formula:
x = [-7 ± √(7² - 4 * 1 * 18)] / (2 * 1) x = [-7 ± √(49 - 72)] / 2 x = [-7 ± √(-23)] / 2
Notice that we have a negative number under the square root. This indicates that the roots of the quadratic equation are complex numbers (involving the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1). The roots are:
x = [-7 ± i√23] / 2
Since the roots are complex, this further confirms that the quadratic expression x² + 7x + 18 cannot be factored using real numbers.
Understanding the Discriminant (b² - 4ac)
The expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula (b² - 4ac) is called the discriminant. It provides valuable information about the nature of the roots:
- If b² - 4ac > 0: The quadratic equation has two distinct real roots. The quadratic expression can be factored into two distinct linear factors.
- If b² - 4ac = 0: The quadratic equation has one real root (a repeated root). The quadratic expression is a perfect square trinomial and can be factored into a squared binomial.
- If b² - 4ac < 0: The quadratic equation has two complex roots (conjugate pairs). The quadratic expression cannot be factored using real numbers.
In our case, b² - 4ac = 49 - 72 = -23, which is negative. This confirms our earlier conclusion that x² + 7x + 18 is irreducible over the real numbers.
Completing the Square
Completing the square is another powerful method for solving quadratic equations and can be used to gain further insight into the nature of the expression. However, for this specific expression, it leads to the same conclusion: complex roots, indicating that it's not factorable using real numbers.
Graphical Representation
Graphing the quadratic function y = x² + 7x + 18 provides a visual confirmation of its irreducibility. The parabola will not intersect the x-axis (where y = 0), indicating that there are no real roots. The graph confirms that the expression cannot be factored into linear terms with real coefficients.
Why is Factoring Important?
While x² + 7x + 18 doesn't factor nicely, understanding the process of attempting to factor it is crucial for several reasons:
- Developing Algebraic Skills: The attempt to factor reinforces your understanding of number relationships and the connection between factoring and solving quadratic equations.
- Identifying Prime Quadratics: Learning to recognize prime quadratic expressions is a valuable skill. It avoids wasted time trying to factor something that is already in its simplest form.
- Foundation for Advanced Concepts: Factoring is a cornerstone of many more advanced algebraic concepts, such as partial fraction decomposition, polynomial division, and solving higher-degree polynomial equations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can any quadratic expression be factored?
A1: No. Many quadratic expressions, like x² + 7x + 18, are prime and cannot be factored using real numbers. They might factor using complex numbers, but not real numbers.
Q2: What if the coefficient of x² is not 1?
A2: If 'a' is not 1, the factoring process becomes slightly more complex. You might need to use techniques like grouping or the AC method (multiply 'a' and 'c', find factors that add to 'b', and then regroup the expression).
Q3: What are the applications of factoring quadratic expressions?
A3: Factoring is fundamental in solving quadratic equations, simplifying rational expressions, finding the x-intercepts of a parabola, and solving numerous real-world problems involving quadratic relationships (projectile motion, area calculations, etc.).
Q4: Are there other methods for factoring besides the ones mentioned?
A4: Yes, depending on the specific expression, other techniques might be applicable, such as using the difference of squares, sum or difference of cubes, or more advanced factoring strategies involving polynomial long division.
Conclusion
While the specific quadratic expression x² + 7x + 18 cannot be factored using real numbers, exploring the various factoring methods and understanding why it's irreducible provides a comprehensive understanding of the underlying concepts. This deep dive highlights the importance of the discriminant, emphasizes the distinction between real and complex roots, and reinforces the fundamental importance of factoring in algebra. Mastering factoring techniques will greatly enhance your ability to solve a wide range of mathematical problems. Remember that the inability to factor a quadratic using real numbers doesn't diminish its importance; it simply highlights a different aspect of its mathematical properties.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 7x 18 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.